| CAS Number | 14797-73-0 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | ClO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 99.450 |
| InChI Key | VLTRZXGMWDSKGL-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| LogP | -4.63 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
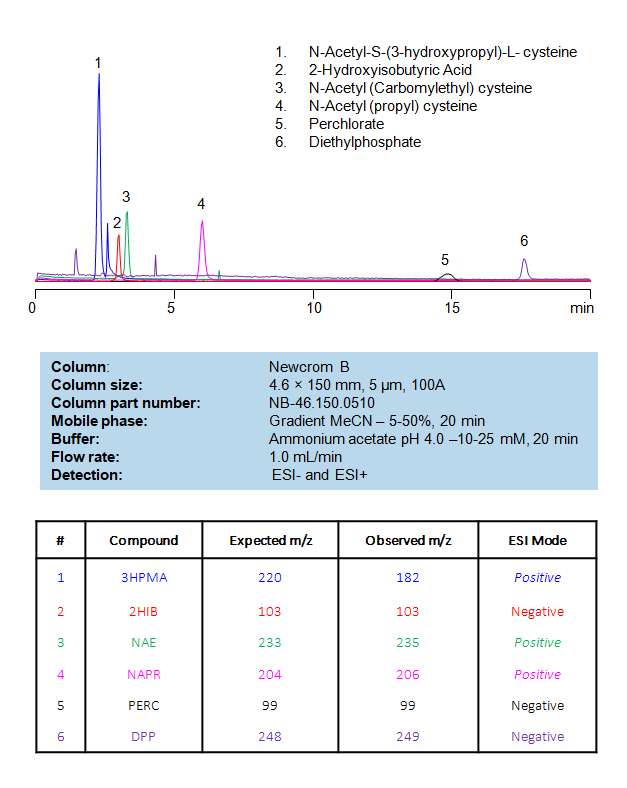
HPLC-MS Method for Separation of Metabolites and Biomarkers on Newcrom B Column
September 8, 2023
HPLC Method for Separation and Analysis of Acidic Toxin Metabolites with an MS-Compatible Mobile Phase on a Newcrom B Column by SIELC Technologies.
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
Metabolites and biomarkers are key terms in the fields of biochemistry, pharmacology, and medicine.
- Metabolites:
- Definition: These are small molecules produced during metabolism, which is the set of chemical reactions that occur within cells to maintain life. Metabolites can be either products of metabolism or the substrates used in metabolic reactions.
- Types: There are primary metabolites, which are directly involved in normal growth, development, and reproduction (like amino acids and sugars), and secondary metabolites, which often have specialized roles such as defense mechanisms in plants (like alkaloids or antibiotics).
- Uses: In the context of drug testing, for instance, the presence of certain metabolites can reveal whether someone has taken a specific drug, even if the drug itself is no longer present in the person’s system.
- Biomarkers:
- Definition: A biomarker, or biological marker, is a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often used to assess the risk or presence of disease, to monitor the progress of disease, or to see how the body responds to a treatment.
- Types: Biomarkers can be specific cells, molecules, genes, enzymes, hormones, or metabolites. They can also be measurements like heart rate or blood pressure.
- Uses: In medicine, biomarkers can be used for early disease detection (like elevated PSA levels indicating potential prostate cancer), monitoring disease progression (like HIV viral load tests to see how well antiretroviral treatment is working), or understanding disease mechanisms. They can also be used to see if a body has been exposed to certain harmful substances, indicating potential harm or risk.
N-Acetyl-S-(3-hydroxypropyl)-L-cysteine (3HPMA) is a common metabolite of the herbicide and pollutant Acrolein. 2-Hydroxyisobutyric Acid (2HIB) is a neuro and adrenal toxin that is a common metabolite of the fuel additives Methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) and Ethyl tert-butyl ether (ETBE). N-Acetyl(Carbomylethyl)cysteine (NAE) is a metabolite of Acrylamide which can act as a neuro toxin in cases of long term exposure. N-Acetyl(propyl)cysteine (NAPR) is a metabolite of the popular industrial organic solvent 1-bromopropane (1-BP). Perchlorate (PERC) inhibits thyroid activity and can be used to treat hyperthyroidism, but can be toxic in large amounts or in regularly-functioning thyroids. Diphenylphosphate (DPP) is a metabolite of the popular flame retardant triphenyl phosphate (TPHP). These acidic toxin metabolites can be retained, separated, and analyzed on a mixed-mode Newcrom B column with a mobile phase consisting of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN), and Ammonium Acetate (AmAc). This analytical method can be detected with high resolution and peak symmetry with many evaporative detection methods, including Evaporative Light Scattering Detection (ELSD), Charged Aerosol Detector (CAD), and Electrospray Ionization (ESI) for Mass Spectrometry (MS).
