| CAS Number | 76-05-1 |
|---|---|
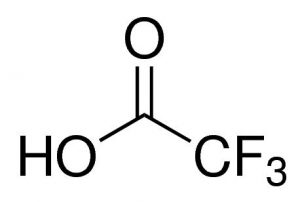
| Molecular Formula | C2HF3O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 114.023 |
| InChI Key | DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 0.766 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
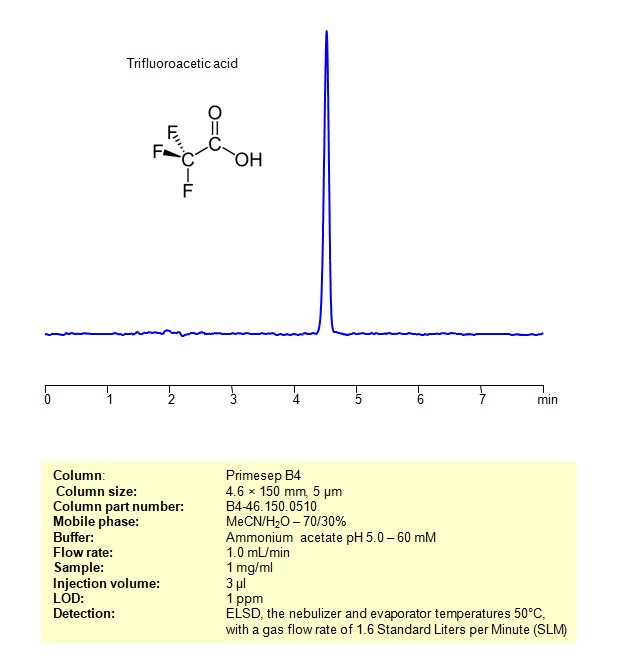
HPLC ELSD Method for Analysis Trifluoroacetic acid on Primesep B4 Column
February 2, 2024
HPLC Method for Analysis of TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid) on Primesep B4 by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid)
Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) is a strong organic acid with the chemical formula CF₃COOH.
Properties:
- TFA is a colorless liquid at room temperature.
- It is a highly corrosive and volatile acid.
- It is miscible with common organic solvents.
Uses:
- Trifluoroacetic acid is commonly used in organic chemistry as a reagent, particularly in peptide synthesis and purification.
- It is used as a strong acid in various chemical reactions.
- TFA is also employed in the analysis of compounds by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy.
Precautions:
- Due to its corrosive nature, trifluoroacetic acid should be handled with care, and appropriate safety measures should be taken, including the use of protective equipment.
Trifluoroacetic acid can be retained and analyzed using an Primesep B4 mixed-mode stationary phase column. The analysis employs an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and ammonium formate as a buffer. Detection is achieved using ELSD
| Column | Primesep B4, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 70/30% |
| Buffer | Ammonium formate pH 3.0 – 60 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, the nebulizer and evaporator temperatures 50°C, with a gas flow rate of 1.6 Standard Liters per Minute (SLM) |
