| CAS Number | 1906-79-2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C7H10BrN |
| Molecular Weight | 188.06 |
| InChI Key | ABFDKXBSQCTIKH-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
HPLC Method for Analysis of 1-Ethylpyridinium Bromide on Newcrom AH Column
July 13, 2023
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
HPLC Method for Analysis of 1-Ethylpyridinium bromide on Newcrom AH by SIELC Technologies
1-Ethylpyridinium bromide is a type of ionic liquid. An ionic liquid is a salt where the ions are poorly coordinated, resulting in these solvents being liquid below 100°C, or even at room temperature (ambient temperature). At least one ion will have a delocalized charge and one component will be organic, which prevents the formation of a stable crystal lattice.
In 1-ethylpyridinium bromide, the cation is an ethylpyridinium ion, a pyridine ring (an aromatic six-membered ring with five carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom) with an ethyl group (a two-carbon alkyl chain) attached. The anion is chloride (Cl-).
Ionic liquids, including 1-ethylpyridinium chloride, have a wide range of applications, such as in electrochemistry, catalysis, and as solvents for a variety of chemical reactions. Their properties, including melting point, viscosity, and solvation potential, can be modified by selecting different cations and anions, which gives them great versatility
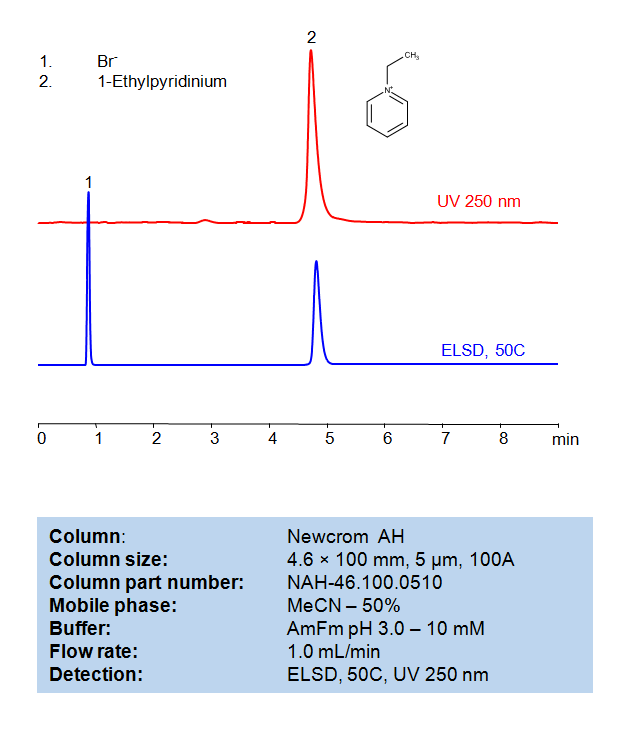
The 1-Ethylpyridinium bromide can be retained, analyzed, on a Newcrom AH column using an isocratic analytical method with a simple mobile phase of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN), and an Ammonium formate (AmFm) ionic modifier. This analysis method can be detected with an Evaporative Light Scattering Detector (ELSD) or any other evaporative detection method (CAD, ESI-MS).
LOD was determined for this combination of instrument, method, and analyte, and it can vary from one laboratory to another even when the same general type of analysis is being performed.
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of 1-Ethylpyridinium bromide
Condition
| Column | Newcrom AH, 4.6 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 50/50% |
| Buffer | AmFm pH 3.0- 10 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, the nebulizer and evaporator temperatures 50 °C, with a gas flow rate of 1.6 Standard Liters per Minute (SLM) (MS- compatible mobile phase) |
| Peak Retention Time | 4.92 min |
| Sample concentration | 0.3 mg/ml |
| Injection volume | 1 µl |
| LOD | UV- 30 ppb, ELSD – 70 ppb |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Pyridinium salts |
| Analyzing Compounds | 1-Ethylpyridinium bromide |
Application Column
Newcrom AH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

HPLC Method for Separation of 1-Butylpyridinium chloride and 1-Ethylpyridinium bromide on Newcrom AH Column
July 12, 2023
HPLC Method for Separation of 1-Ethylpyridinium bromide, 1-Butylpyridinium Chloride on Newcrom AH by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
1-Butylpyridinium chloride and 1-Ethylpyridinium bromide are types of ionic liquids. Ionic liquids are salts in which the ions are poorly coordinated, which results in these solvents being liquid below 100°C, or even at room temperature (ambient temperature). At least one ion has a delocalized charge and one component is organic, which prevents the formation of a stable crystal lattice.