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analyses of Michler’s ketone
Condition
| Column | Newcrom B, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN/H2O – 5-50%, 20 min |
| Buffer | Gradient Ammonium acetate pH 4.0 –10-25 mM, 20 min |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ESI- and ESI |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Metabolites and Biomarkers |
| Analyzing Compounds | Metabolites and Biomarkers |
Application Column
Newcrom B
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Diphenyl phosphate
N-Acetyl (Carbamoylmethyl) cysteine
N-Acetyl-S-(3-hydroxypropyl)-L-cysteine
N-Acetyl-S-propyl-L-cysteine
Perchlorate

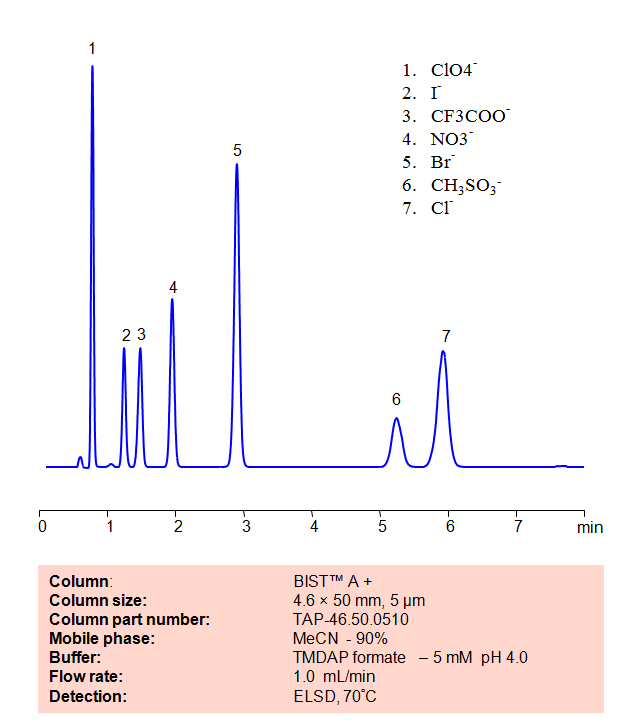
HPLC Method for Analysis of Inorganic anions on BIST™A+ Column
July 7, 2022
Application Column
BIST A+
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 50 mm
