|
Method Development Guide
All Primesep™ columns are reverse phase (RP) columns. They differ from other brands’ reverse phase columns by having an additional charge on a stationary phase surface. This charge allows you to utilize another mechanism of interaction : ion-exchange in addition to hydrophobic interaction.
The column surface charge is greatly influenced by the pH of the mobile phase. Many analytes also change their charge state as a result of changes in solvent pH. If a compound has a positive or negative charge, then in order to obtain an ion-exchange interaction in addition to reverse phase interaction using Primesep columns, the column surface charge and the analyte charge should be opposite . This guide helps you to decide which Primesep column to choose when you just begin to do method development with Primesep mixed-mode columns.
There are three steps in the process of selecting a correct Primesep HPLC column for your method:
- Step 1. Choose the appropriate bar for your compounds based on their pKa value or structure, then find the pH range where your analyte has a charge
- Step 2. Choose the appropriate buffering system with the pH at a point where the analyte has a charge which satisfies your detection and scale up requirements that you have found in step 1
- Step 3. Choose an appropriate Primesep column which has a surface charge opposite to the analyte charge found in Step 1
|
Step 1. Choose the appropriate bar for your compounds based on their pKa value or structure, then find the pH range where your analyte has a charge
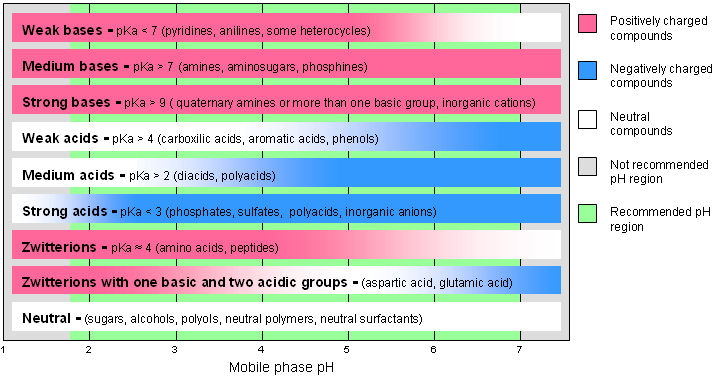
Note : Some compounds have more than one charge state within a working pH range (examples include aspartic acid and glutamic acid). Compounds that have no charge state at any HPLC condition can be analyzed with any Primesep column via the reverse phase mechanism. Besides the reverse phase or hydrophobic mechanisms, other mechanisms of interaction can be utilized in this case (normal phase interaction, HILIC, and pi-pi interaction with Primesep P column).
Back To Top |
|
Step 2. Choose the appropriate buffering system with the pH at a point where the analyte has a charge which satisfies your detection, and scale up requirements that you have found in step 1.
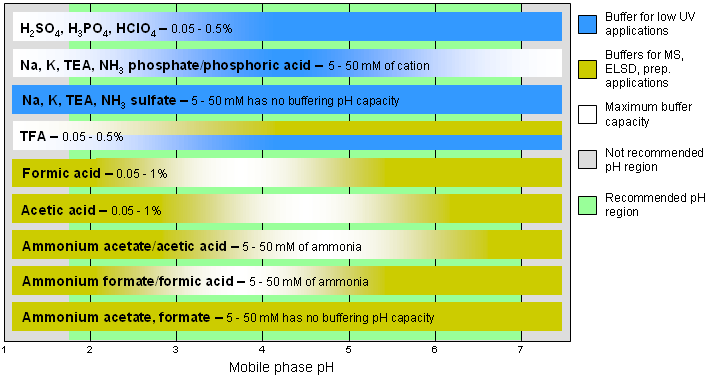
Note: If the analyte and the column surface have opposite charges, elution of the analyte from the column requires the presence of other ions in the mobile phase. Water and acetonitrile alone do not produce enough ions in the mobile phase to efficiently participate in an ion-exchange process. As a result, charged analytes in Primesep column systems result in very long retention time and poor peak shape. Typical HPLC buffers are a good source of ions capable of facilitating an ion-exchange process.
Two distinct types of buffers are available depending on applicable detection requirements:
- Non-volatile buffers for low UV application, and,
- Volatile buffers for MS, ELSD, and preparatory applications
Only a TFA-based buffer can be used for both types of detection. Unfortunately it is not always applicable for MS detection, and does not permit using a lower UV wavelength.
Cation-exchange Primesep columns allow the use of non-buffered solutions. The acidic residue embedded in the column provides the acidic component of the buffer. Ammonium acetate or ammonium formate salts can be used for MS, ELSD, and preparative chromatography applications while potassium sulfate can be used for low UV applications.
Back To Top |
|
Step 3. Choose an appropriate Primesep column which has a surface charge opposite to the analyte charge found in step 1.

Note : Primesep columns in transitional pH gradually lose or change their surface charge. This process is reversible and the column restores its ionic properties with another mobile phase pH. When the column is used without a buffered mobile phase, the surface charge corresponds to the charge at pH 7 on this chart. In order to work and get consistent results in transitional pH, the ionic mobile phase modifier should have sufficient buffering capacity.
Unlike the other Primesep columns, the Primesep AB column is a zwitterionic reverse phase column with a surface charge that is affected by the type of the analyte:
- With basic analytes the Primesep AB column behaves as if it has a negatively charged surface
- With strong acids the Primesep AB column behaves as if it has positively charged surface.
All columns except Primesep B are stable in any buffer system within a pH range of 1.5 – 7. The Primesep B column is recommended at a pH range of 1.5 – 4.5.
Use the chart below to help properly select a column that will interact with the analyte by both the reverse phase and the ion-exchange mechanism.
Back To Top
|
|



