Applications:
UV-Vis Spectrum of Cysteine
August 5, 2025
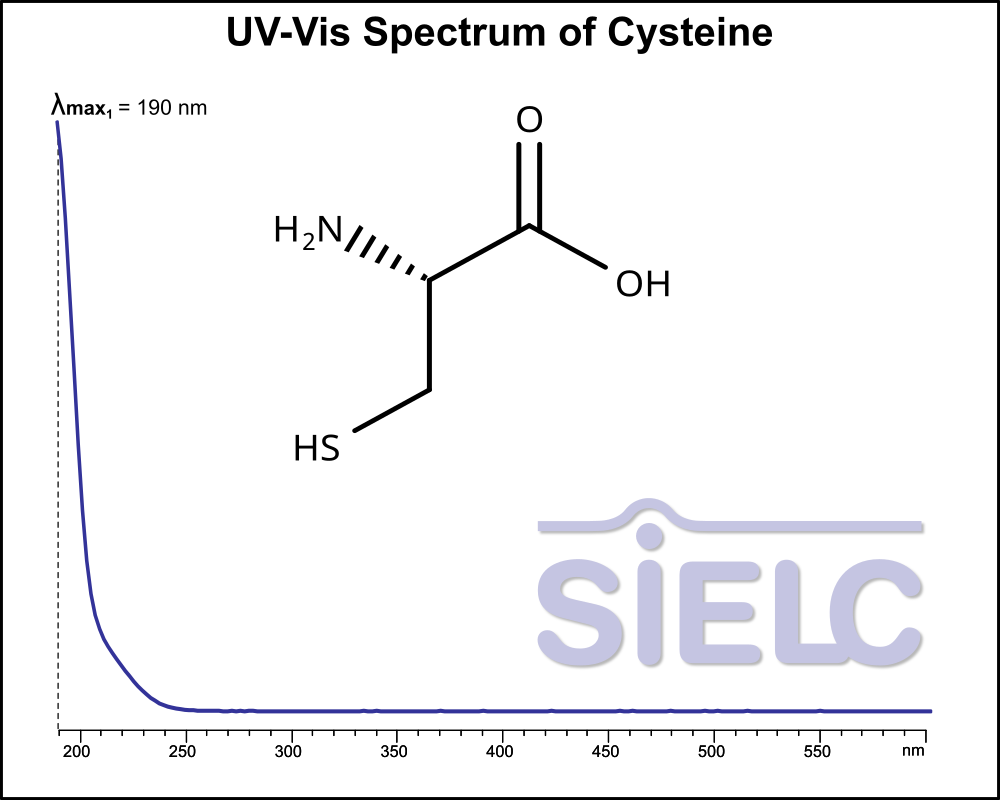
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

HPLC Method for Separation of Sulfur-containing Biomolecules on Primesep 100 Column
June 13, 2023
HPLC Method for Separation of Cysteine, Glutathione, reduced, Cystine, Cysteine-glutathione disulfide, Glutathione oxidized on Primesep 100 by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
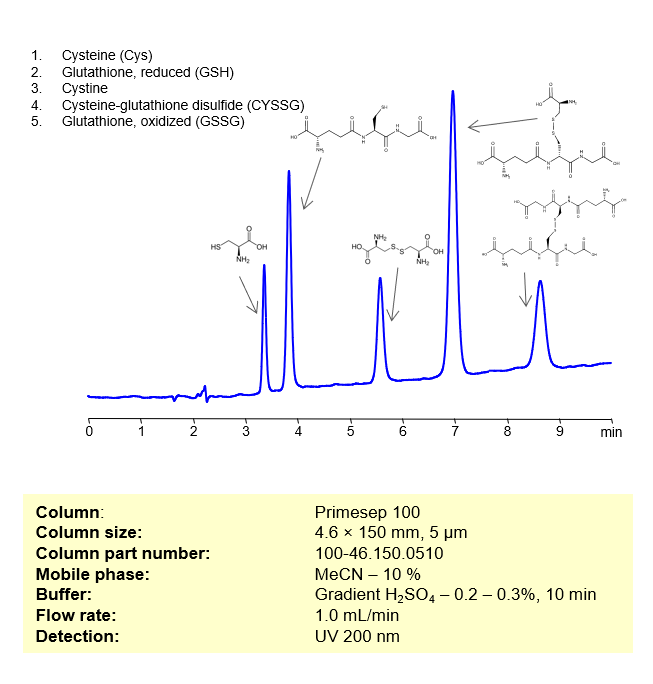
These compounds are all involved in redox reactions and cellular defenses against oxidative stress in biological systems. Here’s a bit more about each of them:
- Cysteine (Cys): This is a sulfur-containing amino acid that’s used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Its thiol side chain often participates in enzymatic reactions, and contributes to the stability of proteins by forming disulfide bonds.
