| CAS Number | 75-75-2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | CH4O3S |
| Molecular Weight | 96.1 |
| InChI Key | AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -0.9 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
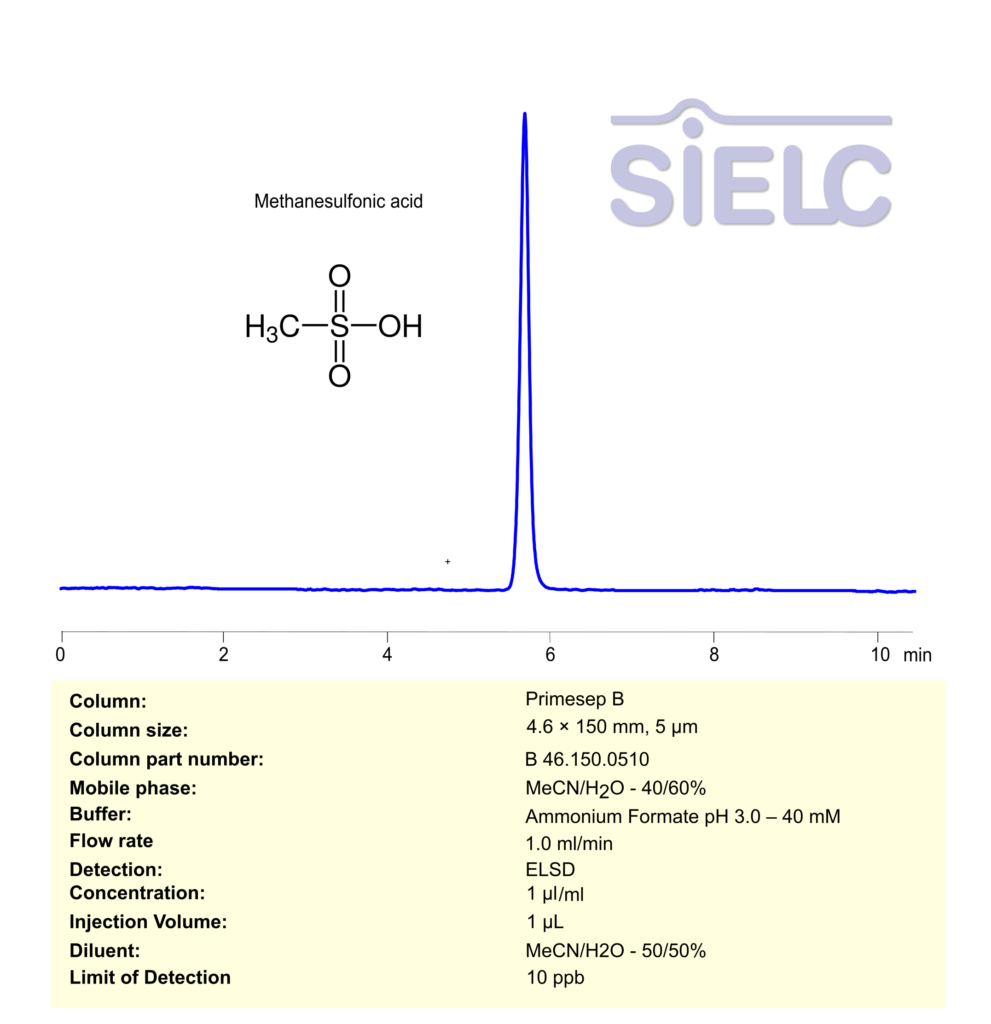
ELSD HPLC Method for Analysis of Methanesulfonic acid on Primesep B Column
January 16, 2025
HPLC Method for Methanesulfonic Acid on Primesep B by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Methanesulfonic Acid
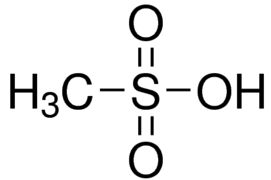
Methanesulfonic acid (MSA) is an organosulfur compound with the chemical formula CH₄O₃S or structurally CH₃SO₃H. It is the simplest alkane sulfonic acid, consisting of a methyl group
Applications:
Catalysis: Used as a strong acid catalyst in organic and industrial chemical reactions, including esterifications and polymerizations.
Electroplating: An electrolyte component in electroplating baths, especially for tin and tin-lead plating.
Cleaning: Employed in industrial cleaning due to its strong acidity and non-oxidizing nature.
Pharmaceuticals: Used in the preparation of certain drugs, intermediates, and active pharmaceutical ingredients.
Alternative to Sulfuric Acid: Often preferred in specific applications because it is non-volatile and less corrosive to metals.
Methanesulfonic Acid can be retained, and analyzed using a Primesep B mixed-mode stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes a gradient method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and phosphoric acid as a buffer. Detection is carried out using UV.
| Column | Primesep B, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN 40% |
| Buffer | Ammonium Formate pH 3.0 – 40 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, the nebulizer and evaporator temperatures 70°C, with a gas flow rate of 1.6 Standard Liters per Minute (SLM) |
| LOD* | 10 ppb |
*LOD was determined for this combination of instrument, method, and analyte, and it can vary from one laboratory to another even when the same general type of analysis is being performed.
| Class of Compounds | Acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Methanesulfonic Acid |
Application Column
Primesep B
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

