| CAS Number | 143-07-7 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H24O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 200.323 |
| InChI Key | POULHZVOKOAJMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 4.60 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
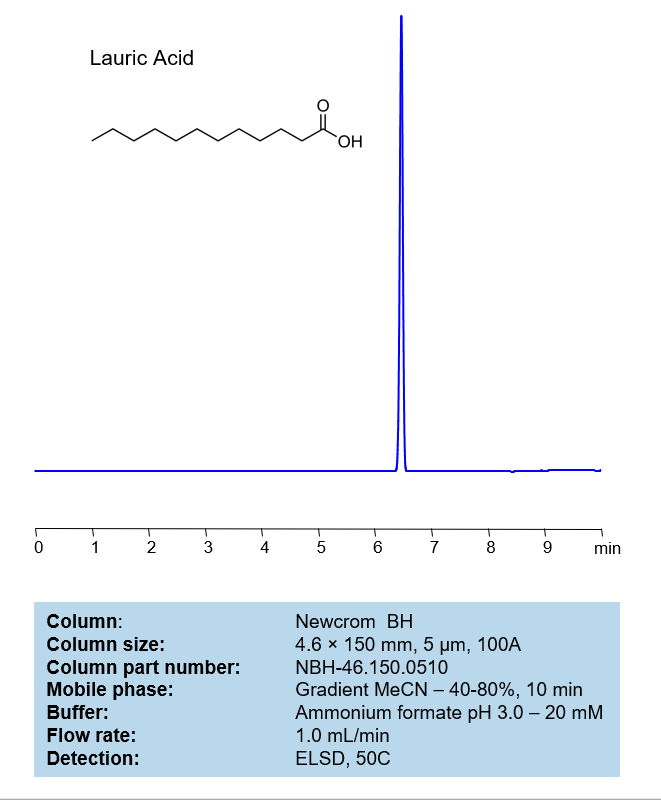
HPLC Method for Analysis of Lauric acid on Newcrom BH Column
July 10, 2023
HPLC Method for Analysis of Dodecanoic acid (Lauric acid) on Newcrom BH by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
Lauric acid, also known as dodecanoic acid, is a saturated fatty acid. Its chemical formula is CH₃(CH₂)₁₀COOH. It is white in color, and it is a solid at room temperature with a melting point of around 44 degrees Celsius (111 degrees Fahrenheit). It is relatively inexpensive and has a long shelf life, which makes it an attractive ingredient in various commercial products.
Lauric acid is found naturally in various plant and animal fats and oils, but the largest amounts of lauric acid are found in coconut oil and palm kernel oil. In these oils, lauric acid can make up to 50% of the total fat content.
Lauric acid is commonly used in the manufacturing of soaps and cosmetics due to its ability to form a lather when mixed with water. It is also used in food for its role in digestion and metabolic processes. It’s a medium-chain fatty acid, which means it is more easily absorbed and utilized by the body compared to long-chain fatty acids.
Research suggests that lauric acid may have several health benefits. For instance, it is believed to have antimicrobial properties, as it can kill harmful pathogens like bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Some studies also suggest that lauric acid could be beneficial for heart health, although more research is needed in this area.
The Lauric acid can be retained and analyzed using a mixed-mode Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended column. The mobile phase for this method consists of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and Ammonium formate, which serves as a buffer. This analytical method can be detected with an Evaporative Light Scattering Detector (ELSD) or any other evaporative detection method (CAD, ESI-MS).
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Dodecanoic acid (Lauric acid)
Condition
| Column | Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN -40-80%, 10 min |
| Buffer | Ammonium formate pH 3.0 – 20 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, the nebulizer and evaporator temperatures 50 °C, with a gas flow rate of 1.6 Standard Liters per Minute (SLM) (MS- compatible mobile phase) |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Aliphatic sulfonic acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Dodecanoic acid (Lauric acid) |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

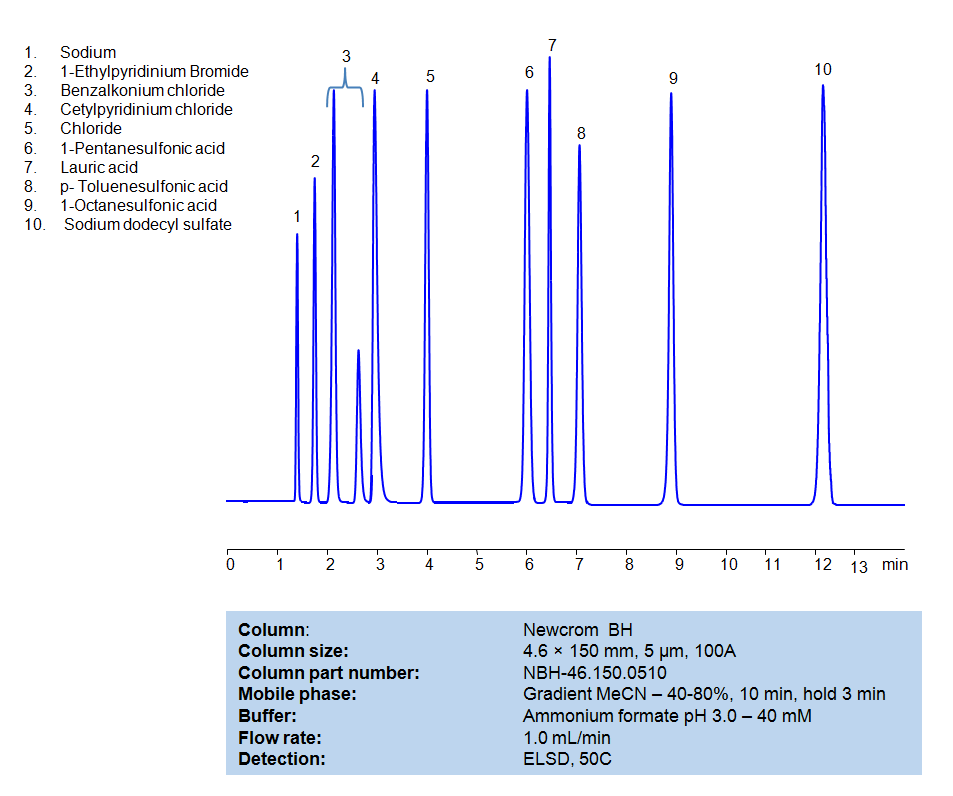
HPLC Method for Separation of Hydrophobic, Cationic and Anionic Surfactants on Newcrom BH Column
July 10, 2023
HPLC Method for Separation of Hydrophobic, Cationic and Anionic Surfactants on Newcrom BH by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
Surfactants, also known as surface-active agents, are compounds that lower the surface tension (or interfacial tension) between two liquids or between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsifiers, foaming agents, or dispersants.
