| CAS Number | 56-87-1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H14N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 146.190 |
| InChI Key | KDXKERNSBIXSRK-YFKPBYRVSA-N |
| LogP | -3.05 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
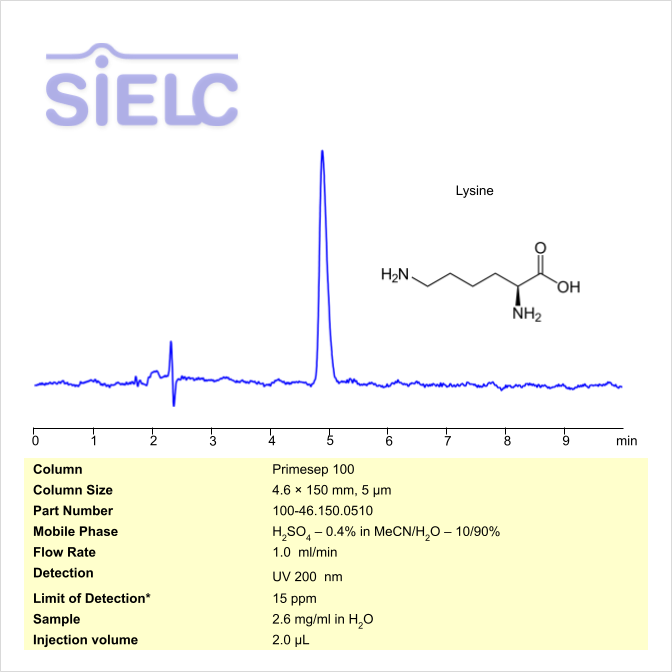
HPLC UV Method for Analysis of Lysine on Primesep 100 Column
January 9, 2026
HPLC Method for Lysine on Primesep 100 by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Lysine.
Lysine is an essential amino acid with the chemical formula C6H14N2O2. It’s primary role is in proteinogenesis, but it also plays a part in uptake of essential mineral nutrients, production of carnitine, and histone modification. Lysine is known in pop culture thanks to Jurassic Park, in which dinosaurs were genetically altered to be unable to produce lysine. While in the story, this made the dinosaurs be unable to survive in the wild due to needing the lysine supplements provided by the staff at Jurassic Park, no real animal can produce lysine naturally. Lysine is another essential amino acid typically found in meat, and also cereal grains. You can find detailed UV spectra of Lysine and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
Lysine can be retained and analyzed using the Primesep 100 stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes a gradient method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water and acetonitrile (MeCN) buffer. Detection is performed using UV.
| Column | Primesep 100, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | H2SO4 – 0.2% |
| Buffer | MeCN/H2O – 10/90% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 mL/min |
| Detection | UV 200 nm |
| LOD* | 15 ppm |
| Class of Compounds | Amino Acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Lysine |
Application Column
Primesep 100
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

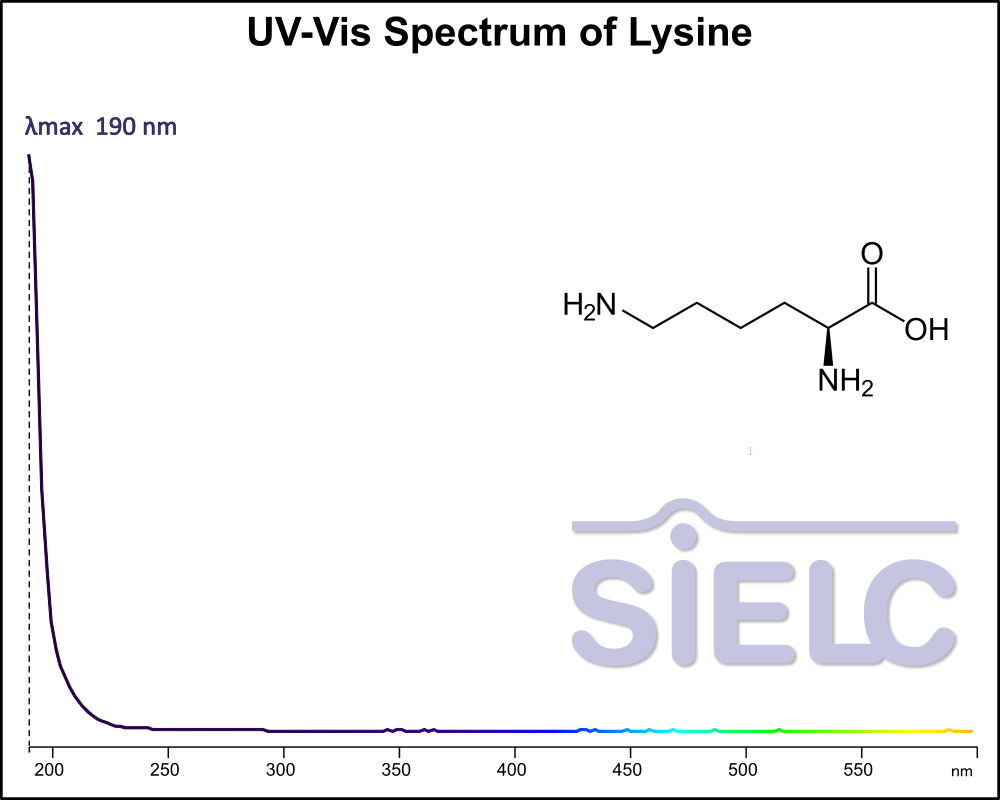
UV-Vis Spectrum of Lysine
July 9, 2024
Access the UV-Vis Spectrum SIELC Library
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Lysine check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.