- Glutathione, reduced (GSH): A tripeptide (small protein) consisting of the amino acids glutamic acid, cysteine, and glycine. GSH serves as an antioxidant, helping to prevent damage to cellular components caused by reactive oxygen species such as free radicals and peroxides.
- Cystine: This is a covalently bonded dimer molecule of two cysteine molecules, connected through a disulfide bond. Disulfide bonds between cysteine residues in peptide chains contribute to the 3D structure of proteins. In dietary supplements and food labeling, this compound is often referred to as a conditionally essential amino acid.
- Cysteine-glutathione disulfide (CySSG): This is a mixed disulfide formed by the reaction of glutathione with the oxidized form of cysteine (cystine). It is one of the forms in which cysteine is stored and transported in plasma.
- Glutathione, oxidized (GSSG): This is the oxidized form of glutathione, produced when two glutathione molecules are linked by a disulfide bond. GSSG is reduced back to GSH by the enzyme glutathione reductase, which also requires NADPH as a cofactor.
Overall, these molecules play vital roles in the body’s antioxidant defenses, detoxification of xenobiotics, modulation of redox-controlled signaling pathways, and regulation of cellular proliferation and apoptosis.
These compounds can be retained, separated, and analyzed using a reverse-phase Primesep 100, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended column. The mobile phase for this method consists of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and Sulfuric acid, which serves as a buffer. This analytical method can be
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Cysteine, Cystine, Cysteine-glutathione disulfide, L-Cysteine
Condition
| Column | Primesep 100, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN -10% |
| Buffer | Gradient H2SO4 0.1-0.3%, 10 min |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200 nm |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Thiol, Amino acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Cysteine, Glutathione, reduced, Cystine, Cysteine-glutathione disulfide, Glutathione oxidized |
Application Column
Primesep 100
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Cysteine-glutathione disulfide
Cystine
L-Cysteine

HPLC Method For Analysis Of Cysteine and Cystine on Primesep 100 Column
March 10, 2022
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
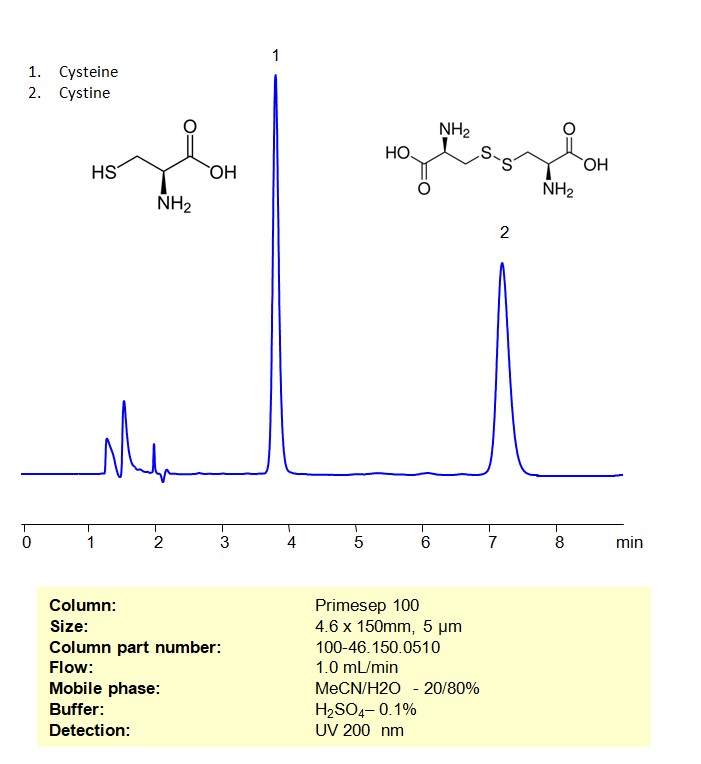
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Cysteine and Cystine
Cysteine is an amino acid that is an essential building block of a wide variety of proteins made and used throughout the entire body. Cystine is an oxidized dimer of cysteine that the body uses for redox reactions and as a linkage for proteins to keep their 3D structures. Cysteine and Cystine can be retained and analyzed on a mixed-mode Primesep 100 column with a mobile phase consisting of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN), and Sulfuric acid (H2SO4). This analytical method can be UV detected at 200 nm with high resolution and peak symmetry.
