HPLC Method for Separation of Cysteine, Glutathione, reduced, Cystine, Cysteine-glutathione disulfide, Glutathione oxidized on Primesep 100 by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
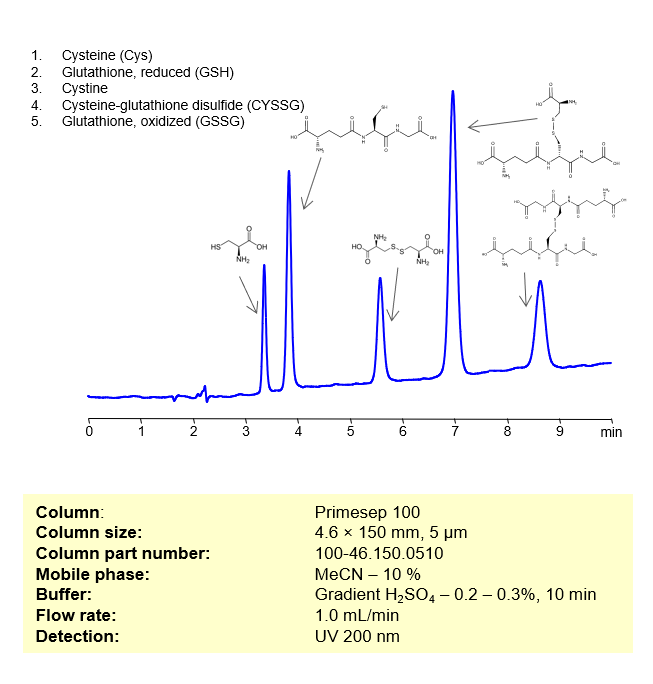
These compounds are all involved in redox reactions and cellular defenses against oxidative stress in biological systems. Here’s a bit more about each of them:
- Cysteine (Cys): This is a sulfur-containing amino acid that’s used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Its thiol side chain often participates in enzymatic reactions, and contributes to the stability of proteins by forming disulfide bonds.
- Glutathione, reduced (GSH): A tripeptide (small protein) consisting of the amino acids glutamic acid, cysteine, and glycine. GSH serves as an antioxidant, helping to prevent damage to cellular components caused by reactive oxygen species such as free radicals and peroxides.
- Cystine: This is a covalently bonded dimer molecule of two cysteine molecules, connected through a disulfide bond. Disulfide bonds between cysteine residues in peptide chains contribute to the 3D structure of proteins. In dietary supplements and food labeling, this compound is often referred to as a conditionally essential amino acid.
- Cysteine-glutathione disulfide (CySSG): This is a mixed disulfide formed by the reaction of glutathione with the oxidized form of cysteine (cystine). It is one of the forms in which cysteine is stored and transported in plasma.
- Glutathione, oxidized (GSSG): This is the oxidized form of glutathione, produced when two glutathione molecules are linked by a disulfide bond. GSSG is reduced back to GSH by the enzyme glutathione reductase, which also requires NADPH as a cofactor.
Overall, these molecules play vital roles in the body’s antioxidant defenses, detoxification of xenobiotics, modulation of redox-controlled signaling pathways, and regulation of cellular proliferation and apoptosis.
These compounds can be retained, separated, and analyzed using a reverse-phase Primesep 100, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended column. The mobile phase for this method consists of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and Sulfuric acid, which serves as a buffer. This analytical method can be
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Cysteine, Cystine, Cysteine-glutathione disulfide, L-Cysteine
Condition
| Column | Primesep 100, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN -10% |
| Buffer | Gradient H2SO4 0.1-0.3%, 10 min |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200 nm |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Thiol, Amino acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Cysteine, Glutathione, reduced, Cystine, Cysteine-glutathione disulfide, Glutathione oxidized |
Application Column
Primesep 100
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Cysteine-glutathione disulfide
Cystine
L-Cysteine





