| CAS Number | 91-84-9 |
|---|---|
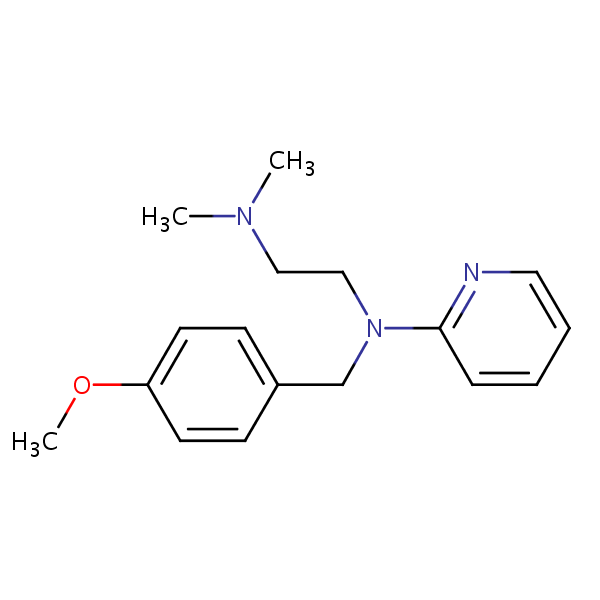
| Molecular Formula | C17H23N3O |
| Molecular Weight | 285.391 |
| InChI Key | YECBIJXISLIIDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 3.27 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
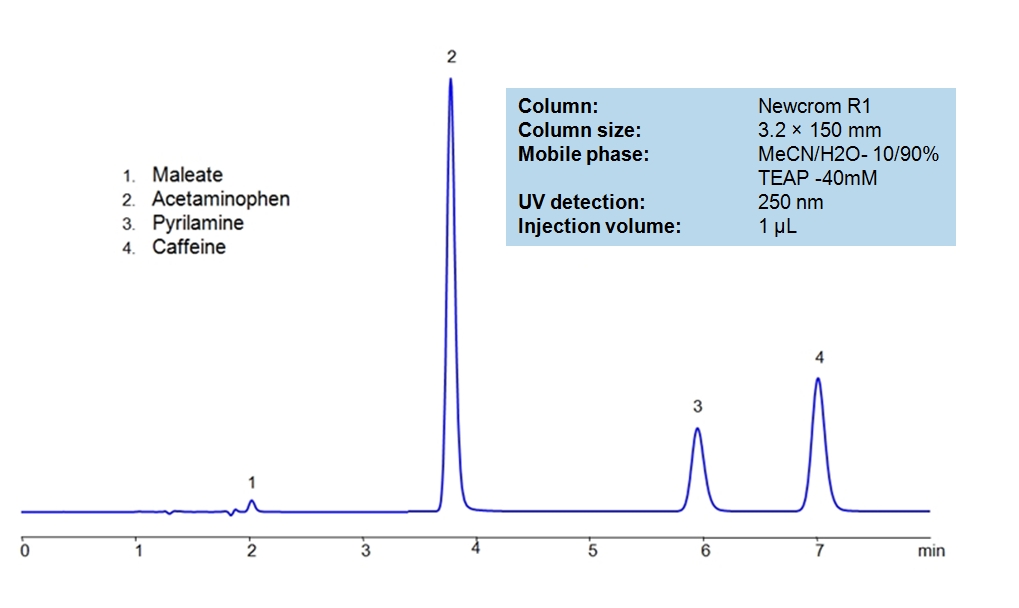
HPLC Separation of Acetaminophen, Caffeine and Pyrilamine maleate
March 2, 2018
Acetaminophen is a p-aminophenol derivative with analgesic and antipyretic activities. It has weak anti-inflammatory properties, may cause liver, blood cell, and kidney damage. It is a nonprescription medication for mild-to-moderate pain and fever. Caffeine is a Central Nervous System (CNS) stimulant. It is an unregulated and legal drug in most parts of the world. It can be found in the seeds and leaves in a number of plants native in Africa, East Asia and South America. Pyrilamine maleate is a histamine H1 antagonist with hypnotic properties. It has multiple uses such as an anesthetic and is used against allergies. Newcrom R1, a column that takes advantage of the newest technologies, does not contain embedded acidic nor basic ionizable groups and can retain Acetaminophen, Caffeine and Pyrilamine maleate. The method is UV compatible and can be used as a general approach for analyzing similar compounds.
Application Column
Newcrom R1
The Newcrom columns are a family of reverse-phase-based columns. Newcrom A, AH, B, and BH are all mixed-mode columns with either positive or negative ion-pairing groups attached to either short (25 Å) or long (100 Å) ligand chains. Newcrom R1 is a special reverse-phase column with low silanol activity.
Select optionsCaffeine
Maleate
Pyrilamine
Pyrilamine maleate

HPLC Separation of Pyrilamine, Trimipramine, Pindolol Using Hydrogen Bonding Mode
June 15, 2012

Application Notes: Many drugs contain small hydrophobic and hydrophilic compounds. There are several ways to retain and analyze these compounds including, reversed-phase chromatography, cation-exchange chromatography, and HILIC. Our method includes separation based on hydrogen-bonding interactions between the analytes and the stationary phase. Hydrogen bonding offers unique selectivity of separation with good peak shape and retention control. Our method is fully compatible with ELSD, LC/MS and preparative chromatography. This approach can also be applied to the analysis of other drug molecules.
Application Columns: SHARC 1, 3.2×100 mm, 5 um, 100A. To learn more about SHARC 1 columns click here. To order this column click here. To see more chromatographic separations check our web site.
Application Compounds: Pyrilamine, trimipramine, and pindolol
Detection Technique: UV, LC/MS
| Column | Sharc 1, 3.2×100 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/MeOH |
| Buffer | AmFm, Formic acid |
| Flow Rate | 0.5 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 270 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | Pyrilamine, Trimipramine, Pindolol |
Application Column
SHARC 1
The SHARC™ family of innovative columns represents the first commercially available columns primarily utilizing separation based on hydrogen bonding. SHARC stands for Specific Hydrogen-bond Adsorption Resolution Column. Hydrogen bonding involves an interaction or attraction between a bound hydrogen atom and molecules containing electronegative atoms, such as oxygen, nitrogen, and fluorine.
Select optionsPyrilamine

HPLC Separation of Drugs
November 21, 2010
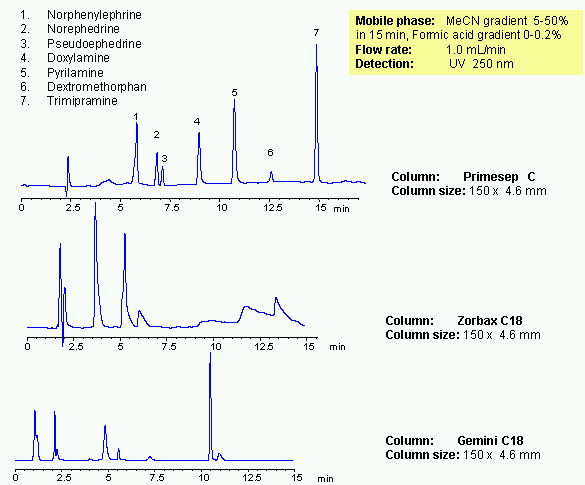
Mixed-mode chromatography allows to separate various hydrophobic and hydrophilic drugs in one HPLC method. Presence of at least two mechanism of retention allows adjust selectivity of separation by changing three parameters: amount of acetonitrile, buffer concentration and buffer pH. Seven common drugs are separated on a Primesep C trimodal HPLC column in gradient method. Method provides alternative selectivity to traditional reversed-phase chromatography. Operational range in which basic compounds are retained the most is from pH 3 to 5. At higher pH, longer retention can be achieved. Mixed-mode chromatography provides longer retention and better peak shapes for basic and acidic analytes. Method can be used in analysis of drugs and pharmaceuticals.
| Column | Primesep C, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN |
| Buffer | Formic Acid |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 250 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Analgetic, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, |
| Analyzing Compounds | Norphenylephrine, Norephedrine, Pseudoephedrine, Doxylamine, Pyrilamine, Dextromethorphan, Trimipramine |
Application Column
Primesep C
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsDoxylamine
Norephedrine
Norphenylephrine
Pseudoephedrine (PSE)
Pyrilamine

Comparison of the Separation of Polar Drugs on Obelisc R and Zorbax SB-AQ
March 3, 2010
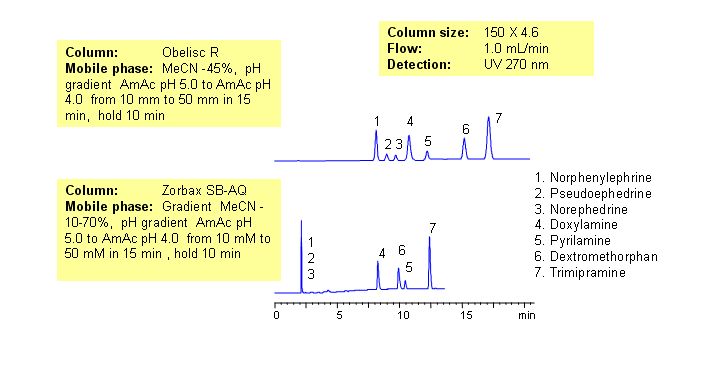
Common hydrophobic basic and hydrophilic basic drugs are separated by mixed-mode chromatography with greater selectivity and resolution than traditional reversed-phase column. Drugs are retained by combination of reversed-phase and cation-exchange mechanisms. Retention time is controlled by amount of acetonitrile, buffer concentration and buffer pH. Available detection techniques are based on buffer selection and include UV, Evaporative Light-Scattering Detector (ELSD), Corona (CAD), LC/MS, etc. This HPLC method can be adopted as general approach for analysis of drugs and pharmaceuticals.
Application Column
Obelisc R
SIELC has developed the Obelisc™ columns, which are mixed-mode and utilize Liquid Separation Cell technology (LiSC™). These cost-effective columns are the first of their kind to be commercially available and can replace multiple HPLC columns, including reversed-phase (RP), AQ-type reversed-phase, polar-embedded group RP columns, normal-phase, cation-exchange, anion-exchange, ion-exclusion, and HILIC (Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography) columns. By controlling just three orthogonal method parameters - buffer concentration, buffer pH, and organic modifier concentration - users can adjust the column properties with pinpoint precision to separate complex mixtures.
Select optionsDextromethorphan
Doxylamine
Norephedrine
Norphenylephrine
Pseudoephedrine (PSE)
Pyrilamine