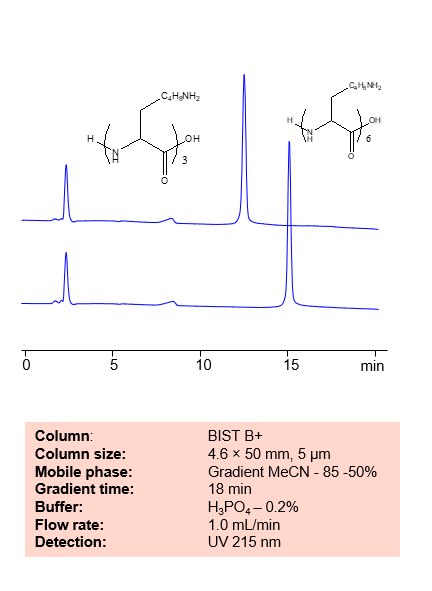
HPLC Method for Separation of Lysine, Dilysine and Trilysine on BIST B+ Column
March 27, 2024
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Lysine, Dilysine, Trilysine on BIST B+ by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
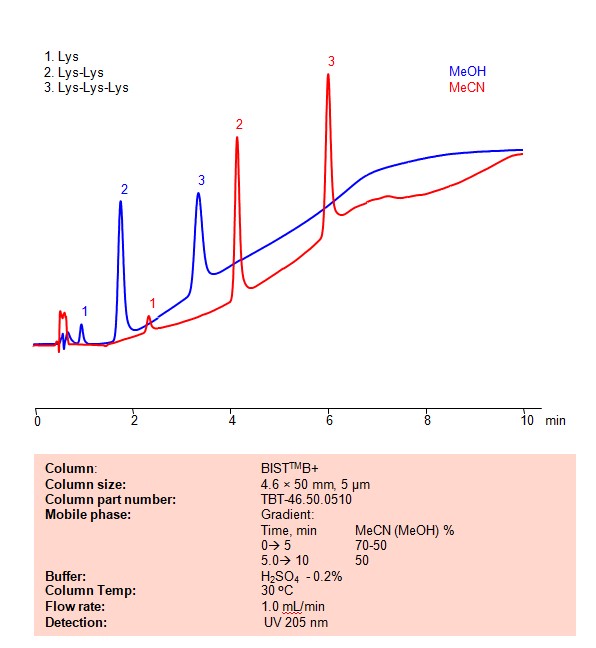
Lysine, dilysine, and trilysine refer to compounds related to the amino acid lysine.
1. Lysine (L-Lysine):
- Type: Lysine is an essential amino acid.
- Structure: It has an α-amino group (which is in the protonated –NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated –COO− form under physiological conditions), and a side chain with a functional group that is a basic, charged (at physiological pH) amino group.
- Role in the Body: As an amino acid, lysine is a building block for proteins. It’s crucial for health, but the body can’t produce it, so it must come from the diet.
- Uses: Lysine has been used in supplements to improve athletic performance, support immune health, and more. It’s also integral in the production of carnitine, a nutrient responsible for converting fatty acids into energy and helping to lower cholesterol.
2. Dilysine:
- Type: This refers to a molecule composed of two lysine units.
- Structure: The two lysine amino acids can be joined via a peptide bond between the carboxyl group of one lysine molecule and the amino group of another, forming a dipeptide. The resulting structure still features the basic side chains of the lysine residues.
- Potential Roles and Uses: While not commonly discussed outside of scientific research, such compounds could play roles in biological signaling or act as building blocks for more complex molecules. They may also be used in certain types of biochemical research or have potential therapeutic properties.
3. Trilysine:
- Type: This compound comprises three lysine molecules.
- Structure: Similar to dilysine, but with three lysine units connected by peptide bonds, resulting in a tripeptide. The basic side chains characteristic of lysine would still be present, and the molecule would carry multiple positive charges under physiological conditions due to these groups.
- Potential Roles and Uses: Trilysine is even less common in general discussion and is primarily a subject of scientific study. It could play a role in biochemical research or be explored for various potential applications, perhaps related to its charge and interaction with other molecules.
For all these compounds, especially dilysine and trilysine, their relevance is often in biochemical research. Scientists may study such peptides to understand cellular mechanisms, explore physiological processes, or develop new materials or medications. The specific properties of these compounds, such as their charge and their ability to participate in various biochemical interactions, can make them valuable for certain applications.
Lysine, dilysine, and trilysine can be retained, separated and analyzed on a BIST B+ mixed-mode stationary phase column using an analytical method with a simple mobile phase of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN) or Methanol (MeOH), and a sulfuric acid as a buffer. This analysis method can be detected using UV at 205 nm.