Particle Size: 10 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Chloride
Iodide
Methanesulfonic Acid
Nitrate
Perchlorate
TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid)

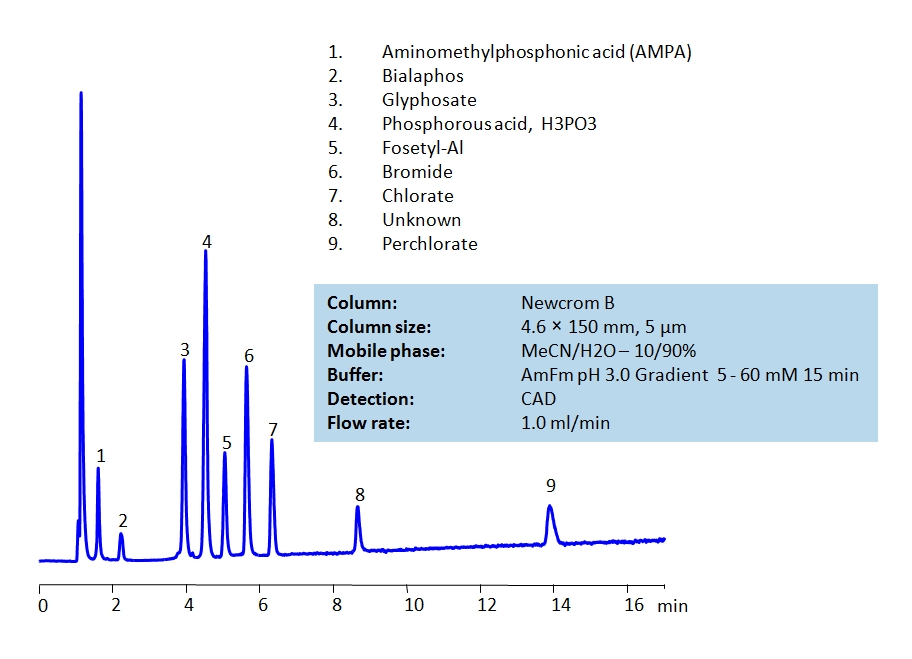
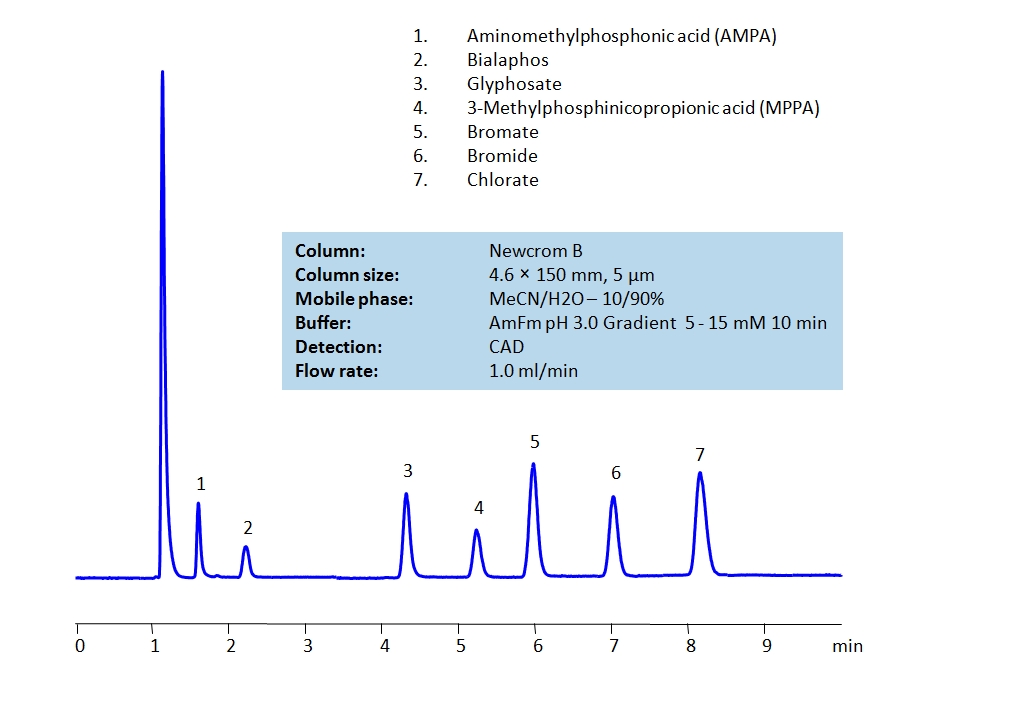
HPLC Separation of Polar Pesticides on Newcrom B Column
November 19, 2020
HPLC Method for Glyphosate, Phosphorous acid, Fosetyl-Al, Bromide, Chlorate, Perchlorate, Bialaphos, Aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA), Bromate, Sodium Bromate, 3-(Methylphosphinico)propionic acid on Newcrom B by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Glyphosate, Phosphorous acid, Fosetyl-Al, Bromide, Chlorate, Perchlorate, Bialaphos, Aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA), Bromate, Sodium Bromate, 3-(Methylphosphinico)propionic acid.
