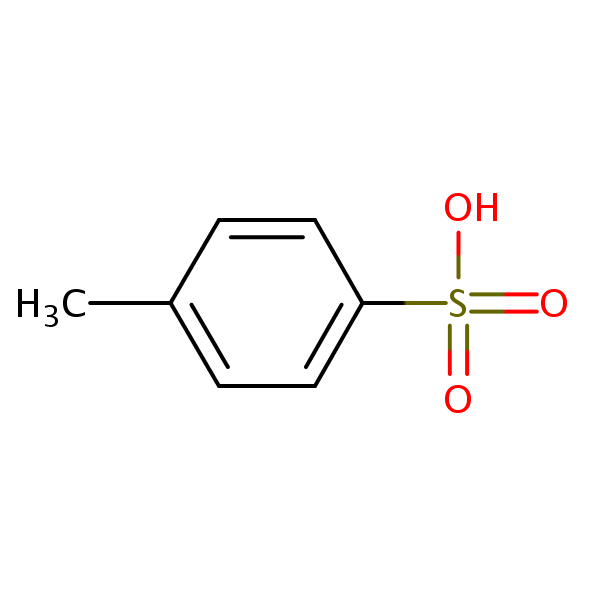
| CAS Number | 104-15-4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C7H8O3S |
| Molecular Weight | 172.200 |
| InChI Key | JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -0.0248 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
UV-Vis Spectrum of p-Toluenesulfonic Acid
August 1, 2024
Access the UV-Vis Spectrum SIELC Library
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA) check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

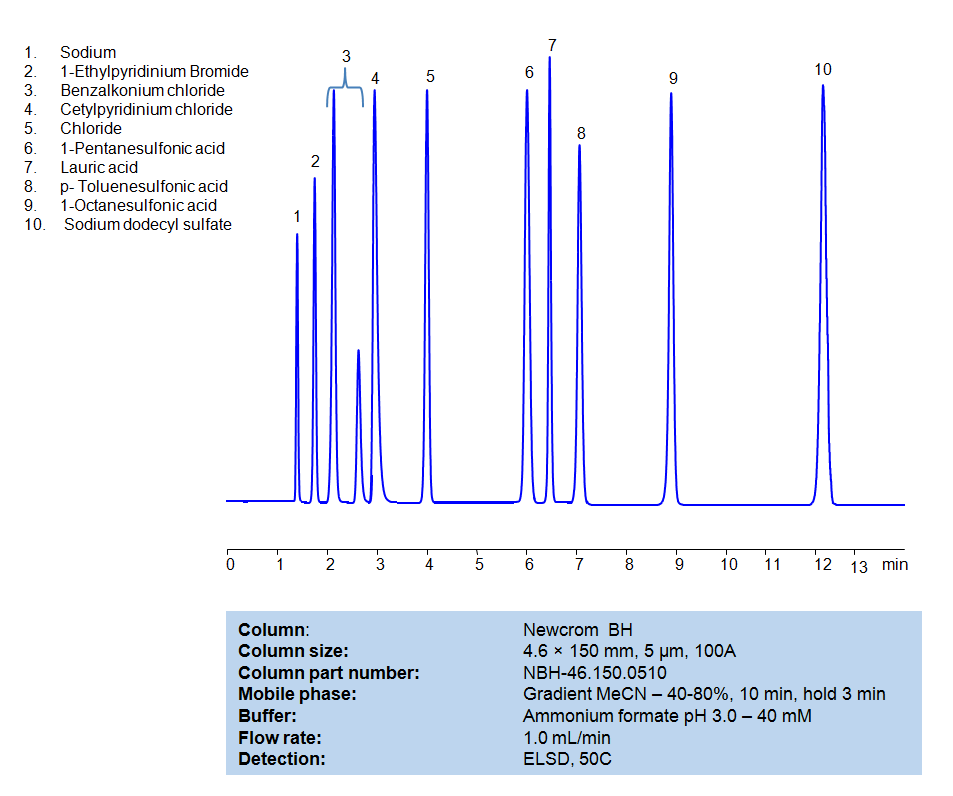
HPLC Method for Separation of Hydrophobic, Cationic and Anionic Surfactants on Newcrom BH Column
July 10, 2023
HPLC Method for Separation of Hydrophobic, Cationic and Anionic Surfactants on Newcrom BH by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
Surfactants, also known as surface-active agents, are compounds that lower the surface tension (or interfacial tension) between two liquids or between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsifiers, foaming agents, or dispersants.