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analyses of Lysine, Dilysine, Trilysine
Condition
| Column | BIST B+, 4.6 x 50 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN or MeOH |
| Buffer | H2SO4 -0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 205 nm |
Description
Application Column
BIST B+
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 50 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Lysine
Trilysine

HPLC Method for Separation of Glucose and Lysine on Primesep S Column
January 25, 2023
HPLC Method for Separation of Glucose and Lysine on Primesep S by SIELC Technologies
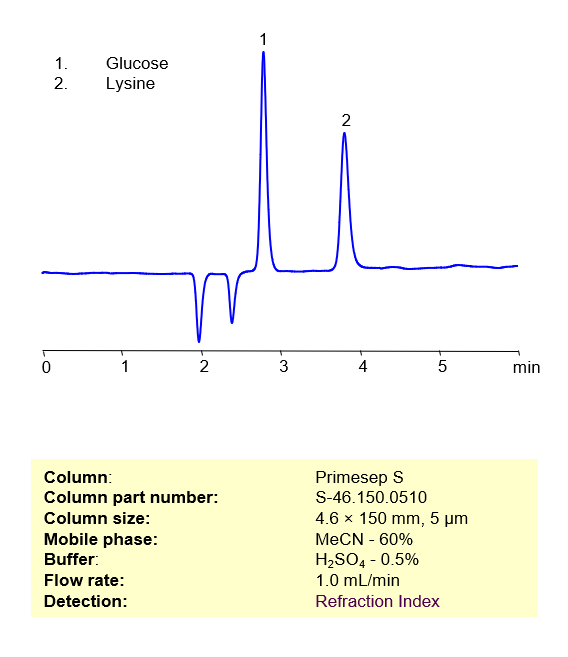
Lysine is an essential amino acid typically found in meat, and also cereal grains. It can be manufactured on a large scale by fermenting glucose, one of the most abundant sugars in the world. These two biological compounds can be retained, separated, and analyzed on a normal-phase Primesep S column with a simple isocratic mobile phase consisting of Acetonitrile (MeCN), water (H2O), and Sulfuric acid (H2SO4). This analysis method can be detected via Refraction Index (RI) Detection.
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Separation of Glucose and Lysine
Condition
| Column | Primesep S , 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 75/25% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.5% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | Refraction Index |
| Peak Retention Time | 4.81 min |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Drug |
| Analyzing Compounds | Glucose, Lysine |
Application Column
Primesep S2
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Lysine

HPLC Method for Analysis of Arginine, Lysine and Histidine Amino Acids on BIST B+
November 30, 2022
HPLC Method for Analysis of Arginine, Lysine, Histidine on BIST B+ by SIELC Technologies.
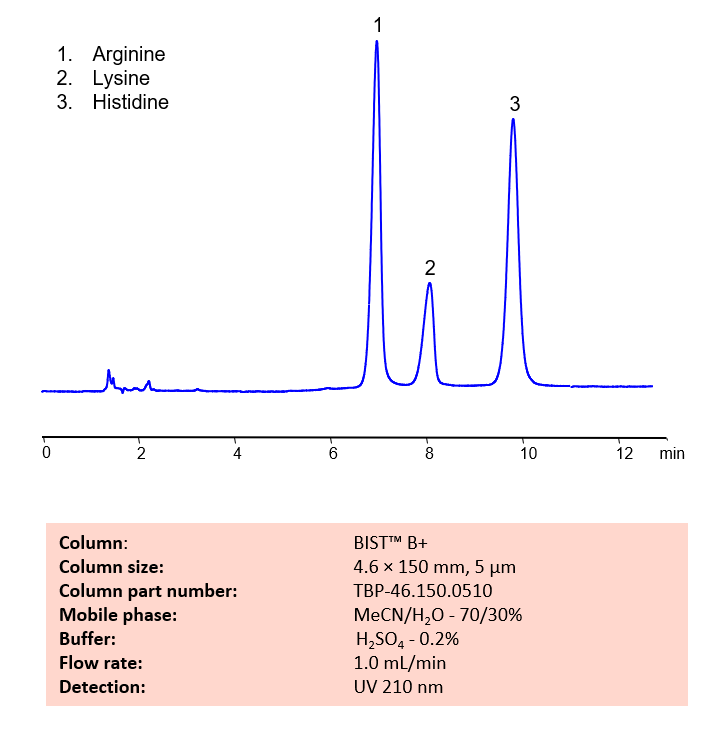
Arginine is a semiessential amino acid with the chemical formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. It was originally isolated from yellow lupin seedlings in 1886 by Ernst Schulze and Enst Steiger. Now, commercially, it is obtained through fermentation. Arginine can be typically found in meat, poultry, and fish. You can find detailed UV spectra of Arginine and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
Lysine is an essential amino acid with the chemical formula C6H14N2O2. It’s primary role is in proteinogenesis, but it also plays a part in uptake of essential mineral nutrients, production of carnitine, and histone modification. Lysine is known in pop culture thanks to Jurassic Park, in which dinosaurs were genetically altered to be unable to produce lysine. While in the story, this made the dinosaurs be unable to survive in the wild due to needing the lysine supplements provided by the staff at Jurassic Park, no real animal can produce lysine naturally. Lysine is another essential amino acid typically found in meat, and also cereal grains. You can find detailed UV spectra of Lysine and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
Histidine is an essential amino acid with the chemical formula C9H9N3O2. It cannot be produced within the body and must be obtained through consuming it. It s fundamental for repair of damaged tissue, growth of muscles, and making of blood cells through biosynthesis of protein. Outside of protein, it also has the unique property of being able to act as a buffer to help maintain stable pH levels in the body. Sources of it include meat, fish, dairy products, beans, and nuts. Histidine, is also typtically found in meat, poultry, and also cereal grains (like rice, wheat, and rye). You can find detailed UV spectra of Lysine and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
Basic amino acids, like Arginine, Lysine, Histidine can be difficult to separate and retain in typical reverse-phase chromatography. Using SIELC’s newly introduced BIST™ method, these three essential amino acids, which protonate in water, can be retained on a positively-charged anion-exchange BIST B+ column. There are two keys to this retention method: 1) a multi-charged, negative buffer, such as Sulfuric acid (H2SO4), which acts as a bridge, linking the positively-charged amino acid analytes to the positively-charged column surface and 2) a mobile phase consisting mostly of organic solvent (such as MeCN) to minimize the formation of a solvation layer around the charged analytes. Using this new and unique analysis method, Arginine, Lysine, and Histidine can be retained and UV detected at 210 nm.