| Samples | 1 mg/ml |
| Injection volume | 3 µl |
| LOD* | 1 ppm |
| Class of Compounds | Quaternity amines |
| Analyzing Compounds | TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid) |
Application Column
Primesep B4
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

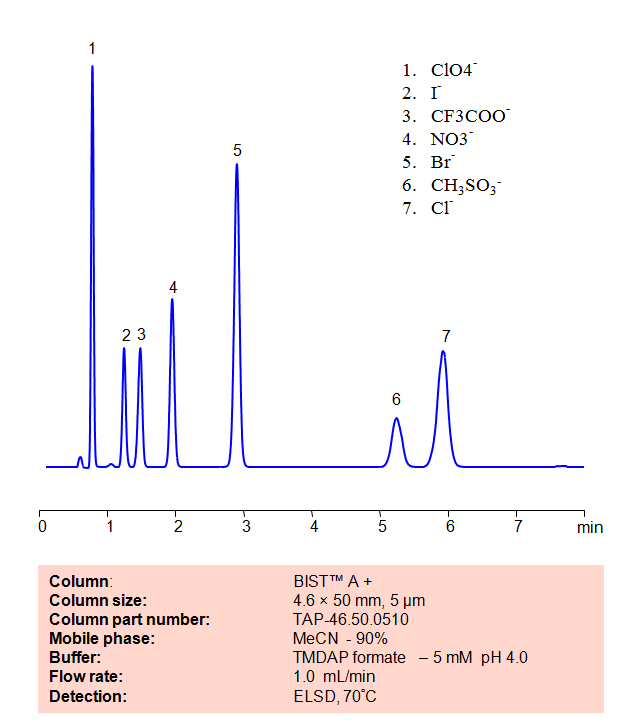
HPLC Method for Analysis of Inorganic anions on BIST™A+ Column
July 7, 2022
Application Column
BIST A+
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 50 mm
Particle Size: 10 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Chloride
Iodide
Methanesulfonic Acid
Nitrate
Perchlorate
TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid)

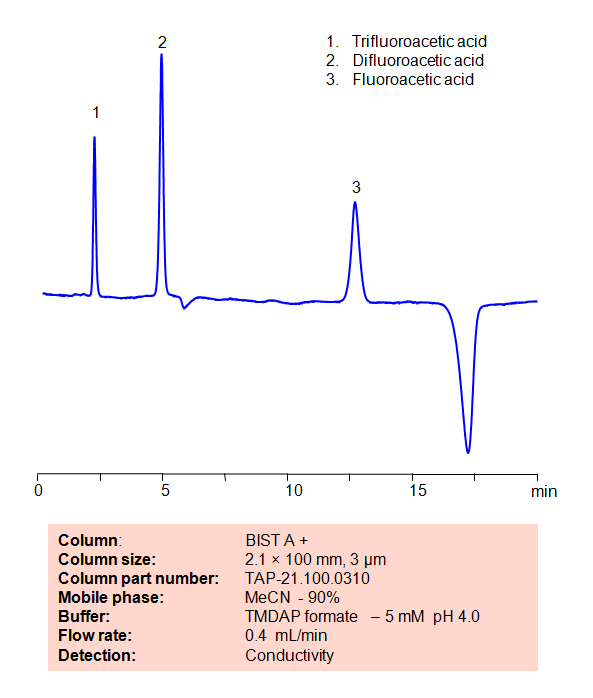
HPLC Method for Analysis of Fluoroacetic acid, Difluoroacetic acid and Trifluoroacetic acid on BIST A+ Column
July 7, 2022
| Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ | ||||||||||||||
| High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Fluoroacetic acid, Difluoroacetic acid and Trifluoroacetic acid | ||||||||||||||
|
Application Column
BIST A+
BIST™ columns offer a unique and effective way to achieve separations that were traditionally challenging or even impossible with other HPLC columns. With the use of a special mobile phase, these ion exchange columns provide very strong retention for analytes with the same charge polarity as the stationary phase, unlocking new chromatography applications. What makes BIST™ columns stand out is their proprietary surface chemistry, which results in superior selectivity, resolution, and sensitivity. These columns offer a simple, efficient solution for a variety of analytical challenges, making them an excellent choice for researchers and analysts across many different fields. To learn more about the technology that powers BIST™ columns and to explore related applications, check out https://BIST.LC.
Select optionsFluoroacetic acid
TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid)

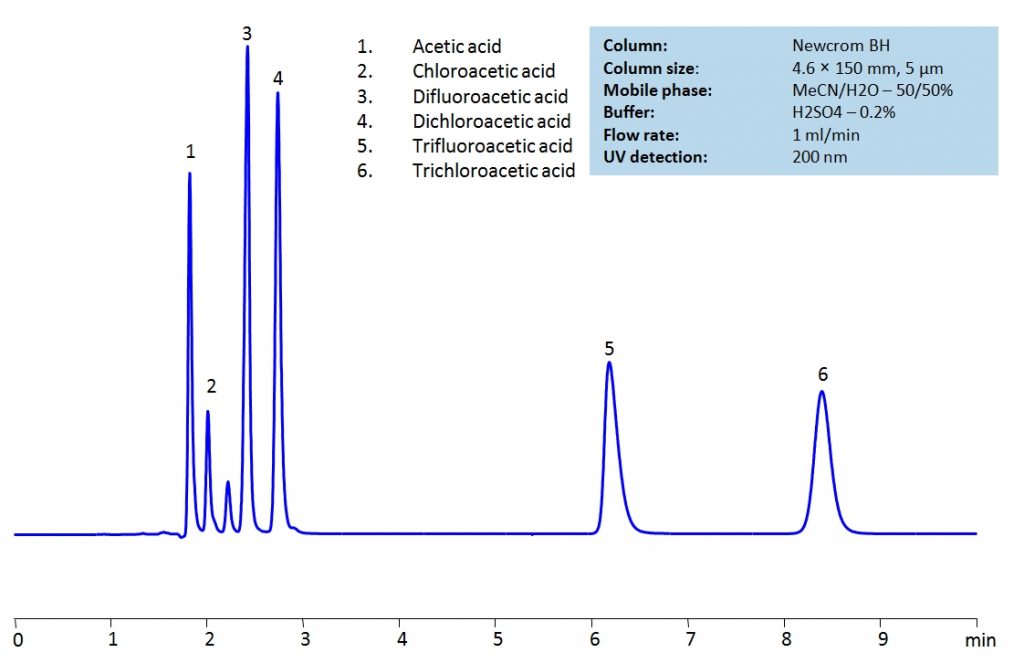
HPLC Separation of Acetic acid, Chloroacetic acid, Dichloroacetic acid, Trifluoroacetic acid, Trichloroacetic acid
May 20, 2020
HPLC Method for TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid), Acetic Acid, Chloroacetic acid, Dichloroacetic acid, Trichloroacetic acid, Difluoroacetic acid on Newcrom BH by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid), Acetic Acid, Chloroacetic acid, Dichloroacetic acid, Trichloroacetic acid, Difluoroacetic acid.
Acetic Acid is the second simplest carboxylic acid with the chemical formula CH3COOH. It is well known for being the active ingredient in vinegar, leading to the belief that it is the earliest mass produced acid, dating back to 3BC. Outside of it’s use in food and household matters, it is also used in production of vinyl acetate and cellulose acetate.
Chloroacetic Acid, also known as monochloroacetic acid (MCA), is a very toxic acid with the chemical formula ClCH2CO2H. It is most often used in the production of other chemicals such as phenoxy herbicides, carboxymethyl cellulose, and carboxymethyl starch. It is considered extremely hazardous as it can cause burns on skin and eyes as well as be fatal if inhaled or swallowed.
Difluoroacetic Acid (DFA) is a dihalogenocarboxylic acid with the chemical formula CHF2COOH. As a solution, it quickly dissociates to form difluoroacetate ions.
Dichloroacetic Acid (DCA), also known as bichloroacetic acid (BCA), is a highly corrosive acid with the chemical formula C2H2Cl2O2. While it is used in personal care items and disinfectants, it is a known carcinogen. Despite that, research shows that it may be a plausible treatment for certain cancers.
Trifluoroacetic Acid (TFA) is a synthetic organofluorine acid with the chemical formula C2HF3O2. It is corrosive and toxic to aquatic life and mammals, causing severe irritation and burns to skin, eyes, and the respiratory tract. Not only that, TFA is also highly mobile and persistent, leading to high retention of it in soil and water. Determination of it’s threat level on the environmental and health levels are still ongoing.
Trichloroacetic Acid (TCA), also known as trichloroethanoic acid, is an analogue of acetic acid with the chemical formula C2HCl3O2. It is often used as a skin peeling treatment to exfoliate damaged skin and encourage collagen production. In laboratory research, it is used for precipitating proteins and to extract and prepare standards for ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) assays.
Acetic acid and its substitution derivatives, chloroacetic acid, dichloroacetic acid, trichloroacetic acid, difluoroacetic acid and trifluoroacetic acid, are heavily used as building blocks for more complex compounds in organic synthesis. All six acids can be isocratically separated in HPLC using Newcrom BH mixed-mode column with acetonitrile (ACN) and water mobile phase with sulfuric acid (H2SO4) as buffer and UV detected at 200nm.
| Column | Newcrom BH, 3.2 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 50/50% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200nm |
| Class of Compounds | Acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid), Acetic Acid, Chloroacetic acid, Dichloroacetic acid, Trichloroacetic acid, Difluoroacetic acid |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 3.2 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Chloroacetic acid
Dichloroacetic acid
Difluoroacetic acid
TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid)
Trichloroacetic acid

HPLC Separation of Haloacetic acids on Newcrom BH Column
May 20, 2020
HPLC Method for Trichloroacetic acid, Dichloroacetic acid, TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid) on Newcrom BH by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Trichloroacetic acid, Dichloroacetic acid, TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid).