Pesticide is a more generic term that includes herbicides, fungicides and insecticides in its definition. Herbicides are used to control unwanted plants, they are also known as weedkillers. Insecticides are used to kill insects. Fungicides are used to kill parasitic fungi. All are heavily used in agriculture. By using HPLC, many different pesticides can be separated and their retention characteristics controlled using the Newcrom B mixed-mode column.
| Column | Newcrom B, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 10/90% |
| Buffer | AmFm pH 3.0 Gradient 5 – 60 mM 15 min |
| Flow Rate | 1 ml/min |
| Detection | CAD |
| Column | Newcrom B, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 10/90% |
| Buffer | AmFm pH 3.0 Gradient 5 – 15 mM 10 min |
| Flow Rate | 1 ml/min |
| Detection | CAD |
| Class of Compounds | Pesticides, Herbicides, Fungicides, Insecticides |
| Analyzing Compounds | Glyphosate, Phosphorous acid, Fosetyl-Al, Bromide, Chlorate, Perchlorate, Bialaphos, Aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA), Bromate, Sodium Bromate, 3-(Methylphosphinico)propionic acid |
Application Column
Newcrom B
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA)
Bialaphos
Bromate
Bromide
Chlorate
Fosetyl-Al
Glyphosate
Perchlorate
Phosphorous acid
Sodium Bromate

Separation of Chlorate, Perchlorate, and Phosphonate Ions on Primesep D Column
June 11, 2020
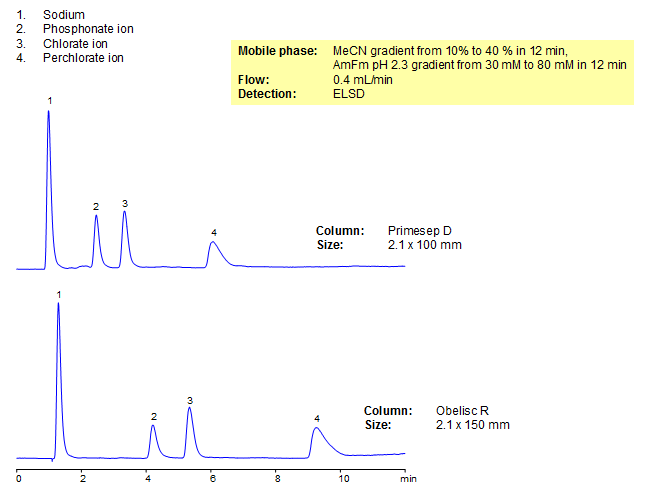
The ionic forms of Chlorate, Perchlorate, and Phosphonates are useful in many industries including medicine, paper and use in explosives. Due to their lack of UV activity, an ELSD was used to detect both the anions and cations of all three sodium salts. The ions were retained on both Primesep D and Obelisc R columns. Primesep D is a reverse phase column with embedded basic ion-pairing groups. Obelisc R is also a reverse phase column, but can be additionally tuned due to embedded ionic groups and a hydrophobic chain.
| Column | Primesep D, 2.1×100 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN – 10-40%, 12 min |
| Buffer | Gradient AmFm pH 2.3- 30-80 mM, 12 min |
| Flow Rate | 0.4 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Chlorate, Perchlorate, Phosphonate Ions |
Application Column
Primesep D
Column Diameter: 2.1 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Perchlorate

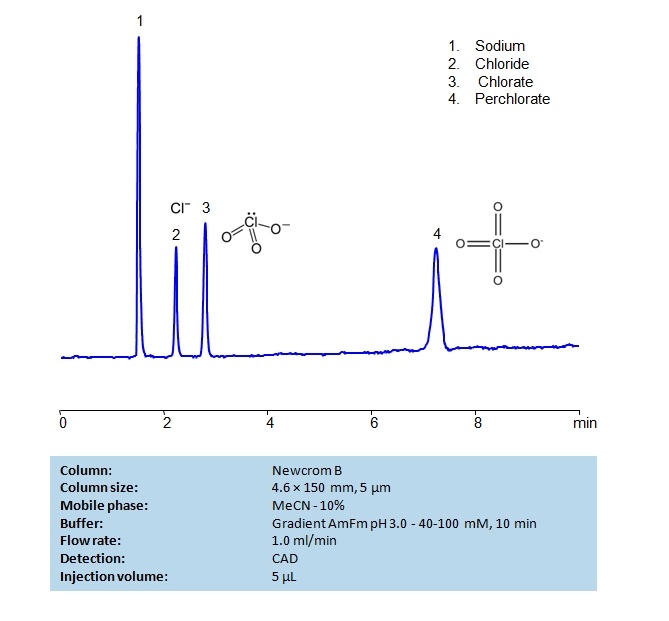
HPLC Determination of Chloride, Chlorate and Perchlorate on Newcrom B Column
December 10, 2019
HPLC Method for Chlorate, Perchlorate, Sodium Chlorate, Chloride on Newcrom B by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Chlorate, Perchlorate, Sodium Chlorate, Chloride
Main source of contamination of environment by perchlorates are rocket fuels, car airbags, and fireworks.