Condition
| Column | BIST B+, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 70% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 210 nm |
| Peak Retention Time | 6.2, 8.0, 9.9 min |
Description
Application Column
BIST B+
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Histidine
Lysine

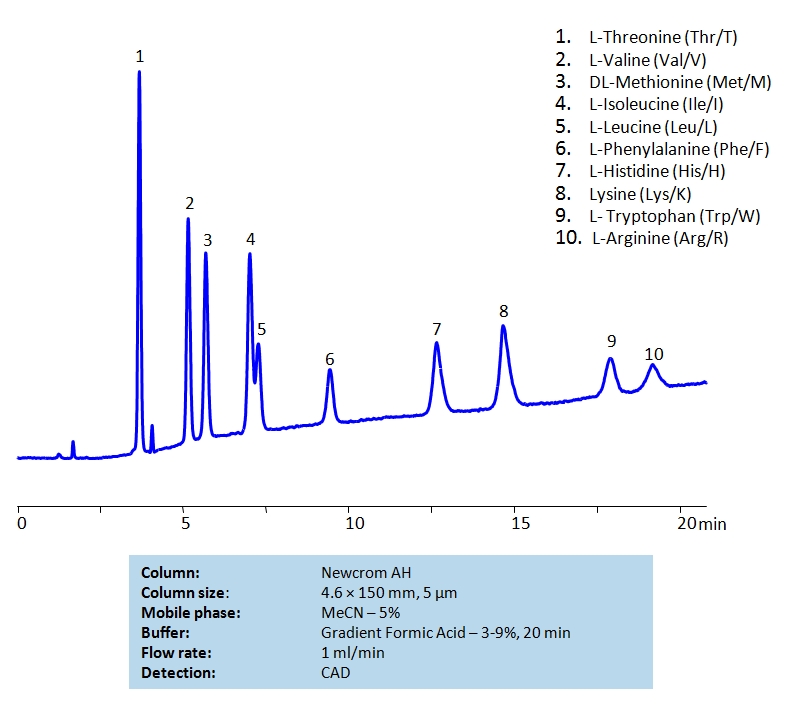
HPLC Separation of Mixture of Nine Essential Amino acids and Arginine on Newcrom AH Column
September 25, 2020
HPLC Method for L-Threonine, Valine, Methionine, Isoleucine, Leucine, Phenylalanine, Histidine, Tryptophan, Lysine, Arginine on Newcrom AH by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of L-Threonine, Valine, Methionine, Isoleucine, Leucine, Phenylalanine, Histidine, Tryptophan, Lysine, Arginine.
Essential amino acids cannot be made by the body. As a result, they must come from food.
The 9 essential amino acids are: histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine.
L-Threonine is an essential amino acid with the chemical formula C4H9NO3. It cannot be produced within the body and must be obtained through consuming it. It’s found in many protein-rich foods, including but not limited to eggs, meat, dairy, legumes, and seeds. It is necessary in the body as a building block of protein like collagen and elastin. The two proteins are crucial for skin, hair, and connective issue.
L-Valine is an essential amino acid with the chemical formula C5H11NO2. It cannot be produced within the body and must be obtained through consuming it. It’s found in foods including but not limited to nuts, legumes, whole grains, and seeds. It is especially beneficial for athletes. It is important for muscle repair, growth, and energy regulation.
DL-Methionine is an essential amino acid with the chemical formula C5H11NO2S. It cannot be produced within the body and must be obtained through consuming it. It is required for protein synthesis. It also helps build and repair tissue including, but not limited to, skin, hair, muscles, and nails. In a veterinary context, DL-Methionine is used to address bladder issues in dogs.
L-Isoleucine is an essential amino acid with the chemical formula C6H13NO2. It cannot be produced within the body and must be obtained through consuming it. It is a building block of protein that are essential for muscle growth, repair, and other bodily functions. It also helps regulate blood sugar levels and supports the immune system. It is found in foods like meat, fish, eggs, dairy, beans, lentils, nuts, and seeds.
L-Leucine is an essential amino acid with the chemical formula C6H13NO2. It cannot be produced within the body and must be obtained through consuming it. It stimulates production of protein that are essential for muscle building and repair. Meats are the easiest way to get L-Leucine in significant amounts.
L-Phenylalanine is an essential amino acid with the chemical formula C6H9NO2. It cannot be produced within the body and must be obtained through consuming it. It is typically found in high protein foods such as meat, eggs, and fish. Outside of being important for creation of protein, it is also used in treatment for skin disorders and depression.