Dichloroacetic Acid (DCA), also known as bichloroacetic acid (BCA), is a highly corrosive acid with the chemical formula C2H2Cl2O2. While it is used in personal care items and disinfectants, it is a known carcinogen. Despite that, research shows that it may be a plausible treatment for certain cancers.
Trifluoroacetic Acid (TFA) is a synthetic organofluorine acid with the chemical formula C2HF3O2. It is corrosive and toxic to aquatic life and mammals, causing severe irritation and burns to skin, eyes, and the respiratory tract. Not only that, TFA is also highly mobile and persistent, leading to high retention of it in soil and water. Determination of it’s threat level on the environmental and health levels are still ongoing.
Trichloroacetic Acid (TCA), also known as trichloroethanoic acid, is an analogue of acetic acid with the chemical formula C2HCl3O2. It is often used as a skin peeling treatment to exfoliate damaged skin and encourage collagen production. In laboratory research, it is used for precipitating proteins and to extract and prepare standards for ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) assays.
Trichloroacetic acid, Dichloroacetic acid, TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid) can be retained and analyzed using the Newcrom BH stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water and acetonitrile (MeCN) with a [buffer] buffer. Detection is performed using UV.
| Column | Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 50/50% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.5% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200nm |
| Class of Compounds | Acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Trichloroacetic acid, Dichloroacetic acid, TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid) |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid)
Trichloroacetic acid

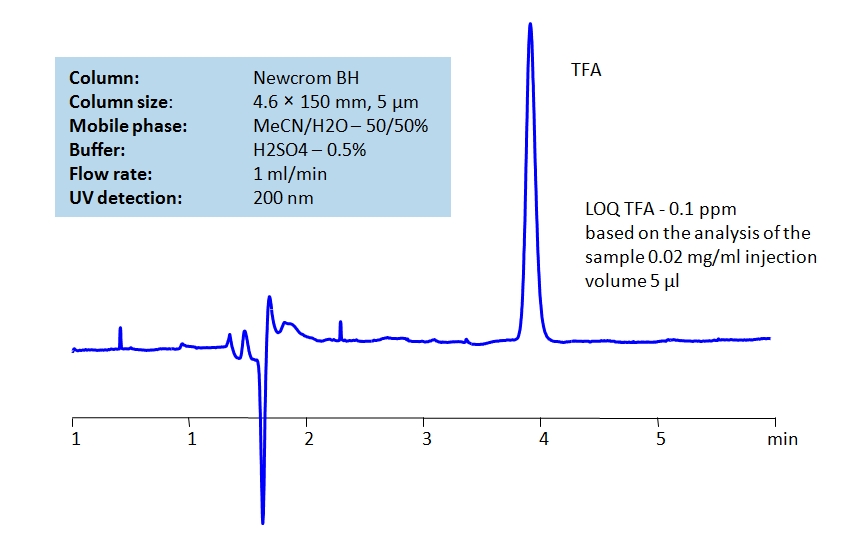
HPLC Determination of TFA on Newcrom BH Column
May 19, 2020
HPLC Method for TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid) on Newcrom BH by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid).
Trifluoroacetic Acid (TFA) is a synthetic organofluorine acid with the chemical formula C2HF3O2. It is a substitution derivative of acetic acid, with fluorine atoms replacing the hydrogen atoms of the acetyl group. It is also a much stronger acid than acetic acid. TFA is widely used in organic synthesis as well as ion pairing reagent or buffer in HPLC. It is corrosive and toxic to aquatic life and mammals, causing severe irritation and burns to skin, eyes, and the respiratory tract. Not only that, TFA is also highly mobile and persistent, leading to high retention of it in soil and water. Determination of it’s threat level on the environmental and health levels are still ongoing.