EPA developed regulation of the perchlorate level in drinking water which already adapted by several states.HPLC analysis of [compound] with Newcrom B. Includes separation method, chromatogram, and mobile phase.
The most convenient, universal and very sensitive way to measure perchlorate is chromatography.
SIELC developed a simple, rugged, and selective HPLC method which allows to measure perchlorate in different matrices including drinking water.
This method allows to measure simultaneously other chloro containing ions such as chloride, and chlorate.
The method shows high selectivity and specificity.
The mobile phase is a simple mixture of water acetonitrile and ammonium formate.
The column used in the analysis has advanced surface chemistry with long chain holding a terminal positively changed functional group.
| Column | Newcrom B, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 10/90% |
| Buffer | Gradient AmFm pH 3.0 – 40-100 mM , 10 min |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | CAD |
| Class of Compounds | Ions, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Chlorate, Perchlorate, Sodium Chlorate, Chloride |
Application Column
Newcrom B
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Chloride
Perchlorate
Sodium Chlorate

HPLC Separation of Inorganic Anions on Newcrom BH Column
October 23, 2019
HPLC Method for Sodium, Phosphate, Chloride, Bromide, Nitrate, Sulfate, Iodine, Perchlorate, Iodide on Newcrom BH by SIELC Technologies
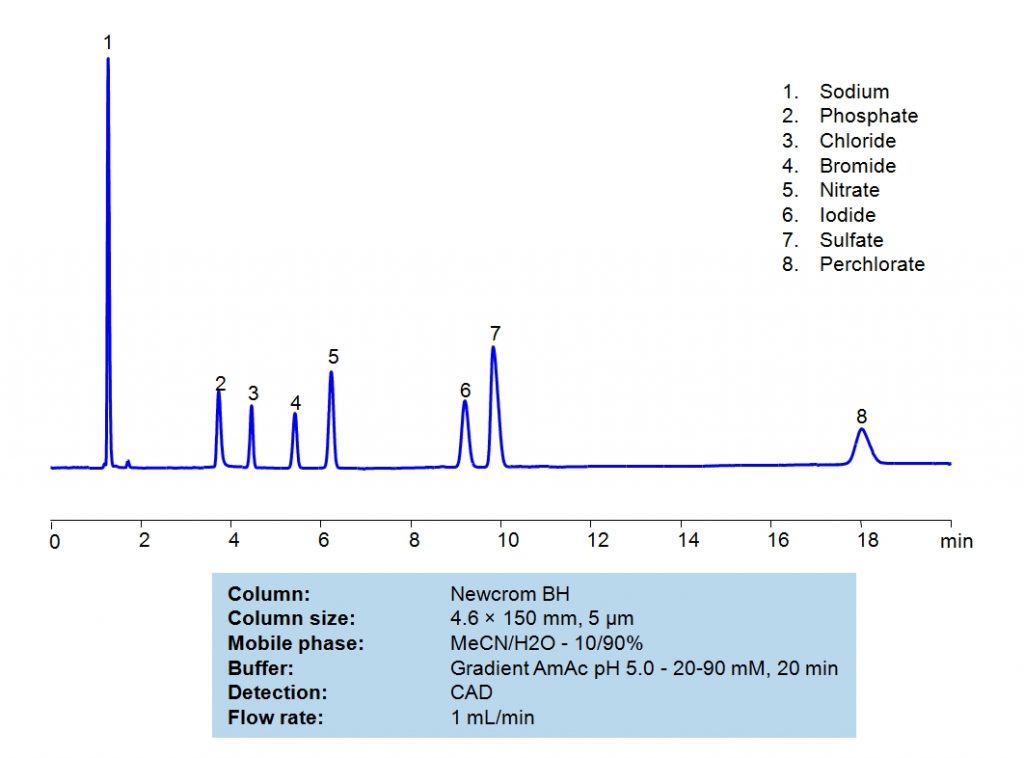
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Sodium, Phosphate, Chloride, Bromide, Nitrate, Sulfate, Iodine, Perchlorate, Iodide
Sodium, which has a chemical symbol of Na, is a soft alkali metal that is highly reactive. It is found in abundance in everyday materials like table salt, sea water, and even the Earth’s crust. It is crucial for the body’s function and fluid balance.