L-Histidine is an essential amino acid with the chemical formula C9H11N3O2. It cannot be produced within the body and must be obtained through consuming it. It s fundamental for repair of damaged tissue, growth of muscles, and making of blood cells. Outside of protein, it also has the unique property of being able to act as a buffer to help maintain stable pH levels in the body. Sources of it include meat, fish, dairy products, beans, and nuts.
L-Tryptophan is an essential amino acid with the chemical formula C11H12N2O2. It cannot be produced within the body and must be obtained through consuming it. Like the other essential proteins, it is a building block for protein and muscle tissue, but it is also converted in the body into serotonin, which affects mood. L-Tryptophan is also used in treatments for severe PMS symptoms, depression, and insomnia. It is naturally found in red meat, poultry eggs, and dairy.
Lysine is an essential amino acid used in the synthesis of proteins. In biological conditions, it is a basic, charged molecule.
L-Arginine is an essential amino acid used in the synthesis of proteins.
L-Threonine, Valine, Methionine, Isoleucine, Leucine, Phenylalanine, Histidine, Tryptophan, Lysine, Arginine can be retained and analyzed using the Newcrom AH stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes a gradient method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water and acetonitrile (MeCN) with a Formic Acid buffer. Detection is performed using CAD.
| Column | Newcrom AH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 5% |
| Buffer | Gradient Formic Acid – 3-9%, 20 min |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | CAD |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements, Amino acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | L-Threonine, Valine, Methionine, Isoleucine, Leucine, Phenylalanine, Histidine, Tryptophan, Lysine, Arginine |
Application Column
Newcrom AH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Histidine
Isoleucine
L-Threonine
Leucine
Lysine
Methionine
Phenylalanine
Tryptophan
Valine

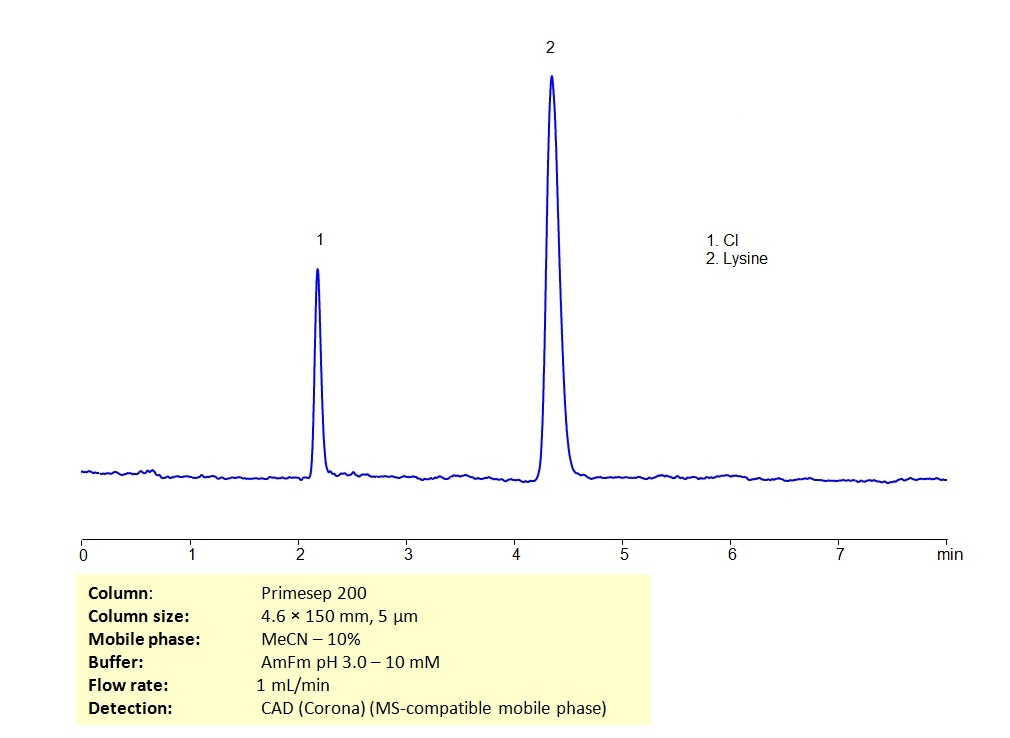
HPLC Determination of Lysine on Primesep 200 column in MS-compatible conditions
September 16, 2019
HPLC Method for Lysine, D-Lysine on Primesep 200 by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Lysine, D-Lysine
Lysine is an essential amino acid used in the synthesis of proteins. In biological conditions, it is a basic, charged molecule. Lysine can be retained on Primesep 200 mixed-mode column which has embedded weak acidic ion-pairing groups for retention of basic analytes in HPLC. The mobile phase consisting of acetonitrile (ACN) and water with ammonium formate (AmFm) makes this method analysis MS-compatible.