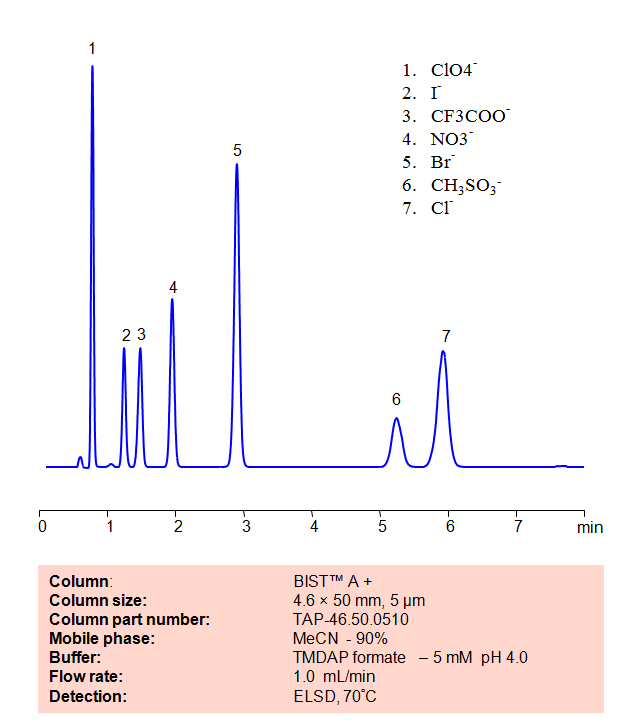
HPLC Method for Analysis of Inorganic anions on BIST™A+ Column
July 7, 2022
Application Column
BIST A+
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 50 mm
Particle Size: 10 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Chloride
Iodide
Methanesulfonic Acid
Nitrate
Perchlorate
TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid)