Phosphate, PO43-, is a compound that plays an important part in biological energy transfer. It contains phosphorus, which is also a key component in bones and teeth. It is also a buffer, which helps maintain pH levels in a body.
Chloride is typically used to refer to a compound or molecule that contains a chlorine anion: Cl–. It is an electrolyte that is essential for bodily functions including blood pH, fluid balance, cellular functions, and more. Imbalance of chloride can indicate underlying health problems.
Bromide is typically used to refer to a compound or molecule that contains a bromide anion: Br–. It is often found in anticonvulsants, flame-retardant materials, and cell stains.
Nitrate, NO3–, is a compound of nitrogen and oxygen. It is essential as a nutrient in plants; therefore, it is often used in fertilizers. It is easily found in leafy greens. While it is important for cardiovascular health, too high of exposure to it can be dangerous.
Iodide, the Ionic form of Iodine, I– is essential for thyroid hormone production. Lack of it can lead to iodine deficiency disorders. It is typically found in Iodized salt and occasionally as an antiseptic.
Sulfate is an ionic chemical with the formula SO42-. In nature, it is usually found in geodes like gypsum. It is also created in atmosphere from sulfur dioxide. It is used for a variety of applications, but most notably, coloring wood and creating light-reflecting paints.
Perchlorate is an inorganic compound with the formula ClO4–. It is most typically used for explosives. For example, fireworks and rocket propellants. Due to it’s water solubility, it can easily contaminate it. When ingested, it can pose a health risk and cause developmental harm.
Sodium, Phosphate, Chloride, Bromide, Nitrate, Sulfate, Iodine, Perchlorate, Iodide can be retained and analyzed using the Newcrom BH stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water and acetonitrile (MeCN) with a Ammonium Acetate buffer. Detection is performed using CAD.
| Column | Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 10/90% |
| Buffer | Gradient AmAc pH 5.0 – 20-90 mM , 20 min |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | CAD (Corona) (MS-compatible mobile phase) |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Chloride
Iodide
Iodine
Nitrate
Perchlorate
Phosphate
Sodium
Sulfate

Separation of Chlorate, Perchlorate, and Phosphonate Ions on Obelisc R Column
July 30, 2015
HPLC Method for Chlorate, Perchlorate, Phosphonate, Sodium on Obelisc R by SIELC Technologies

High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Chlorate, Perchlorate, Phosphonate, Sodium.
The ionic forms of Chlorate, Perchlorate, and Phosphonates are useful in many industries including medicine, paper and use in explosives. Due to their lack of UV activity, an ELSD was used to detect both the anions and cations of all three sodium salts. The ions were retained on both Primesep D and Obelisc R columns. Primesep D is a reverse phase column with embedded basic ion-pairing groups. Obelisc R is also a reverse phase column, but can be additionally tuned due to embedded ionic groups and a hydrophobic chain.