| Column | Primesep 200, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 10/90% |
| Buffer | AmFM pH 3.0 – 10 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | CAD (Corona), MS- compatible phase |
| Class of Compounds |
Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Carboxylic acid, Drug, Amino Acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Lysine, D-Lysine |
Application Column
Primesep 200
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Lysine

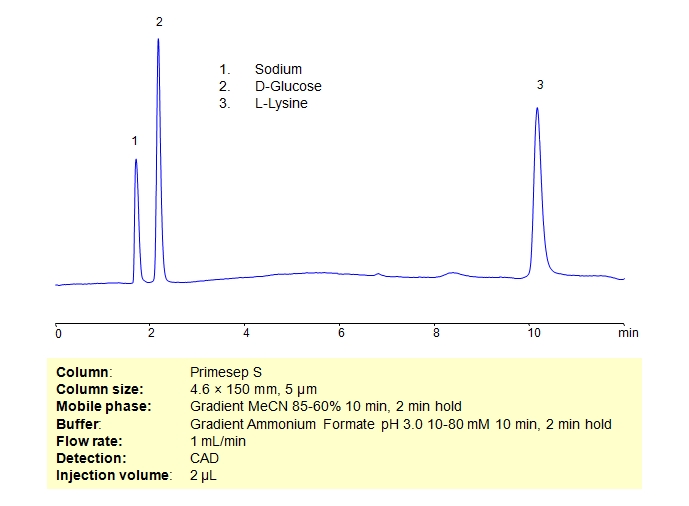
HPLC Separation of Mixture of D-Glucose and L-Lysine on Primesep S Column
February 7, 2019
HPLC Method for Glucose, Lysine on Primesep S by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Glucose, Lysine.
Sodium, which has a chemical symbol of Na, is a soft alkali metal that is highly reactive. It is found in abundance in everyday materials like table salt, sea water, and even the Earth’s crust. It is crucial for the body’s function and fluid balance.
D-Glucose is a simple sugar that is generated during photosynthesis. In humans, it is produced during hepatic gluconeogenesis. In many living organisms, it acts as an essential energy source. It is the most commonly occurring isomer of glucose in nature. It’s chemical formula is C₆H₁₂O₆.
L-Lysine is an essential amino acid with the chemical formula C6H14N2O2. As an amino acid, lysine is a building block for proteins. It’s crucial for health, but the body can’t produce it, so it must come from the diet. Lysine has been used in supplements to improve athletic performance, support immune health, and more. It’s also integral in the production of carnitine, a nutrient responsible for converting fatty acids into energy and helping to lower cholesterol.
Glucose, Lysine can be retained and analyzed using the Primesep S stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes a gradient method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water and acetonitrile (MeCN) with an ammonium formate buffer. Detection is performed using CAD.
| Column | Primesep S, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN – 85-60%, 10 min 2 min hold |
| Buffer | Gradient AmFm pH 3.0, 10-80 mM, 10 min 2 min hold |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | CAD (Corona) MS- compatible mobile phase |
| Class of Compounds |
Sugar, Amino Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | Glucose, Lysine |
Application Column
Primesep S
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Lysine

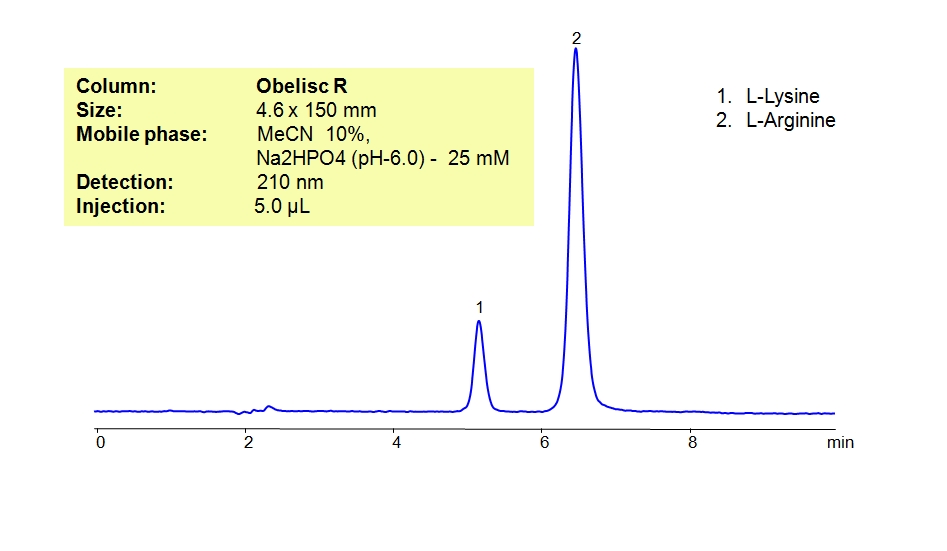
HPLC Method for Analysis of L-Lysine and L-Arginine
February 28, 2018
HPLC Method for Lysine, D-Lysine, Arginine, N-Nitro-L-arginine on Obelisc R by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Lysine, D-Lysine, Arginine, N-Nitro-L-arginine
L-Lysine is an essential amino acid required for growth and tissue repair, it can also help with anxiety. The amino acid is most often found in red meats,beans, fish, and dairy products. L-Arginine is an essential amino acid that is used to treat congestive heart failure, combat fatigue and circulatory diseases. It is also used to stimulate the immune system. Obelisc R is a reverse-phase column. It contains embedded ionic groups and can retain L-Lysine and L-Arginine. The method is UV compatible and can be used as a general approach for analyzing similar compounds.
