HPLC Method for TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid), Acetic Acid, Chloroacetic acid, Dichloroacetic acid, Trichloroacetic acid, Difluoroacetic acid on Newcrom BH by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid), Acetic Acid, Chloroacetic acid, Dichloroacetic acid, Trichloroacetic acid, Difluoroacetic acid.
Acetic Acid is the second simplest carboxylic acid with the chemical formula CH3COOH. It is well known for being the active ingredient in vinegar, leading to the belief that it is the earliest mass produced acid, dating back to 3BC. Outside of it’s use in food and household matters, it is also used in production of vinyl acetate and cellulose acetate.
Chloroacetic Acid, also known as monochloroacetic acid (MCA), is a very toxic acid with the chemical formula ClCH2CO2H. It is most often used in the production of other chemicals such as phenoxy herbicides, carboxymethyl cellulose, and carboxymethyl starch. It is considered extremely hazardous as it can cause burns on skin and eyes as well as be fatal if inhaled or swallowed.
Difluoroacetic Acid (DFA) is a dihalogenocarboxylic acid with the chemical formula CHF2COOH. As a solution, it quickly dissociates to form difluoroacetate ions.
Dichloroacetic Acid (DCA), also known as bichloroacetic acid (BCA), is a highly corrosive acid with the chemical formula C2H2Cl2O2. While it is used in personal care items and disinfectants, it is a known carcinogen. Despite that, research shows that it may be a plausible treatment for certain cancers.
Trifluoroacetic Acid (TFA) is a synthetic organofluorine acid with the chemical formula C2HF3O2. It is corrosive and toxic to aquatic life and mammals, causing severe irritation and burns to skin, eyes, and the respiratory tract. Not only that, TFA is also highly mobile and persistent, leading to high retention of it in soil and water. Determination of it’s threat level on the environmental and health levels are still ongoing.
Trichloroacetic Acid (TCA), also known as trichloroethanoic acid, is an analogue of acetic acid with the chemical formula C2HCl3O2. It is often used as a skin peeling treatment to exfoliate damaged skin and encourage collagen production. In laboratory research, it is used for precipitating proteins and to extract and prepare standards for ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) assays.
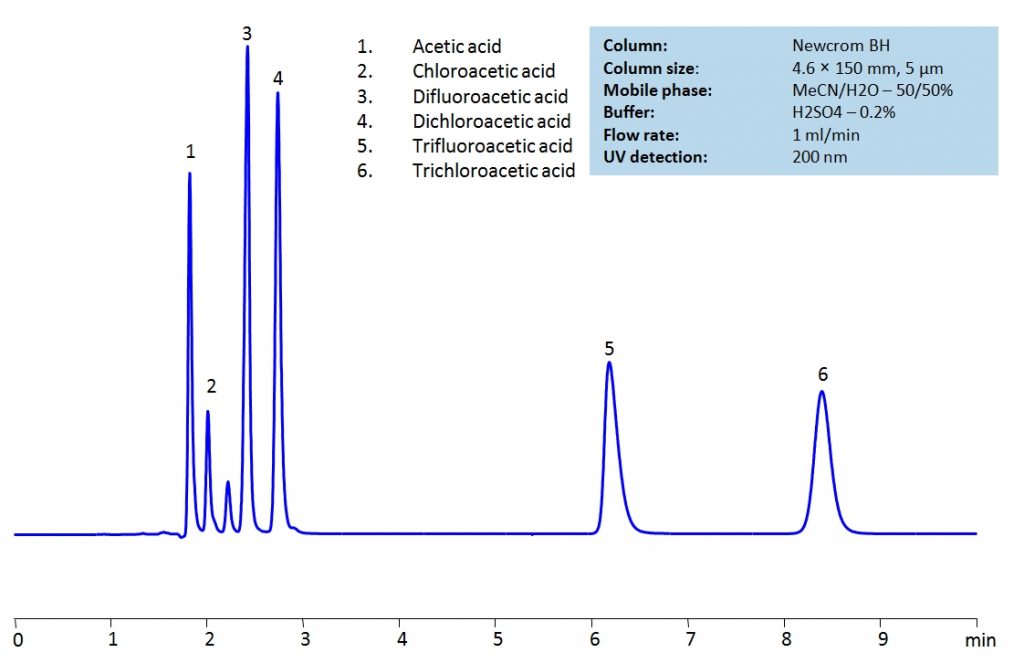
Acetic acid and its substitution derivatives, chloroacetic acid, dichloroacetic acid, trichloroacetic acid, difluoroacetic acid and trifluoroacetic acid, are heavily used as building blocks for more complex compounds in organic synthesis. All six acids can be isocratically separated in HPLC using Newcrom BH mixed-mode column with acetonitrile (ACN) and water mobile phase with sulfuric acid (H2SO4) as buffer and UV detected at 200nm.
| Column | Newcrom BH, 3.2 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 50/50% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200nm |
| Class of Compounds | Acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid), Acetic Acid, Chloroacetic acid, Dichloroacetic acid, Trichloroacetic acid, Difluoroacetic acid |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 3.2 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Chloroacetic acid
Dichloroacetic acid
Difluoroacetic acid
TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid)
Trichloroacetic acid