| Column | Obelisc R, 2.1 x 50 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN – 10-40%, 12 min |
| Buffer | Gradient AmFm pH 2.3- 30-80 mM, 12 min |
| Flow Rate | 0.4 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Chlorate, Perchlorate, Phosphonate, Sodium |
Application Column
Obelisc R
Column Diameter: 2.1 mm
Column Length: 50 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Perchlorate
Phosphonate
Sodium

HPLC Analysis of Basic Drugs and Acidic Counter-Ions by Mixed-Mode Chromatography
July 16, 2009
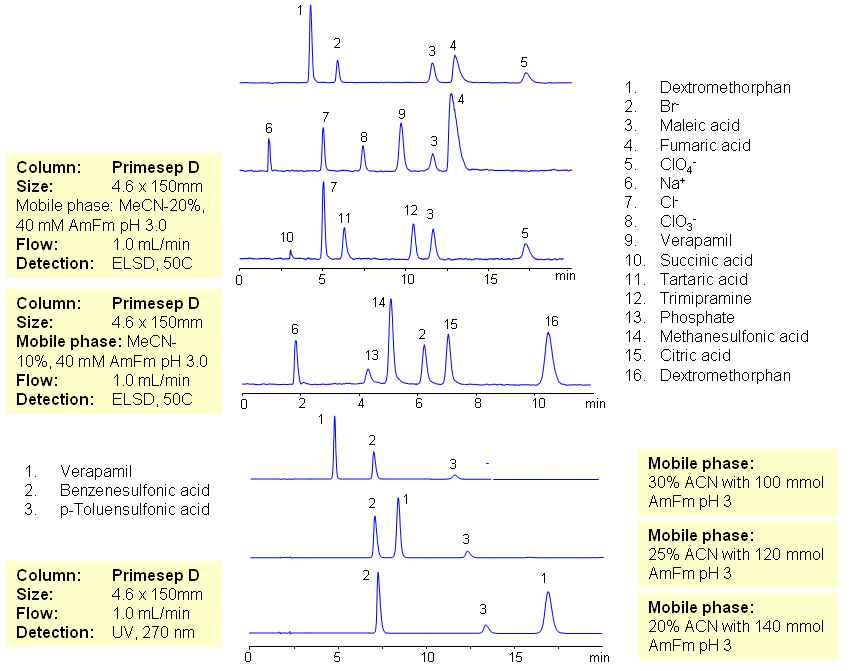
The majority of drugs in the pharmaceutical industry are administered in salt form. The presence of two counter-ions very often necessitates the use of two methods. The nature of these counterparts in drugs can be an inorganic cation and organic acid, inorganic anion and organic base, and organic cation and organic anion. Furthermore, the properties of the molecules will result in a differing stoichiometry. The task of simultaneous quantitation of counter-ions can be achieved by using mixed-mode columns. The general approach for analysis is based on properties of corresponding counter-ions. Hydrophobic basic drugs, like dextromethorphan, verapamil, trimipramine, and corresponding acidic counter-ions (chloride, chlorate, bromide, bromate, perchlorate, maleate, fumarate,tartrate, succinate, phosphate, citrate, benzosulfonate, toleuensulfonate) can be separated and quantitated in the same run on reversed-phase anion-exchange column. Basic hydrophobic drugs are retained by the reversed-phase mechanism, and counter-ions are retained by the reversed-phase and anion-exchange mechanism. Some polar counter-ions are retained only by the anion-exchange mechanism. Retention time and selectivity of HPLC separation of drugs and counter-ions can be achieved by changing the amount of acetonitrile and the amount of ions in the mobile phase. The detection technique depends on the properties of the counter-ions. In case of low or no UV activity, ELSD can be employed if the counter-ion forms a non-volatile salt with the mobile phase additive (ammonium formate). This HPLC method can be used for simultaneous quantitation of other basic drugs and counter-ions. The presence of two mechanisms of retention allows control over retention times of drug and counter-ion independently, and even allows a change of order of elution when necessary.
| Column | Primesep D , 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | AmFm pH 3.0 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, UV 270 |
| Class of Compounds | Ions, Hydrophilic, Hydrophobic, Base, Acids, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Sodium Chloride, Sodium chloride, Sodium Chlorate, Sodium bromide, Sodium bromate, Perchloric Acid, Maleic Acid, Fumaric Acid, Tartaric Acid, Succinic Acid, Phosphoric Acid, Citric acid, Benzosulfonic acid, Dextromethorphan, Verapamil, Trimipramine |
Application Column
Primesep D
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsBromide
Chlorate
Chloride
Citric Acid
Dextromethorphan
Fumaric Acid
Maleic Acid
Organic Acids
Perchlorate
Phosphoric Acid
Pyrilamine
Succinic Acid
Tartaric Acid
Verapamil
p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA)
UV Detection