1-Butylpyridinium chloride has a butyl group attached to a pyridinium ring, and its counterion is chloride (Cl-).
1-Ethylpyridinium bromide, on the other hand, has an ethyl group attached to a pyridinium ring, and its counterion is bromide (Br-).
These compounds are part of a larger class of pyridinium-based ionic liquids. They have various applications, including in electrochemistry, organic synthesis, and as solvents for polymers. Like other ionic liquids, their properties (such as melting point, viscosity, and solvation potential) can be adjusted by selecting different counterions or changing the groups attached to the pyridinium ring.
1-Butylpyridinium chloride and 1-Ethylpyridinium bromide,” belong to a class of compounds known as pyridinium salts. These compounds are derived from the parent compound pyridine, which is a six-membered aromatic ring containing one nitrogen atom.
These pyridinium salts often have unique physical and chemical properties due to the presence of the charged pyridinium cation. They are commonly used in various applications, including as catalysts, ionic liquids, and electrolytes in electrochemical systems. The specific properties and applications of these compounds can vary depending on the nature of the alkyl group and the anion associated with the pyridinium cation
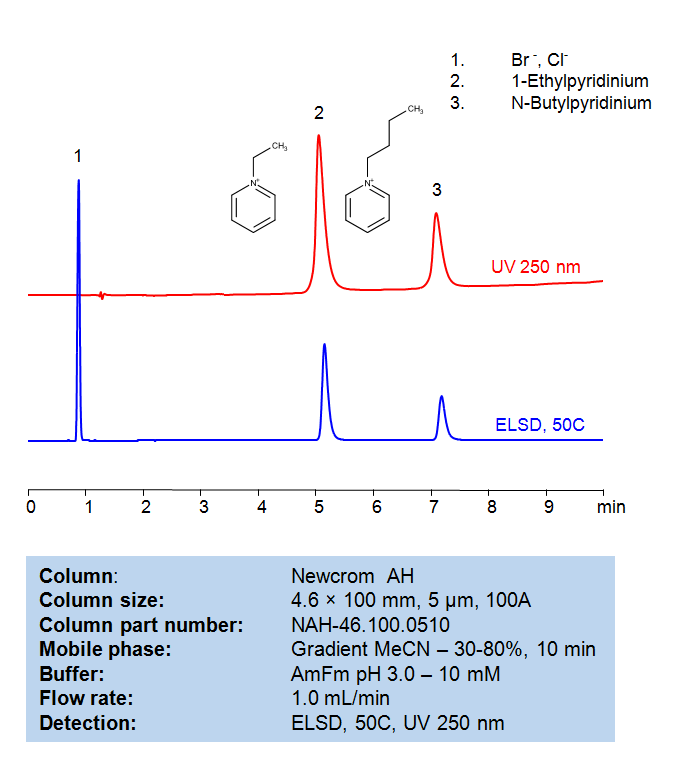
Both compounds can be retained, separated, and analyzed, on a Newcrom AH column using an isocratic analytical method with a simple mobile phase of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN), and an Ammonium formate (AmFm) ionic modifier. This analysis method can be detected with an Evaporative Light Scattering Detector (ELSD) or any other evaporative detection method (CAD, ESI-MS).
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of 1-Ethylpyridinium bromide, 1-Butylpyridinium Chloride
Condition
| Column | Newcrom AH, 4.6 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN/H2O – 30-80%, 10 min |
| Buffer | AmFm pH 3.0- 10 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, the nebulizer and evaporator temperatures 50 °C, with a gas flow rate of 1.6 Standard Liters per Minute (SLM) (MS- compatible mobile phase) |
| Peak Retention Time | 5.12, 7.18 min |
| Sample concentration | 0.3 mg/ml |
| Injection volume | 1µl |
| LOD | UV- 30 ppb, ELSD – 70 ppb |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Pyridinium salts |
| Analyzing Compounds | 1-Ethylpyridinium bromide, 1-Butylpyridinium Chloride |
Application Column
Newcrom AH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
1-Ethylpyridinium bromide

HPLC Method for Separation of Hydrophobic, Cationic and Anionic Surfactants on Newcrom BH Column
July 10, 2023
HPLC Method for Separation of Hydrophobic, Cationic and Anionic Surfactants on Newcrom BH by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
Surfactants, also known as surface-active agents, are compounds that lower the surface tension (or interfacial tension) between two liquids or between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsifiers, foaming agents, or dispersants.