HPLC Method for Analysis of Sulfonic acids on BIST A+ Column
June 16, 2022
Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
HPLC Method for Analysis of Sulfonic acids on BIST A+ Column by SIELC Technologies
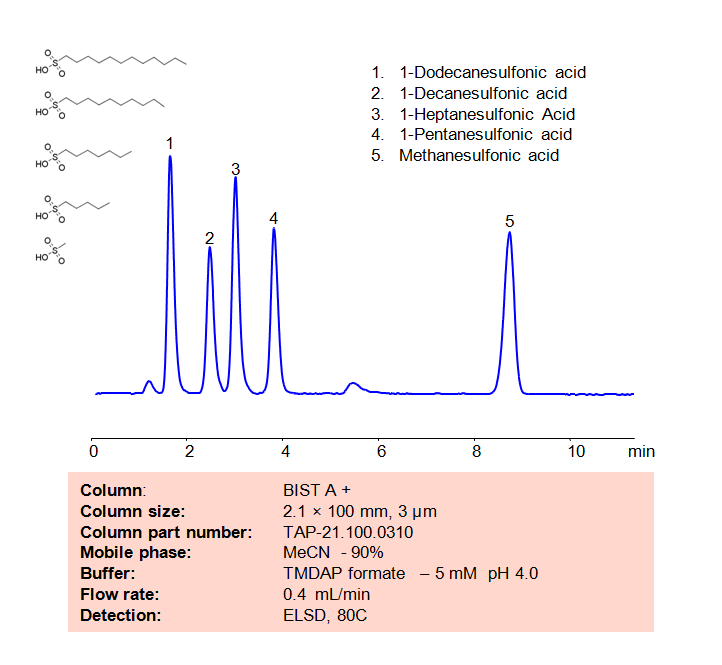
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Sulfonic acid
Methanesulfonic acid is a popular non-volatile catalyst used in organic reactions due to it being a strong acid. Other sulfonic acids, like 1-Pentanesulfonic acid, 1-Heptanesulfonic acid, 1-Decanesulfonic acid, and 1=Dodecanesulfonic acid are typically used in ion chromatography and for organic syntheses. Using SIELC’s newly introduced BIST™ method, a mixture of these Sulfonic acids can be separated on a negatively-charged, cation-exchange BIST™ A+ column, contrary to conventional chromatographic wisdom. There are two keys to this retention method: 1) a multi-charged, positive buffer, such as N,N,N’,N’-Tetramethyl-1,3-propanediamine (TMDAP), which acts as a bridge, linking the negatively-charged anion analytes to the negatively-charged column surface and 2) a mobile phase consisting mostly of organic solvent (such as MeCN) to minimize the formation of a solvation layer around the charged analytes. Other positively-charged buffers that can generate BIST™ include Calcium acetate and Magnesium acetate. Using this new and unique analysis method, these Sulfonic acids can be separated, retained, and detected through ELSD. This method is also compatible with Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) and CAD.
Condition
| Column | BIST™ A+, 2.1×100 mm, 3 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 90% |
| Buffer | TMDAP formate pH 4.0 – 5,0 mM |
| Flow Rate | 0.4 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, 80C |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Acid, Sulfonic acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | 1-Dodecanesulfonic acid, 1-Decanesulfonic acid, 1-Heptanesulfonic Acid, 1-Pentanesulfonic acid, Methanesulfonic acid |
Application Column
BIST A+
BIST™ columns offer a unique and effective way to achieve separations that were traditionally challenging or even impossible with other HPLC columns. With the use of a special mobile phase, these ion exchange columns provide very strong retention for analytes with the same charge polarity as the stationary phase, unlocking new chromatography applications. What makes BIST™ columns stand out is their proprietary surface chemistry, which results in superior selectivity, resolution, and sensitivity. These columns offer a simple, efficient solution for a variety of analytical challenges, making them an excellent choice for researchers and analysts across many different fields. To learn more about the technology that powers BIST™ columns and to explore related applications, check out https://BIST.LC.
Select options1-Dodecanesulfonic acid
1-Heptanesulfonic acid
1-Pentanesulfonic acid
Methanesulfonic Acid

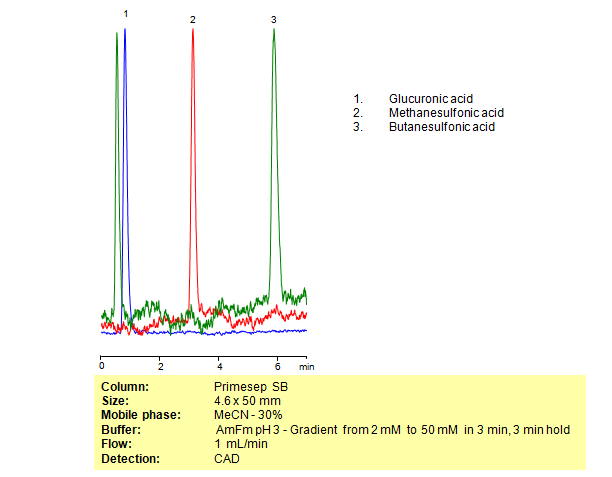
HPLC Separation of Organic Acids Glucuronic Acid, Methanesulfonic Acid, and Butanesulfonic Acid on Primesep SB Column
May 11, 2015
The organic acids glucuronic acid, methanesulfonic acid, and butanesulfonic acid were separated using Primesep SB mixed-mode column. Primesep SB is a reverse-phase column with embedded basic ion-pairing groups.
| Column | Primesep SB, 4.6×50 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 30/70% |
| Buffer | Gradient AmFm pH 3.0- 2-50 mM, 3 min, 3 min hold |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | CAD |
| Class of Compounds |
Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Glucuronic acid, Methanesulfonic acid, Butanesulfonic acid |
Application Column
Primesep SB
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsGlucuronic acid
Methanesulfonic Acid
UV Detection