TFA can be detected at low UV. Using Newcrom BH mixed-mode column, a mobile phase of acetonitrile (ACN) and water with sulfuric acid (H2SO4) buffer can be used to retain TFA and UV detect it at 200nm.
| Column | Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 50/50% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.5% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200nm |
| Class of Compounds | Acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid) |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

HPLC Analysis of Trifluoroacetic and Acetic Acid on Obelisc N Mixed-Mode HPLC Column
May 11, 2015
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
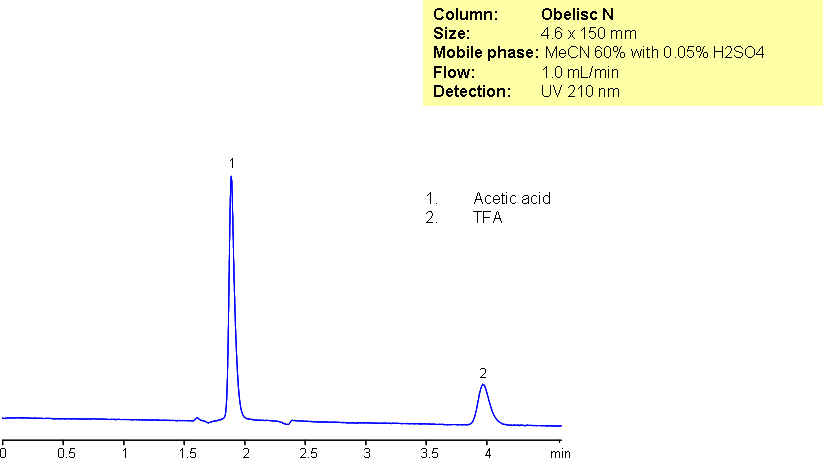
Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) and acetic acid (AcOH) are very commonly used in organic chemistry. They were separated using an Obelisc N column which uses HILIC/anion-exchange. The mixed-mode of Obelisc N allows for better peak shape and retention of carboxylic acids. Sulfuric acid was used to enhance polar retention by suppressing ionization of the strong acid TFA.
| Column | Obelisc N, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 60% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.05% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 210 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), Acetic acid (AcOH) |
Application Column
Obelisc N
SIELC has developed the Obelisc™ columns, which are mixed-mode and utilize Liquid Separation Cell technology (LiSC™). These cost-effective columns are the first of their kind to be commercially available and can replace multiple HPLC columns, including reversed-phase (RP), AQ-type reversed-phase, polar-embedded group RP columns, normal-phase, cation-exchange, anion-exchange, ion-exclusion, and HILIC (Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography) columns. By controlling just three orthogonal method parameters - buffer concentration, buffer pH, and organic modifier concentration - users can adjust the column properties with pinpoint precision to separate complex mixtures.
Select optionsTFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid)

HPLC Separation of Inorganic Anions
November 21, 2010
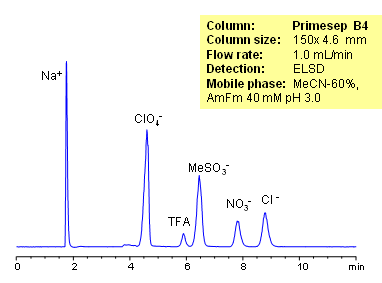
Organic and inorganic acids and ions can be separated on a Primesep B4 column based on their ionic properties. Method can be used for quantitation of residual acids in various products and sample matrices. Trifluoracetic, hydrochloric, methanesulfonic, and nitric acids are separated using ACN-water-ammonium formate. Ions can be detected by ELSD, CAD or LC/MS.
