Revolutionizing Oligonucleotide Analysis
Simplified, Precise, and Efficient
Envision achieving precise, efficient analysis with a simple mobile phase of just H₂O and MeCN. This advancement streamlines your process, ensuring outstanding results with minimal effort. Our unique approach simplifies oligonucleotide analysis while delivering the precision you can trust.
The Bridge Ion Separation Technique (BIST®)
Recently, we reported on a novel liquid chromatography technique that we have named the Bridge Ion Separation Technique (BIST®). Integrated into our Oligonucleotide technology, BIST® revolutionizes the separation of these complex multicharged molecules, providing unmatched efficiency and precision in their analysis.
How BIST® Works for Oligonucleotides
The BIST® method requires:
-
- A cation exchange stationary phase with a double-charged positive ion.
- A small amount of organic modifier in the mobile phase.
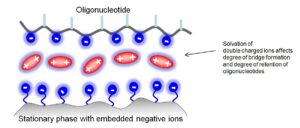
The key to BIST® is the formation of a “bridge” between the negatively charged oligonucleotides and the negatively charged stationary phase, facilitated by a double-charged positive ion. Extensive research has shown that Mg²⁺ ions yield the best results for this bridge formation.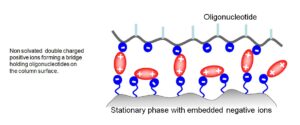
Why BIST® is a Game-Changer for Adjustable Retention in Oligonucleotide Analysis
- The Role of Solvation:
The amount of water in the mobile phase is critical for influencing the solvation of double-charged ions. By carefully reducing the organic modifier, oligonucleotides can be eluted from the column more easily, which enhances the overall efficiency of the analysis. - Correlation with Nucleobase Number:
In BIST®, the retention time is directly correlated with the number of nucleobases in the oligonucleotide chain. Longer oligonucleotide chains contain more phosphate groups, providing additional negative charges for bridging. As a result, these longer chains demonstrate stronger retention. This behavior is essential in BIST®, as the increased negative phosphate groups create more opportunities for forming bridges with the stationary phase, leading to longer retention times. - Impact of Oligonucleotide Sequence Diversity:
The diversity of oligonucleotide sequences also affects retention, with different sequences of the same length exhibiting varying retention times. This variation arises from the unique arrangements of nucleobases within each sequence, highlighting the precision of BIST® in addressing the complexities of oligonucleotide analysis.
Discover More
Our innovative approach is set to revolutionize the field of oligonucleotide analysis, offering unmatched efficiency and ease of use. For detailed examples and in-depth information, check out our newsletter for the latest updates and results on oligonucleotide applications.