| Column | Obelisc R, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 10/90% |
| Buffer | Na2HPO4 pH 6.0 – 25 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 210 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements, Amino acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Lysine, D-Lysine, Arginine, N-Nitro-L-arginine |
Application Column
Obelisc R
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
D-Lysine
Lysine
N-Nitro-L-arginine

HPLC Separation of Lysine and Arginine from Other Amino Acids
July 10, 2012
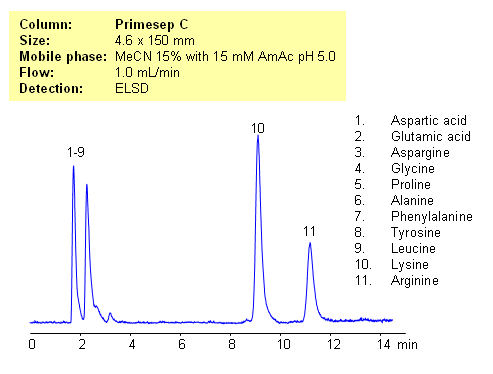
Application Notes: Amino acids are polar ionic compounds which are not retained on reversed-phase column without ion-pairing reagent. In our application, lysine and arginine can be separated from other amino acids. Amino acids with a pH between 3 and 5 and with one basic and one acidic group become very polar. Therefore these amino acids don’t have strong ion-exchange interaction with Primesep C stationary phase. Amino acids with two amino groups still carry positive net charge and can interact with stationary phase by cations-exchange mechanism. pH variation of the mobile phase can be an effective tool to adjust selectivity of separation for zwitter-ionic, basic and acidic compounds. This method can be used for separation of mono-charged compounds from compounds having an extra charge.
Application Columns: Primesep C
Application compounds: Aspartic acid, Glutamic acid, Aspargine, Glycine, Proline, Alanine, Phenylalanine, Tyrosine, Leucine, Lysine, Arginine
Detection technique: UV, LC/MS, ELSD/CAD
| Column | Primesep C, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 15% |
| Buffer | AmAc pH 5.0- 15 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | Aspartic acid, Glutamic acid, Aspargine, Glycine, Proline, Alanine, Phenylalanine, Tyrosine, Leucine, Lysine, Arginine |
Application Column
Primesep C
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsArginine
Asparagine
Aspartic Acid
Glutamic Acid
Glycine
Leucine
Lysine
Phenylalanine
Proline
Tyrosine
UV Detection

Separation of Small Lysine-based Peptide Oligomers on BIST B+ Column
July 8, 2011
Polylysine includes a large group of similar polymers with various uses. Some are used as food preservatives, while others are used for drug delivery in pharmaceuticals. Polymers with charged monomeric units, such as polylysine, are often difficult to separate using typical ion-exchange chromatography due to very strong and often irreversible interactions with the oppositely charged column surface. Therefore, an extremely high concentration of the buffer, up to several molar, is usually needed to facilitate an ion-exchange process. This high buffer concentration, however, is not desirable because of the significantly increased viscosity of the mobile phase and the salt formation in the pump components. With BIST™, these polymers can be separated and retained with relatively weak buffers (in the mM regime) and a fairly simple gradient. Using this new and unique analysis method, polylysine can be retained and UV detected at 215 nm.
| Column | BIST B+, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | H3PO4 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 215 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | Lysine-based Peptide Oligomers |
Application Column
BIST B+
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Polylysine
UV Detection

HPLC Separation of Amino Acids in Zero Organic Mode on Primesep 200 column
July 8, 2011
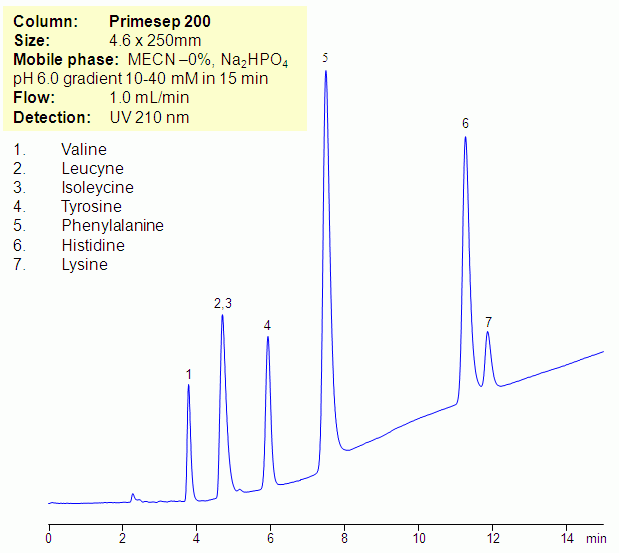
Essential and non-essential amino acids can be retained and separated in zero-organic mode on Primesep mixed-mode HPLC columns. Zero-organic mode is required to monitor isotopes of carbon. Amino acids are retained by combination of reversed-phase and cation-exchange mechanisms. At lower pH, some of the amino acids are more hydrophobic. Buffer pH will affect ionization state of amino acids, and at higher pH (above 2.5), the amino acids will be less hydrophobic and retentive in zero-organic mode. Amino acids can be monitored by low UV. Method can be used in archeological research for analysis of various molecules where presence of organic component of the mobile phase interferes with analysis.
| Column | Primesep 200, 4.6×250 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | Na2HPO4 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 210 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | Valine, Leucyne, Isoleycine, Tyrosine, Phenylalanine, Histidine, Lysine |
Application Column
Primesep 200
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsIsoleucine
Leucine
Lysine
Phenylalanine
Tyrosine
Valine

HPLC Analysis of Active Drug and Amino Acids in a Formulation
October 14, 2010
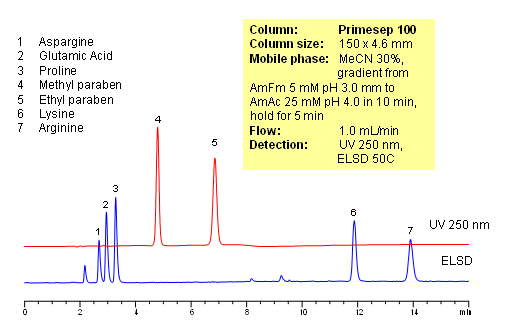
Polar amino acids are very often used as components of vitamin and supplement composition. Analysis of such complex composition is a challenging task. In this application, 5 amino acids (asparagine, glutamic acid, proline and arginine) and two preservatives (methyl paraben and propyl paraben) are separated on a Primesep 100 reversed-phase cation-exchange column with LC/MS compatible mobile phase. Method does not require ion-pairing reagent in the mobile phase. Compounds are monitored by ELSD and UV. Method is validated for quantitation of underivatized amino acids in complex mixtures. The method is simple and robust and can be used for analysis of various vitamin formulations.
| Column | Primesep 100, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | AmFm |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD 50C, UV 250 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | Glutamic acid, Aspargine, Proline, Lysine, Arginine, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben |
Application Column
Primesep 100
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsAsparagine
Ethylparaben
Glutamic Acid
Lysine
Methylparaben
Proline
UV Detection

HPLC Method for Determination of Lysine in Ibuprofen Lysine Composition
July 16, 2009
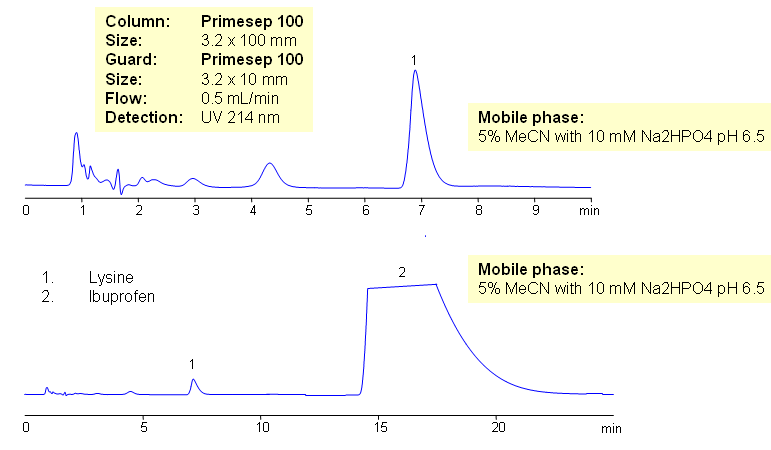
Ibuprofen lysine is ibuprofen based medication which is uses lysine as counter-ion of the ibuprofen. The use of lysine makes the drug more soluble in water. Lysine is very hydrophilic compound with low UV activity, while ibuprofen is hydrophobic compound with good UV activity. These properties are making straight analysis of Ibuprofen Lysine (ibuprofen lysinate) a challenging task. Ion-pairing reagent required for retention of lysine in reversed-phase chromatography. Both compounds can be quantitated in one run without use of IP reagent. Because of the huge difference in UV activity of ibuprofen and lysine, a separate method for quantitation of lysine in ibuprofen lysinate might be required. Separation involving switching valve and guard column allows to trap ibuprofen on the guard and wash it away during analysis of lysine. This HPLC method allows to quantitate lysine separately from ibuprofen. Detailed set up of switching valve/guard system is described in our newsletter. Method can be adapted to quantitation of single compound in complex mixtures.
Lysine

HPLC-ELSD Method for Analysis of Amino Acids on Primesep 100 Column
September 18, 2006
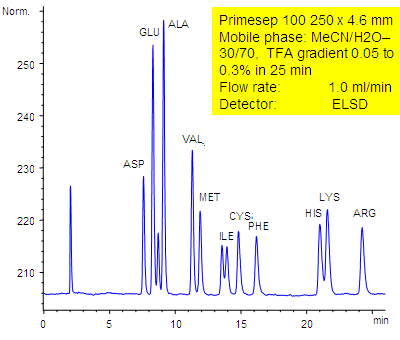
11 underivatized amino acids (aspartic acid, glutamic acid, alanine, valine, methionine, isoleucine, cysteine, phenylalanine, histidine, lysine, and arginine) are separated by a Primesep 100 HPLC column by reversed-phase and ion-exchange mechanisms with LC/MS compatible conditions without the use of ion-pair reagents. The HPLC separation uses a TFA (trifluoroacetic acid) gradient in a mobile phase of water acetonitrile (MeCN, ACN with evaporative light scattering detection (ELSD).
| Column | Primesep 100, 4.6×250 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 30/70% |
| Buffer | TFA , gradient 0.05-0.3 % , 25 min |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | Aspartic acid, Glutamic acid, Alanine, Valine, Methionine, Isoleucine, Cysteine, Phenylalanine, Histidine, Lysine, Arginine |
Application Column
Primesep 100
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsAmino Acids
Arginine
Aspartic Acid
Cysteine
Glutamic Acid
Histidine
Isoleucine
Lysine
Methionine
Phenylalanine
Valine