| Column | Primesep B4, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | AmFm |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Ions, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Sodium, Phosphate, Chloride, Nitrate, Sulfate, Iodide, Perchlorate, Trifluoracetic |
Application Column
Primesep B4
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsMethanesulfonic Acid
Nitrate
Nitric Acid
Organic Acids
Perchloric Acid
TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid)

HPLC Analysis of Components of Ionic Liquids by Mixed-Mode Chromatography
September 14, 2008
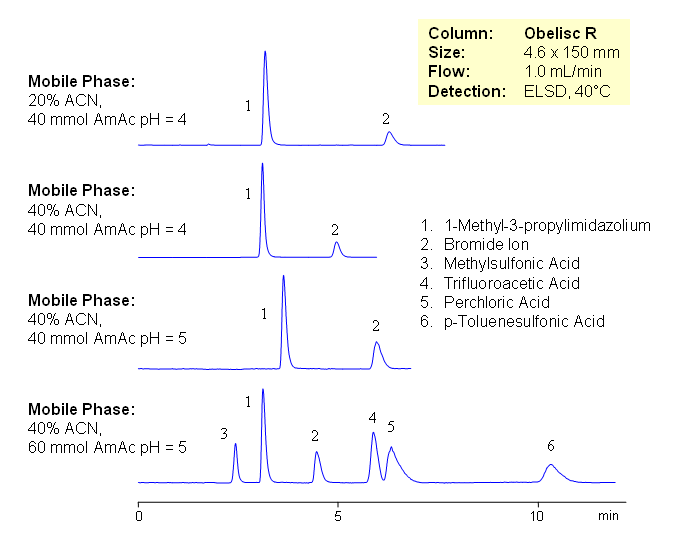
Ionic liquid is an ionic compound which is liquid at room (or close to room) temperature. Most of the ionic liquids are in a dynamic equilibrium where at any time more than 99.99% of the liquid is made up of ionic, rather than molecular, species. Room-temperature ionic liquids consist of bulky cation (for example, substituted imidazolium) compounds. A wide range of anions is used as counter ions in ionic liquids: organic and inorganic anions such as chloride, iodide, tetrafluoroborate, hexafluorophosphate, bistriflimide, triflate, tosylate. Ionic liquids are widely used as solvents in organic reactions. When products are isolated from ionic liquids, they need to be analyzed for residual ionic liquid content.
Because both constituents of the ionic liquid are very different in terms of charge and hydrophobic properties, it is impossible to analyze entire ionic liquids by traditional chromatography. An effective and universal method for analysis of ionic liquids is developed on an Obelisc R HPLC column. Components on the ionic liquids are retained based on ionic and hydrophobic interactions. Obelisc R column has both positively and negatively charged ionic groups, making it possible to retain and separate cations and anions of ionic liquids on one column. Method can be used for quantitative of various ionic liquids containing organic and inorganic ions. Retention time of basic component can be effectively adjusted by pH, stronger anionic and hydrophobic counter-ions might require higher buffer concentration. Composition can be monitored by combination of UV and ELSD or by LC/MS.
| Column | Obelisc R , 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | AmAc |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | 1-Methyl-3-propylimidazolium, Bromide Ion, Methylsulfonic Acid, Trifluoroacetic Acid, Perchloric Acid, p-Toluenesulfonic Acid |
Application Column
Obelisc R
SIELC has developed the Obelisc™ columns, which are mixed-mode and utilize Liquid Separation Cell technology (LiSC™). These cost-effective columns are the first of their kind to be commercially available and can replace multiple HPLC columns, including reversed-phase (RP), AQ-type reversed-phase, polar-embedded group RP columns, normal-phase, cation-exchange, anion-exchange, ion-exclusion, and HILIC (Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography) columns. By controlling just three orthogonal method parameters - buffer concentration, buffer pH, and organic modifier concentration - users can adjust the column properties with pinpoint precision to separate complex mixtures.