| Column | Primesep 100, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 20/80% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.1% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 200 nm |
| Class of Compounds | Amino Acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Cysteine, Cystine |
Application Column
Primesep 100
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Cystine
L-Cysteine

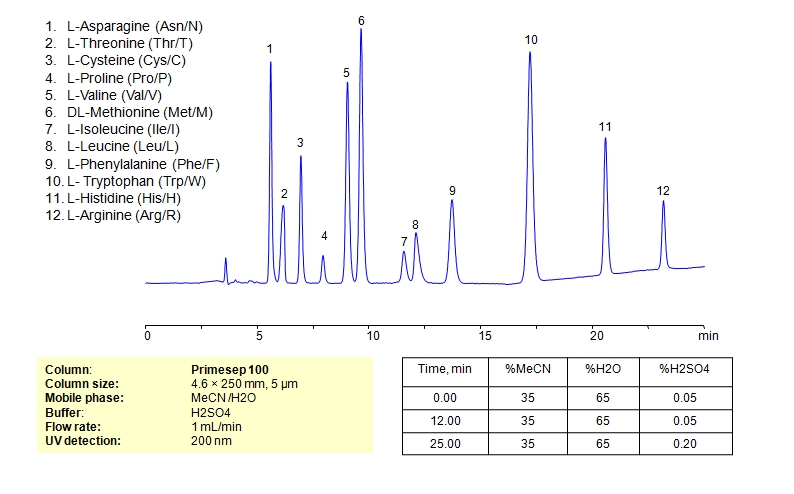
HPLC Separation of Mixture of 12 Amino Acids on Primesep 100 Column
March 11, 2019
HPLC Method for Asparagine, L-Cysteine, Cysteine, Proline, Valine, D-Valine, Methionine, L-Methionine, Isoleucine, D-Isoleucine, DL-Isoleucine, D-Leucine, Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, Histidine, Arginine, Amino Acids, Leucine, L-Threonine on Primesep 100 by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Asparagine, L-Cysteine, Cysteine, Proline, Valine, D-Valine, Methionine, L-Methionine, Isoleucine, D-Isoleucine, DL-Isoleucine, D-Leucine, Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, Histidine, Arginine, Amino Acids, Leucine, L-Threonine.
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Based on their dietary requirement, they are classified into essential and non-essential amino acids. Essential amino acids cannot be synthesized by the human body in sufficient quantities and must be obtained from the diet. Non-essential amino acids, on the other hand, can be synthesized by the body and are not dependent on dietary intake.
It’s worth noting that while these amino acids are considered “non-essential” for adults under normal circumstances because the body can synthesize them, there are situations where some may become “conditionally essential.” This means that under certain conditions like illness, stress, or trauma, the body might not produce them in sufficient quantities, and dietary intake becomes necessary. Arginine, for instance, is considered conditionally essential, especially during periods of rapid growth, illness, or trauma.
Amino acids can be retained, separeted and analyzed on a Primesep 100 mixed-mode stationary phase column using an isocratic analytical method with a simple mobile phase of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN), and a sulfuric acid (H2SO4) as a buffer. This analysis method can be detected in the UV regime at 200 nm.
| Column | Primesep 100, 4.6 x 250 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 35/65% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 0.05% 12 min hold, gradient 0.05-0.20, 13 min |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 200 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements, Amino acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Asparagine, L-Cysteine, Cysteine, Proline, Valine, D-Valine, Methionine, L-Methionine, Isoleucine, D-Isoleucine, DL-Isoleucine, D-Leucine, Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, Histidine, Arginine, Amino Acids, Leucine, L-Threonine |
Application Column
Primesep 100
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 250 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Arginine
Asparagine
Cysteine
D-Isoleucine
D-Leucine
D-Valine
DL-Isoleucine
Histidine
Isoleucine
L-Cysteine
L-Methionine
L-Threonine
Leucine
Methionine
Phenylalanine
Proline
Tryptophan
Valine

HPLC Separation of Mixture of Conditionally Essential Amino Acids on Primesep 100 Column
March 11, 2019
HPLC Method for L-Glutamine, Glycine, Cysteine, L-Cysteine, Proline, Tyrosine, Arginine, Amino Acids on Primesep 100 by SIELC Technologies
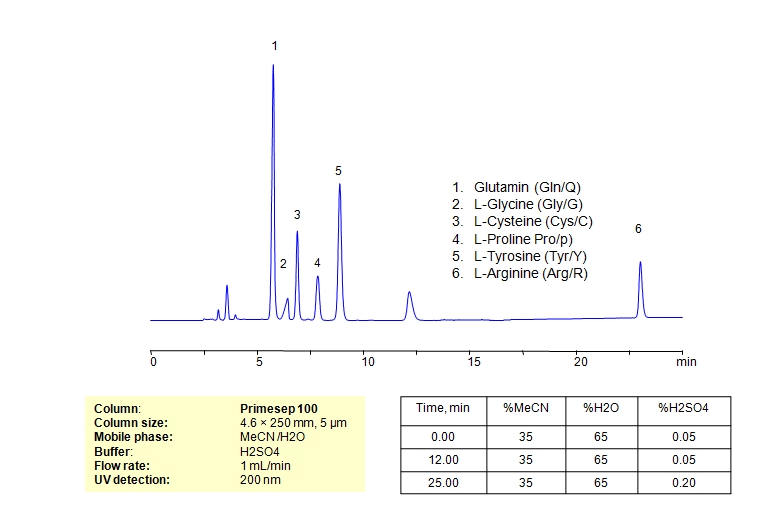
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of L-Glutamine, Glycine, Cysteine, L-Cysteine, Proline, Tyrosine, Arginine, Amino Acids.
Glutamine is an amino acid with the chemical formula C5H10N2O3. It is a building block for protein, but it also supports the immune system, gut health, and detoxification. It is usually found in meat, fish, eggs, dairy, and whole grains; though some consider it the most abundant amino acid in the body. People also take glutamine as treatment for sickle cell disease, healing of burns, recovery after surgery, and injuries.
L-Glycine is an important amino acid compounds widely used in pharmaceutical, biochemical, and peptide research. It has he chemical formula C₂H₅NO₂. It is water-soluble and plays a critical role in protein synthesis, peptide modification, and metabolic studies. It can be found in meat., eggs. and bones.
L-Cysteine is an amino acid with the chemical formula C5H10N2O3. It is primarily a building block for protein, but it also has antioxidant effects. On occasion, ot os used to support people dealing with cancer, diabetes, and hangover, but there is yet to be substantial evidence that it works. Poultry, egg, beef, and whole grains are rich sources of the amino acid.
L-Proline is an amino acid with the chemical formula C5H9NO2. It is naturally produced in the body, but it is also recommended to be consumed through the diet. It can be found in meat, fish, and dairy. It is used for skin healing and treatment of other skin conditions as it is an essential component of collagen. It is important for upkeep of joints and tendons, as well as heart muscles.