HPLC Separation of Inorganic Anions
November 21, 2010
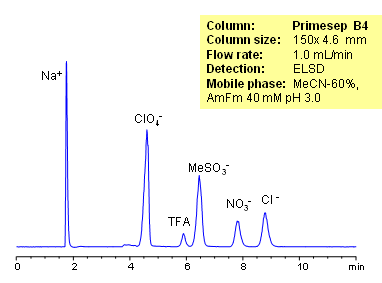
Organic and inorganic acids and ions can be separated on a Primesep B4 column based on their ionic properties. Method can be used for quantitation of residual acids in various products and sample matrices. Trifluoracetic, hydrochloric, methanesulfonic, and nitric acids are separated using ACN-water-ammonium formate. Ions can be detected by ELSD, CAD or LC/MS.
| Column | Primesep B4, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | AmFm |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Ions, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Sodium, Phosphate, Chloride, Nitrate, Sulfate, Iodide, Perchlorate, Trifluoracetic |
Application Column
Primesep B4
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsMethanesulfonic Acid
Nitrate
Nitric Acid
Organic Acids
Perchloric Acid
TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid)

HPLC Separation of Potassium, Perchlorate, Methanesulfonic, Chloride, Bromide, and Nitrate Ions on Obelisc N
March 3, 2010
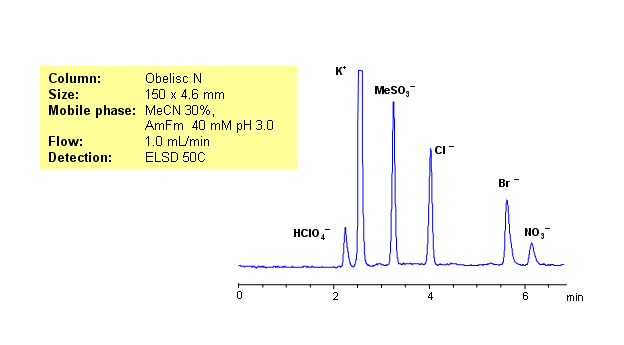
Ion chromatography is usually used for analysis of hydrophilic organic and inorganic ions. Same separation can be achieved on HILIC/mixed-mode Obelisc N HPLC columns. Obelisc N HPLC columns have very polar groups on their surface: one of the groups is basic and the other acidic. In case of low organic concentration, two groups are connected by hydrophilic linker. Obelisc N column can be used as cation-exchange and anion-exchange column. This allows to separate positively and negatively charged molecules in one run. Five anions (chloride, bromide, methanesulfonate, nitrate and perchlorate) along with one cation (sodium) were separated in one run. Method is compatible with ELSD, CAD and LC/MS and can be used for analysis of various hydrophilic and hydrophobic cations and anions in one HPLC run.
| Column | Obelisc N, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | AmFm |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Hydrophilic, Ions |
| Analyzing Compounds | Chloride, Nitrate, Chlorate, Bromide, Potassium |
Application Column
Obelisc N
SIELC has developed the Obelisc™ columns, which are mixed-mode and utilize Liquid Separation Cell technology (LiSC™). These cost-effective columns are the first of their kind to be commercially available and can replace multiple HPLC columns, including reversed-phase (RP), AQ-type reversed-phase, polar-embedded group RP columns, normal-phase, cation-exchange, anion-exchange, ion-exclusion, and HILIC (Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography) columns. By controlling just three orthogonal method parameters - buffer concentration, buffer pH, and organic modifier concentration - users can adjust the column properties with pinpoint precision to separate complex mixtures.
Select optionsChloride
Methanesulfonic Acid
Nitrate
Nitric Acid
Potassium

Separation of Sulphonium Ions in Polar Organic Mode
October 4, 2005

The separation of steroids on Primesep 100 demonstrates the versatility of Primesep columns in both polar organic and ion-exchange modes in the separation of sulfonium ions. The high organic mobile phase retains methane sulfonic acid by a polar organic mechanism and separates methoxydimethylsulphonium and trimethylsulfphonium cations by polar organic and cation exchange modes. The separation method uses a mobile phase mixture of water, acetonitrile (MeCN, ACN), and trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) with evaporative light scattering detection (ELSD).
| Column | Primesep 100, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 90/10% |
| Buffer | TFA – 0.1% |
| Flow Rate | 1.5 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Sulphonium Ions, Methoxydimethylsulphonium, Trimethylsulfphonium |
Application Column
Primesep 100
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Methoxydimethylsulphonium
Sulfonium Ions
Trimethylsulfonium