They are often classified according to the charge of the polar head group:
Anionic Surfactants: These surfactants have a negative charge on their polar head group. Common examples include soap, sodium laureth sulfate, and sodium lauryl sulfate. They are commonly used in detergents and shampoos due to their ability to emulsify oils and hold dirt in suspension, so it can be rinsed away.
Cationic Surfactants: These surfactants have a positive charge on their polar head group. Examples include cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) and benzalkonium chloride. These are often used as antiseptics and can also be found in hair conditioners because they reduce static cling.
Nonionic Surfactants: These surfactants have no charge on their polar head group. Examples include alcohol ethoxylates, nonylphenol ethoxylates, and polysorbates. Nonionic surfactants are often used in laundry and dishwasher detergents.
All compounds can be retained, separated, and analyzed using a reverse-phase Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended column. The mobile phase for this method consists of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and Ammonium formate, which serves as a buffer. This analytical method can be detected with an Evaporative Light Scattering Detector (ELSD) or any other evaporative detection method (CAD, ESI-MS).
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Benzalkonium chloride, Cetylpyridinium Chloride, 1-Pentanesulfonic acid, Dodecanoic acid (Lauric acid), p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA), 1-Octanesulfonic acid, Sodium dodecyl sulfate, 1-Ethylpyridinium bromide
Condition
| Column | Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN -40-80%, 10 min |
| Buffer | Ammonium formate pH 3.0 – 40 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, 50C |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Surfactants |
| Analyzing Compounds | Benzalkonium chloride, Cetylpyridinium Chloride, 1-Pentanesulfonic acid, Dodecanoic acid (Lauric acid), p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA), 1-Octanesulfonic acid, Sodium dodecyl sulfate, 1-Ethylpyridinium bromide |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
1-Octanesulfonic acid
1-Pentanesulfonic acid
Benzalkonium chloride
Cetylpyridinium Chloride
Dodecanoic acid (Lauric acid)
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA)

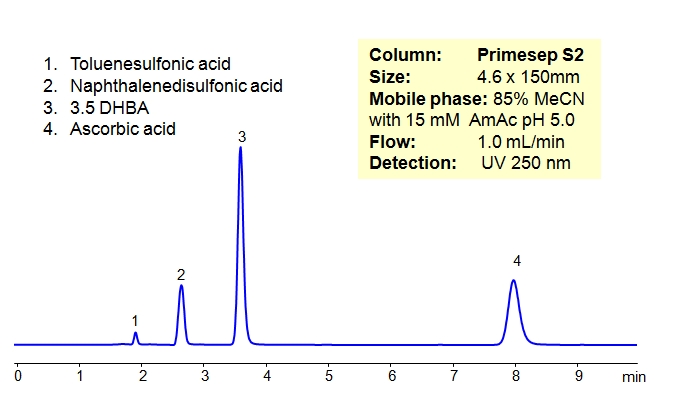
HPLC Separation of Organic Acids in HILIC and Anion-Exclusion Mode on Primesep S2 Column
July 14, 2011
Organic acids were separated on a HILIC/cation-exchange column in HILIC/anion-exclusion mode. This column can be used for analysis of polar compounds in HILIC mode. If compounds are ionizable, additional mode of interaction can be added (cation-exchange or anion-exclusion).
| Column | Primesep S2, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 85/15% |
| Buffer | AmAc pH 5.0 15 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, 50C UV 250 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Nucleosides, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Toluenesulfonic acid, Naphthalenedisulfonic acid, 3.5 DHBA, Ascorbic acid, |
Application Column
Primesep S2
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select options3,5-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid
Ascorbic Acid
Organic Acids
p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA)

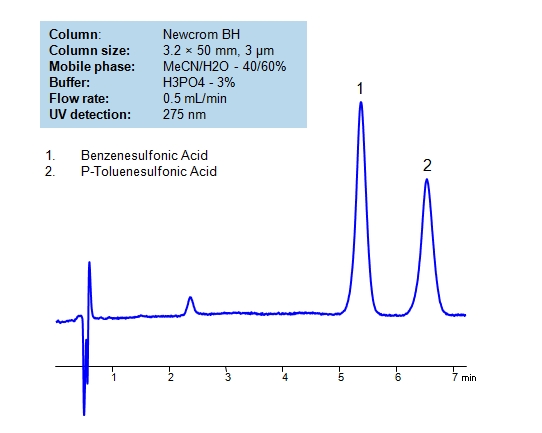
HPLC Separation of Benzenesulfonic and p-Toluenesulfonic Acids on Newcrom BH Column
December 6, 2010
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
| Column | Newcrom BH, 3.2×50 mm, 3 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 40/60% |
| Buffer | H3PO4 – 3% |
| Flow Rate | 0.5 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 275nm |
| Class of Compounds | Acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Benzenesulfonic, p-Toluenesulfonic Acids |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
The Newcrom columns are a family of reverse-phase-based columns. Newcrom A, AH, B, and BH are all mixed-mode columns with either positive or negative ion-pairing groups attached to either short (25 Å) or long (100 Å) ligand chains. Newcrom R1 is a special reverse-phase column with low silanol activity.