HPLC Analysis of Basic Drugs and Acidic Counter-Ions by Mixed-Mode Chromatography
July 16, 2009
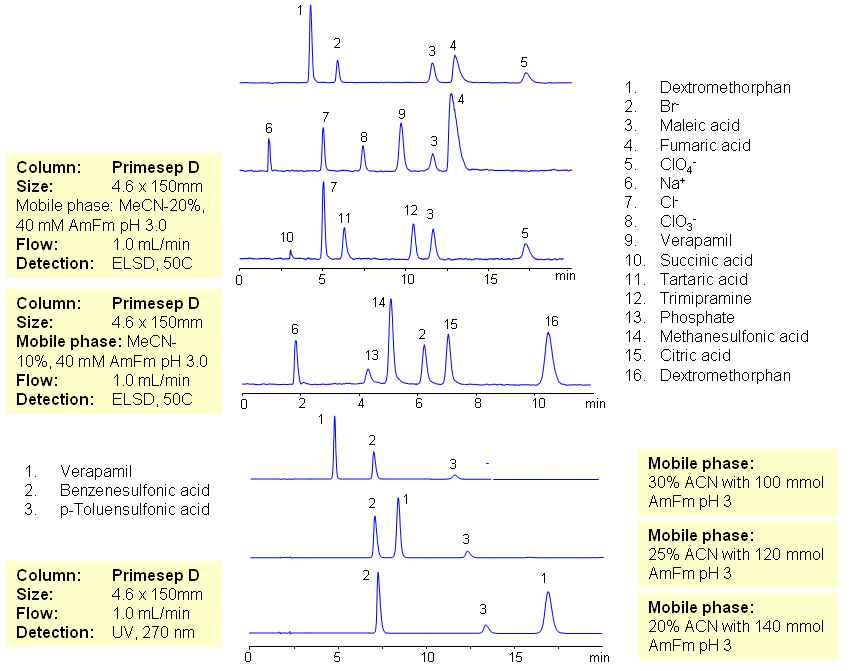
The majority of drugs in the pharmaceutical industry are administered in salt form. The presence of two counter-ions very often necessitates the use of two methods. The nature of these counterparts in drugs can be an inorganic cation and organic acid, inorganic anion and organic base, and organic cation and organic anion. Furthermore, the properties of the molecules will result in a differing stoichiometry. The task of simultaneous quantitation of counter-ions can be achieved by using mixed-mode columns. The general approach for analysis is based on properties of corresponding counter-ions. Hydrophobic basic drugs, like dextromethorphan, verapamil, trimipramine, and corresponding acidic counter-ions (chloride, chlorate, bromide, bromate, perchlorate, maleate, fumarate,tartrate, succinate, phosphate, citrate, benzosulfonate, toleuensulfonate) can be separated and quantitated in the same run on reversed-phase anion-exchange column. Basic hydrophobic drugs are retained by the reversed-phase mechanism, and counter-ions are retained by the reversed-phase and anion-exchange mechanism. Some polar counter-ions are retained only by the anion-exchange mechanism. Retention time and selectivity of HPLC separation of drugs and counter-ions can be achieved by changing the amount of acetonitrile and the amount of ions in the mobile phase. The detection technique depends on the properties of the counter-ions. In case of low or no UV activity, ELSD can be employed if the counter-ion forms a non-volatile salt with the mobile phase additive (ammonium formate). This HPLC method can be used for simultaneous quantitation of other basic drugs and counter-ions. The presence of two mechanisms of retention allows control over retention times of drug and counter-ion independently, and even allows a change of order of elution when necessary.
| Column | Primesep D , 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | AmFm pH 3.0 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, UV 270 |
| Class of Compounds | Ions, Hydrophilic, Hydrophobic, Base, Acids, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Sodium Chloride, Sodium chloride, Sodium Chlorate, Sodium bromide, Sodium bromate, Perchloric Acid, Maleic Acid, Fumaric Acid, Tartaric Acid, Succinic Acid, Phosphoric Acid, Citric acid, Benzosulfonic acid, Dextromethorphan, Verapamil, Trimipramine |
Application Column
Primesep D
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsBromide
Chlorate
Chloride
Citric Acid
Dextromethorphan
Fumaric Acid
Maleic Acid
Organic Acids
Perchlorate
Phosphoric Acid
Pyrilamine
Succinic Acid
Tartaric Acid
Verapamil
p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA)
UV Detection