Select optionsBromide
Ionic Liquid
Methylsulfonic Acid
Perchloric Acid
TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid)
p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA)
UV Detection

Retention of TFA on Atlantis and Obelisc N
August 22, 2008
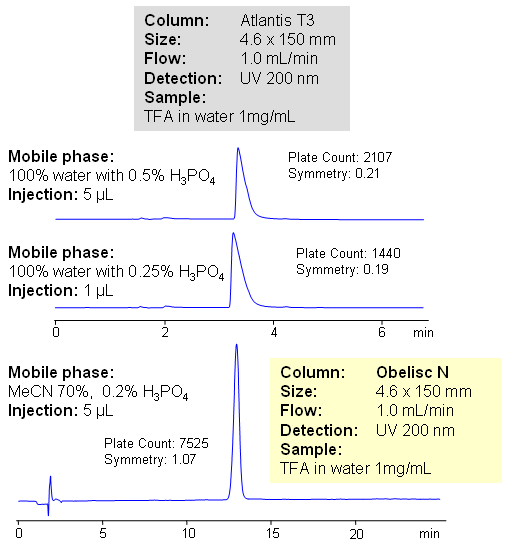
Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) is a strong carboxylic acid, with pKa of 0.3. TFA is widely used in chemistry as reagent and as counter-ion for basic drugs and other compounds. TFA is very polar in nature, and has low UV activity. It is often required to quantitate trifluoracetic acid in various formulations. HPLC method for determination of trifluoroacetic acid on Obelisc N column provides a viable alternative for quantitation of TFA. TFA is retained by ion-exchange mechanism on mixed-mode HILIC column. Relative comparison shows high loadability of the method. Obelisc N columns show much better peak shape and retention than traditional HPLC columns (Atlantis T3 from Waters). Perfect peak symmetry is achieved by adjusting amount of acetonitrile, buffer pH and buffer concentration. TFA is monitored by low UV (200 nm). Alternatively trifluoroacetic acid can be analyzed by ESLD with ammonium formate in the mobile phase. TFA forms non-volatile salt with ammonia, thus giving ability to quantitate it.
Application Column
Obelisc N
SIELC has developed the Obelisc™ columns, which are mixed-mode and utilize Liquid Separation Cell technology (LiSC™). These cost-effective columns are the first of their kind to be commercially available and can replace multiple HPLC columns, including reversed-phase (RP), AQ-type reversed-phase, polar-embedded group RP columns, normal-phase, cation-exchange, anion-exchange, ion-exclusion, and HILIC (Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography) columns. By controlling just three orthogonal method parameters - buffer concentration, buffer pH, and organic modifier concentration - users can adjust the column properties with pinpoint precision to separate complex mixtures.
Select options
HPLC Analysis of TFA
July 5, 2008
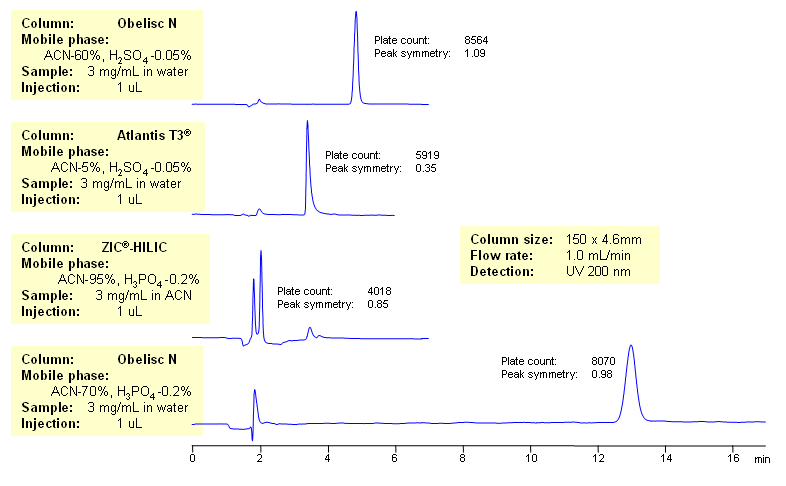
Dual functionality of Obelisc N column allows to retain and provide efficient peaks of strong carboxylic acids such as TFA. Simple UV quantitation and identification method became possible due to the unique properties of this stationary phase. In case of an RP separation poor retention and peak symmetry was obtained at a very low concentration of ACN. Sulfuric acid was used to suppress ionization of TFA to increase the hydrophobicity. In case of a typical HILIC column the phosphoric acid was used to increase ionization to make TFA more polar to enhance polar retention. The types of columns that do not have the mixed mode nature of Obelisc N can’t provide significant retention and efficiency.
Application Column
Obelisc N
SIELC has developed the Obelisc™ columns, which are mixed-mode and utilize Liquid Separation Cell technology (LiSC™). These cost-effective columns are the first of their kind to be commercially available and can replace multiple HPLC columns, including reversed-phase (RP), AQ-type reversed-phase, polar-embedded group RP columns, normal-phase, cation-exchange, anion-exchange, ion-exclusion, and HILIC (Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography) columns. By controlling just three orthogonal method parameters - buffer concentration, buffer pH, and organic modifier concentration - users can adjust the column properties with pinpoint precision to separate complex mixtures.
Select options