They are often classified according to the charge of the polar head group:
Anionic Surfactants: These surfactants have a negative charge on their polar head group. Common examples include soap, sodium laureth sulfate, and sodium lauryl sulfate. They are commonly used in detergents and shampoos due to their ability to emulsify oils and hold dirt in suspension, so it can be rinsed away.
Cationic Surfactants: These surfactants have a positive charge on their polar head group. Examples include cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) and benzalkonium chloride. These are often used as antiseptics and can also be found in hair conditioners because they reduce static cling.
Nonionic Surfactants: These surfactants have no charge on their polar head group. Examples include alcohol ethoxylates, nonylphenol ethoxylates, and polysorbates. Nonionic surfactants are often used in laundry and dishwasher detergents.
All compounds can be retained, separated, and analyzed using a reverse-phase Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended column. The mobile phase for this method consists of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and Ammonium formate, which serves as a buffer. This analytical method can be detected with an Evaporative Light Scattering Detector (ELSD) or any other evaporative detection method (CAD, ESI-MS).
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Benzalkonium chloride, Cetylpyridinium Chloride, 1-Pentanesulfonic acid, Dodecanoic acid (Lauric acid), p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA), 1-Octanesulfonic acid, Sodium dodecyl sulfate, 1-Ethylpyridinium bromide
Condition
| Column | Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN -40-80%, 10 min |
| Buffer | Ammonium formate pH 3.0 – 40 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, 50C |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Surfactants |
| Analyzing Compounds | Benzalkonium chloride, Cetylpyridinium Chloride, 1-Pentanesulfonic acid, Dodecanoic acid (Lauric acid), p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA), 1-Octanesulfonic acid, Sodium dodecyl sulfate, 1-Ethylpyridinium bromide |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
1-Octanesulfonic acid
1-Pentanesulfonic acid
Benzalkonium chloride
Cetylpyridinium Chloride
Dodecanoic acid (Lauric acid)
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA)

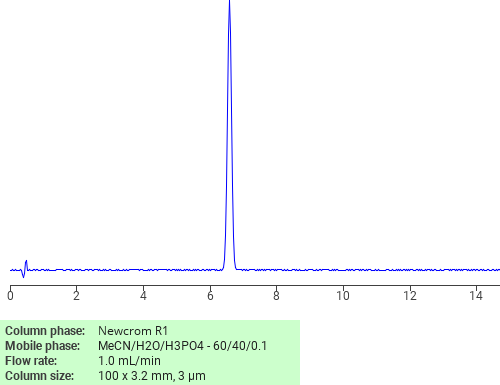
Separation of Dodecanoic acid on Newcrom R1 HPLC column
February 16, 2018
Dodecanoic acid can be analyzed by this reverse phase (RP) HPLC method with simple conditions. The mobile phase contains an acetonitrile (MeCN), water, and phosphoric acid. For Mass-Spec (MS) compatible applications the phosphoric acid needs to be replaced with formic acid. Smaller 3 µm particles columns available for fast UPLC applications. This liquid chromatography method is scalable and can be used for isolation impurities in preparative separation. It also suitable for pharmacokinetics.
Application Column
Newcrom R1
The Newcrom columns are a family of reverse-phase-based columns. Newcrom A, AH, B, and BH are all mixed-mode columns with either positive or negative ion-pairing groups attached to either short (25 Å) or long (100 Å) ligand chains. Newcrom R1 is a special reverse-phase column with low silanol activity.
Select options