L-Tyrosine is an amino acid with the chemical formula C9H11NO3. It is naturally used in the body to create neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine. While it is produced in the body naturally, it can also be consumed in beef, pork, fish, dairy products, and beans. As a supplement, it is also used to treat Phenylketonuria (PKU).
L-Arginine is an amino acid with the chemical formula C9H11NO3. It is a precursor for nitric acid, making it crucial for blood flow and general cardiovascular health. It can help lower blood pressure, help with chest pain, and improve symptoms of Peripheral arterial disease (PAD).
L-Glutamine, Glycine, Cysteine, L-Cysteine, Proline, Tyrosine, Arginine, Amino Acids can be retained and analyzed using the Primesep 100 stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water and acetonitrile (MeCN) with a sulfuric acid buffer. Detection is performed using UV.
| Column | Primesep 100, 4.6 x 250 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 35/65% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 0.05% 12 min hold, gradient 0.05-0.20, 13 min |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 200 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements, Amino acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | L-Glutamine, Glycine, Cysteine, L-Cysteine, Proline, Tyrosine, Arginine, Amino Acids |
Application Column
Primesep 100
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 250 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Arginine
Cysteine
Glycine
L-Cysteine
L-Glutamine
Proline
Tyrosine

HPLC-ELSD Method for Analysis of Amino Acids on Primesep 100 Column
September 18, 2006
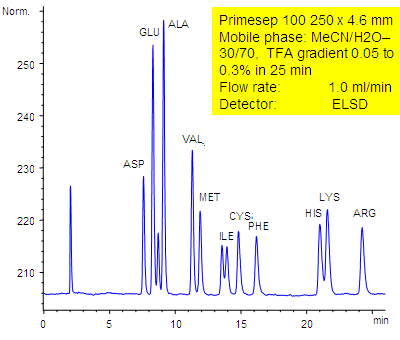
11 underivatized amino acids (aspartic acid, glutamic acid, alanine, valine, methionine, isoleucine, cysteine, phenylalanine, histidine, lysine, and arginine) are separated by a Primesep 100 HPLC column by reversed-phase and ion-exchange mechanisms with LC/MS compatible conditions without the use of ion-pair reagents. The HPLC separation uses a TFA (trifluoroacetic acid) gradient in a mobile phase of water acetonitrile (MeCN, ACN with evaporative light scattering detection (ELSD).
| Column | Primesep 100, 4.6×250 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 30/70% |
| Buffer | TFA , gradient 0.05-0.3 % , 25 min |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | Aspartic acid, Glutamic acid, Alanine, Valine, Methionine, Isoleucine, Cysteine, Phenylalanine, Histidine, Lysine, Arginine |
Application Column
Primesep 100
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsAmino Acids
Arginine
Aspartic Acid
Cysteine
Glutamic Acid
Histidine
Isoleucine
Lysine
Methionine
Phenylalanine
Valine

Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Compound Separation
September 25, 2003
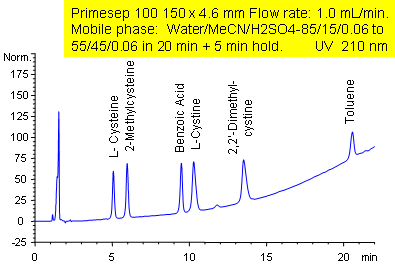
Primesep 100 separates a mixture of polar and nonpolar compounds in one analytical run. The amino acid cysteine; amino acid derivatives L-cystine, 2,2-dimethylcystine, and 2-methylcysteine; the polar acid benzoic acid; and the nonpolar neutral toluene are separated by a gradient using a combination of polar and hydrophobic interactions. The separation method uses a mobile phase mixture of water, acetonitrile (MeCN, ACN) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4) with UV detection at 210 nm.
| Column | Primesep 100, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | H2SO4 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 210 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Nonpolar, Polar, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | Cysteine, L-cystine, 2,2-dimethylcystine, 2-methylcysteine, Benzoic Acid, Toluene |
Application Column
Primesep 100
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select options2-Methylcysteine
Amino Acids
Benzoic Acid
Cysteine
L-Cystine
Toluene