They are often classified according to the charge of the polar head group:
Anionic Surfactants: These surfactants have a negative charge on their polar head group. Common examples include soap, sodium laureth sulfate, and sodium lauryl sulfate. They are commonly used in detergents and shampoos due to their ability to emulsify oils and hold dirt in suspension, so it can be rinsed away.
Cationic Surfactants: These surfactants have a positive charge on their polar head group. Examples include cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) and benzalkonium chloride. These are often used as antiseptics and can also be found in hair conditioners because they reduce static cling.
Nonionic Surfactants: These surfactants have no charge on their polar head group. Examples include alcohol ethoxylates, nonylphenol ethoxylates, and polysorbates. Nonionic surfactants are often used in laundry and dishwasher detergents.
All compounds can be retained, separated, and analyzed using a reverse-phase Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended column. The mobile phase for this method consists of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and Ammonium formate, which serves as a buffer. This analytical method can be detected with an Evaporative Light Scattering Detector (ELSD) or any other evaporative detection method (CAD, ESI-MS).
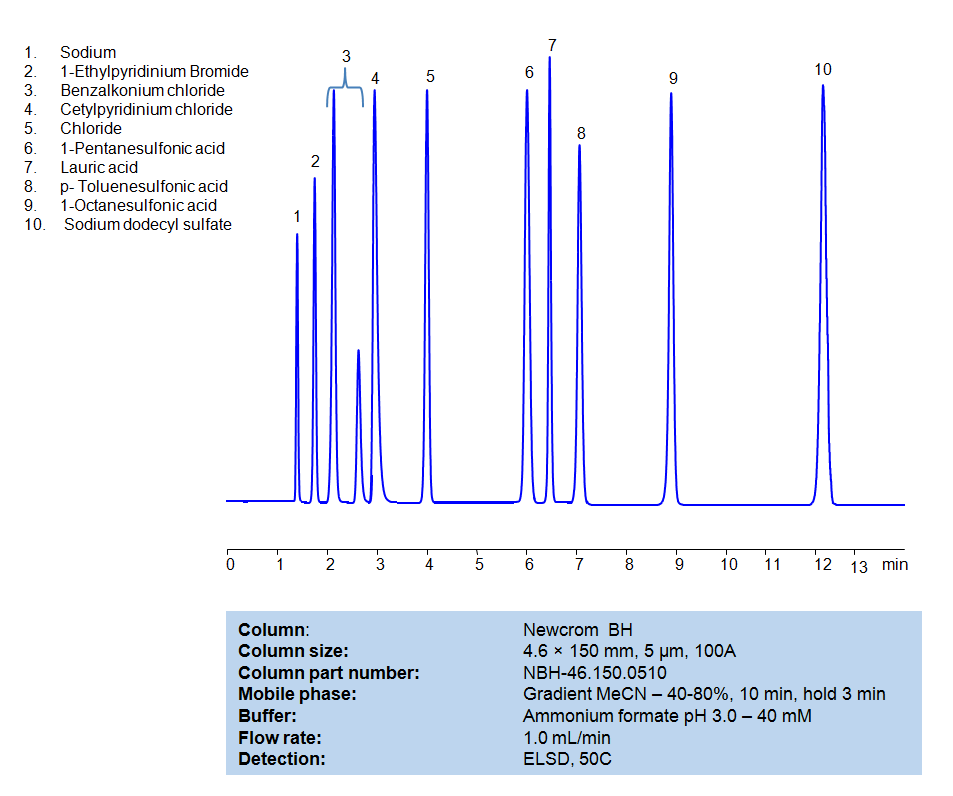
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Benzalkonium chloride, Cetylpyridinium Chloride, 1-Pentanesulfonic acid, Dodecanoic acid (Lauric acid), p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA), 1-Octanesulfonic acid, Sodium dodecyl sulfate, 1-Ethylpyridinium bromide
Condition
| Column | Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN -40-80%, 10 min |
| Buffer | Ammonium formate pH 3.0 – 40 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, 50C |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Surfactants |
| Analyzing Compounds | Benzalkonium chloride, Cetylpyridinium Chloride, 1-Pentanesulfonic acid, Dodecanoic acid (Lauric acid), p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA), 1-Octanesulfonic acid, Sodium dodecyl sulfate, 1-Ethylpyridinium bromide |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
1-Octanesulfonic acid
1-Pentanesulfonic acid
Benzalkonium chloride
Cetylpyridinium Chloride
Dodecanoic acid (Lauric acid)
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA)