Applications:
HPLC Method for Analysis of Polylysine on BIST™ B+ Column
November 30, 2022
HPLC Method for Polylysine on BIST B+ by SIELC Technologies
Polylysine is a group of lysine homopolymers with the chemical formula (C6H12N2O)n. Due to its’ high positive charge density, it is often used in drug delivery for complexes with negatively charged macromolecules. They have been especially useful in delivery of DNA and proteins.
Polylysine includes a large group of similar polymers with various uses. Some are used as food preservatives, while others are used for drug delivery in pharmaceuticals. Polymers with charged monomeric units, such as polylysine, are often difficult to separate using typical ion-exchange chromatography due to very strong and often irreversible interactions with the oppositely charged column surface. Therefore, an extremely high concentration of the buffer, up to several molar, is usually needed to facilitate an ion-exchange process. This high buffer concentration, however, is not desirable because of the significantly increased viscosity of the mobile phase and the salt formation in the pump components. With BIST™, these polymers can be separated and retained with relatively weak buffers (in the mM regime) and a fairly simple gradient. Using this new and unique analysis method, Polylysine can be retained and UV detected at 205 nm.
Condition
| Column | BIST B+, 4.6 x 50 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 205 nm |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Peptide, Homopolypeptide |
| Analyzing Compounds | Polylysine |
Application Column
BIST B+
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 50 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

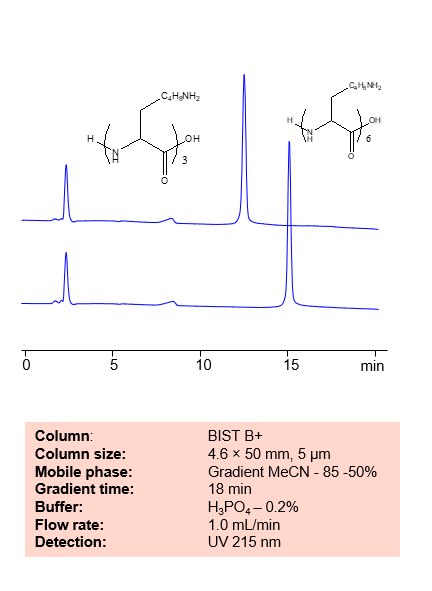
HPLC Method for Analysis of Low MW Polylysine on BIST™ B+ Column
November 30, 2022
HPLC Method for Polylysine on BIST B+ by SIELC Technologies

Polylysine is a group of lysine homopolymers with the chemical formula (C6H12N2O)n. Due to its’ high positive charge density, it is often used in drug delivery for complexes with negatively charged macromolecules. They have been especially useful in delivery of DNA and proteins.
Polylysine includes a large group of similar polymers with various uses. Some are used as food preservatives, while others are used for drug delivery in pharmaceuticals. Polymers with charged monomeric units, such as polylysine, are often difficult to separate using typical ion-exchange chromatography due to very strong and often irreversible interactions with the oppositely charged column surface. Therefore, an extremely high concentration of the buffer, up to several molar, is usually needed to facilitate an ion-exchange process. This high buffer concentration, however, is not desirable because of the significantly increased viscosity of the mobile phase and the salt formation in the pump components. With BIST™, these polymers can be separated and retained with relatively weak buffers (in the mM regime) and a fairly simple gradient. Using this new and unique analysis method, Polylysine can be retained and UV detected at 205 nm.
Condition
| Column | BIST B+, 4.6 x 50 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 205 nm |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Peptide, Homopolypeptide |
| Analyzing Compounds | Polylysine |
Application Column
BIST B+
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 50 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

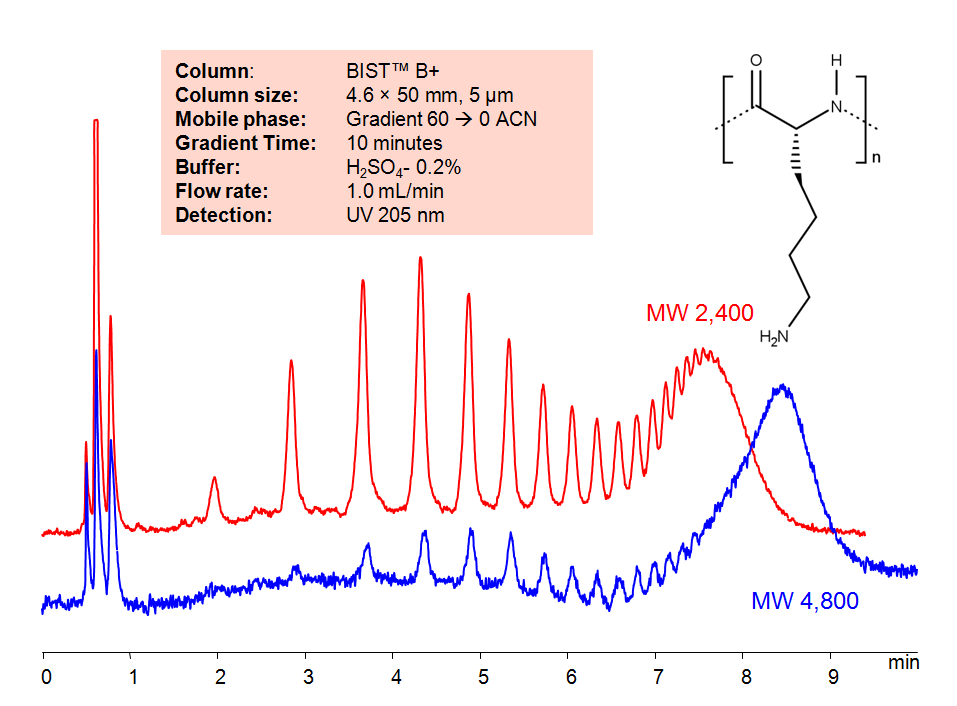
HPLC Method for Analysis of Narrow Fractions of Polylysine on BIST B+ Column
November 30, 2022
HPLC Method for Analysis of Narrow Fractions of Polylysine on BIST B+ by SIELC Technologies.
Polylysine is a group of lysine homopolymers with the chemical formula (C6H12N2O)n. Due to its’ high positive charge density, it is often used in drug delivery for complexes with negatively charged macromolecules. They have been especially useful in delivery of DNA and proteins.
Polylysine includes a large group of similar polymers with various uses. Some are used as food preservatives, while others are used for drug delivery in pharmaceuticals. Polymers with charged monomeric units, such as Polylysine, are often difficult to separate using typical ion-exchange chromatography due to very strong and often irreversible interactions with the oppositely charged column surface. Therefore, an extremely high concentration of the buffer, up to several molar, is usually needed to facilitate an ion-exchange process. This high buffer concentration, however, is not desirable because of the significantly increased viscosity of the mobile phase and the salt formation in the pump components. With BIST™, these polymers can be separated and retained with relatively weak buffers (in the mM regime) and a fairly simple gradient. Using this new and unique analysis method, Polylysine can be retained and UV detected at 210 nm.
Condition
| Column | BIST B+, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 205 nm |
| Peak Retention Time | 2.9 min |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Peptide, Homopolypeptide |
| Analyzing Compounds | Polylysine |
Application Column
BIST B+
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

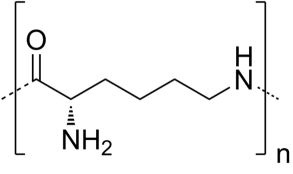
Separation of Small Lysine-based Peptide Oligomers on BIST B+ Column
July 8, 2011
Polylysine includes a large group of similar polymers with various uses. Some are used as food preservatives, while others are used for drug delivery in pharmaceuticals. Polymers with charged monomeric units, such as polylysine, are often difficult to separate using typical ion-exchange chromatography due to very strong and often irreversible interactions with the oppositely charged column surface. Therefore, an extremely high concentration of the buffer, up to several molar, is usually needed to facilitate an ion-exchange process. This high buffer concentration, however, is not desirable because of the significantly increased viscosity of the mobile phase and the salt formation in the pump components. With BIST™, these polymers can be separated and retained with relatively weak buffers (in the mM regime) and a fairly simple gradient. Using this new and unique analysis method, polylysine can be retained and UV detected at 215 nm.
| Column | BIST B+, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | H3PO4 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 215 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | Lysine-based Peptide Oligomers |
Application Column
BIST B+
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Polylysine
UV Detection

HPLC Analysis of Polylysine on Primesep AP Column
October 14, 2010
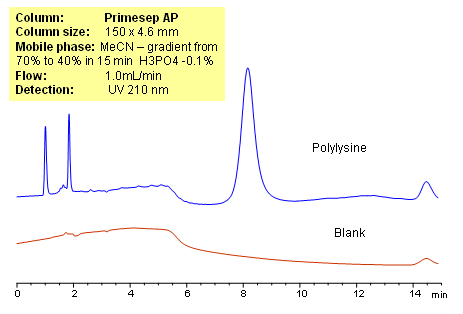
Polylysine is a small natural homo-polymer made out of amino acid lysine that is produced by bacterial fermentation. Due to the fact that it is a complex mixture of polymers with different molecular weight it is very hard to obtain a single sharp peak for this compound. Polylysine was successfully analyzed on a Primesep AP column in HILIC/cation-exclusion mode. Cation-exclusion mode on a Primesep AP column allows to obtain sharper peak. Presence of the basic groups on the surface of silica eliminated silanol interactions between basic sites of polylysine and acidic sites of Primesep AP column.
Application Column
Primesep AP
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select options