Select optionsOrganic Acids
p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA)

HPLC Analysis of Basic Drugs and Acidic Counter-Ions by Mixed-Mode Chromatography
July 16, 2009
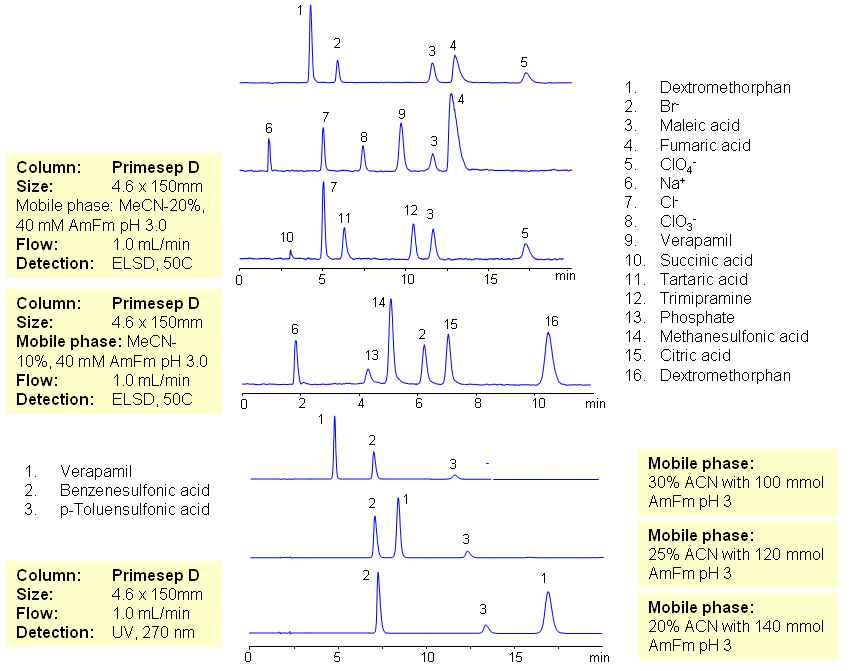
The majority of drugs in the pharmaceutical industry are administered in salt form. The presence of two counter-ions very often necessitates the use of two methods. The nature of these counterparts in drugs can be an inorganic cation and organic acid, inorganic anion and organic base, and organic cation and organic anion. Furthermore, the properties of the molecules will result in a differing stoichiometry. The task of simultaneous quantitation of counter-ions can be achieved by using mixed-mode columns. The general approach for analysis is based on properties of corresponding counter-ions. Hydrophobic basic drugs, like dextromethorphan, verapamil, trimipramine, and corresponding acidic counter-ions (chloride, chlorate, bromide, bromate, perchlorate, maleate, fumarate,tartrate, succinate, phosphate, citrate, benzosulfonate, toleuensulfonate) can be separated and quantitated in the same run on reversed-phase anion-exchange column. Basic hydrophobic drugs are retained by the reversed-phase mechanism, and counter-ions are retained by the reversed-phase and anion-exchange mechanism. Some polar counter-ions are retained only by the anion-exchange mechanism. Retention time and selectivity of HPLC separation of drugs and counter-ions can be achieved by changing the amount of acetonitrile and the amount of ions in the mobile phase. The detection technique depends on the properties of the counter-ions. In case of low or no UV activity, ELSD can be employed if the counter-ion forms a non-volatile salt with the mobile phase additive (ammonium formate). This HPLC method can be used for simultaneous quantitation of other basic drugs and counter-ions. The presence of two mechanisms of retention allows control over retention times of drug and counter-ion independently, and even allows a change of order of elution when necessary.
| Column | Primesep D , 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | AmFm pH 3.0 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, UV 270 |
| Class of Compounds | Ions, Hydrophilic, Hydrophobic, Base, Acids, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Sodium Chloride, Sodium chloride, Sodium Chlorate, Sodium bromide, Sodium bromate, Perchloric Acid, Maleic Acid, Fumaric Acid, Tartaric Acid, Succinic Acid, Phosphoric Acid, Citric acid, Benzosulfonic acid, Dextromethorphan, Verapamil, Trimipramine |
Application Column
Primesep D
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsBromide
Chlorate
Chloride
Citric Acid
Dextromethorphan
Fumaric Acid
Maleic Acid
Organic Acids
Perchlorate
Phosphoric Acid
Pyrilamine
Succinic Acid
Tartaric Acid
Verapamil
p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA)
UV Detection

HPLC Analysis of Components of Ionic Liquids by Mixed-Mode Chromatography
September 14, 2008
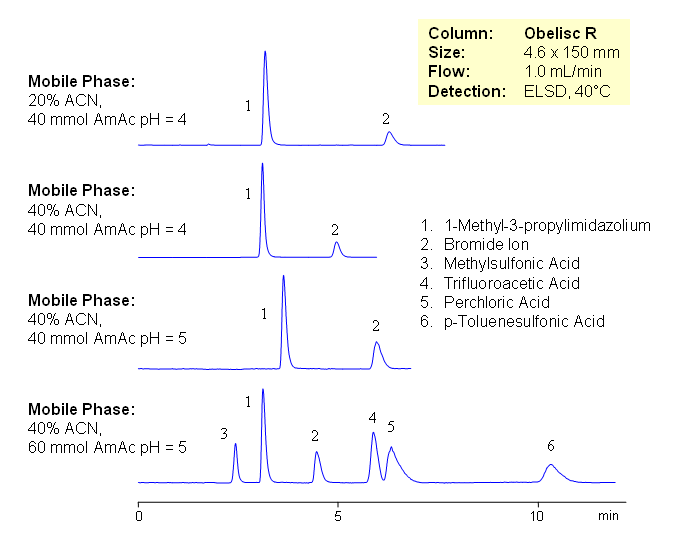
Ionic liquid is an ionic compound which is liquid at room (or close to room) temperature. Most of the ionic liquids are in a dynamic equilibrium where at any time more than 99.99% of the liquid is made up of ionic, rather than molecular, species. Room-temperature ionic liquids consist of bulky cation (for example, substituted imidazolium) compounds. A wide range of anions is used as counter ions in ionic liquids: organic and inorganic anions such as chloride, iodide, tetrafluoroborate, hexafluorophosphate, bistriflimide, triflate, tosylate. Ionic liquids are widely used as solvents in organic reactions. When products are isolated from ionic liquids, they need to be analyzed for residual ionic liquid content.
Because both constituents of the ionic liquid are very different in terms of charge and hydrophobic properties, it is impossible to analyze entire ionic liquids by traditional chromatography. An effective and universal method for analysis of ionic liquids is developed on an Obelisc R HPLC column. Components on the ionic liquids are retained based on ionic and hydrophobic interactions. Obelisc R column has both positively and negatively charged ionic groups, making it possible to retain and separate cations and anions of ionic liquids on one column. Method can be used for quantitative of various ionic liquids containing organic and inorganic ions. Retention time of basic component can be effectively adjusted by pH, stronger anionic and hydrophobic counter-ions might require higher buffer concentration. Composition can be monitored by combination of UV and ELSD or by LC/MS.
| Column | Obelisc R , 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | AmAc |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | 1-Methyl-3-propylimidazolium, Bromide Ion, Methylsulfonic Acid, Trifluoroacetic Acid, Perchloric Acid, p-Toluenesulfonic Acid |
Application Column
Obelisc R
SIELC has developed the Obelisc™ columns, which are mixed-mode and utilize Liquid Separation Cell technology (LiSC™). These cost-effective columns are the first of their kind to be commercially available and can replace multiple HPLC columns, including reversed-phase (RP), AQ-type reversed-phase, polar-embedded group RP columns, normal-phase, cation-exchange, anion-exchange, ion-exclusion, and HILIC (Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography) columns. By controlling just three orthogonal method parameters - buffer concentration, buffer pH, and organic modifier concentration - users can adjust the column properties with pinpoint precision to separate complex mixtures.
Select optionsBromide
Ionic Liquid
Methylsulfonic Acid
Perchloric Acid
TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid)
p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA)
UV Detection