| CAS Number | 58-61-7 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H13N5O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 267.245 |
| InChI Key | OIRDTQYFTABQOQ-KQYNXXCUSA-N |
| LogP | -1.05 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
HPLC Method for Separation of Adenine, Deoxyadenosine and Adenosine on BIST B+ Column
November 28, 2022
HPLC Method for Separation of Adenine, Deoxyadenosine and Adenosine on BIST B+ by SIELC Technologies.
Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
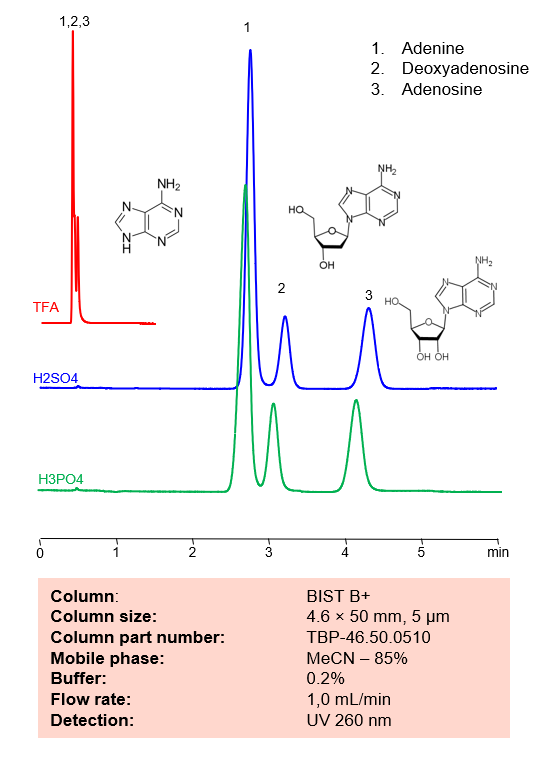
Condition
| Column | BIST B+, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 85% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 260 nm |
| Peak Retention Time | 2.8, 3.2, 4.3 min |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Nucleosides |
| Analyzing Compounds | Adenine, Deoxyadenosine and Adenosine |
Application Column
BIST B+
BIST™ columns offer a unique and effective way to achieve separations that were traditionally challenging or even impossible with other HPLC columns. With the use of a special mobile phase, these ion exchange columns provide very strong retention for analytes with the same charge polarity as the stationary phase, unlocking new chromatography applications. What makes BIST™ columns stand out is their proprietary surface chemistry, which results in superior selectivity, resolution, and sensitivity. These columns offer a simple, efficient solution for a variety of analytical challenges, making them an excellent choice for researchers and analysts across many different fields. To learn more about the technology that powers BIST™ columns and to explore related applications, check out https://BIST.LC.
Select optionsAdenosine
Deoxyadenosine

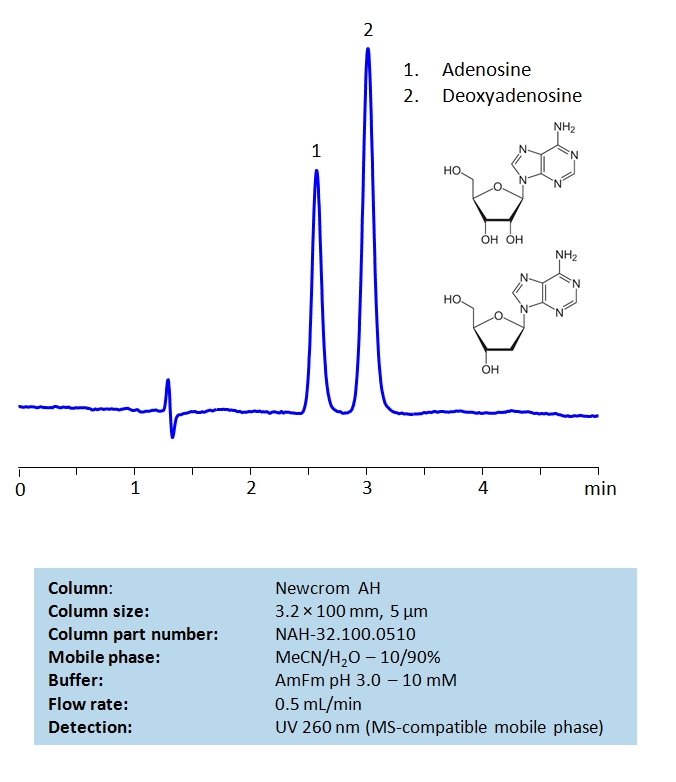
HPLC Separation of Adenosine and Deoxyadenosine on Newcrom AH Column
May 26, 2021
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method of Adenosine and Deoxyadenosine.
Nucleosides are the building blocks for DNA and RNA as well as other roles in biomechanical processes such as signal transduction. By using a Newcrom AH mixed-mode column with a cation-exchange mechanism, nucleosides: adenosine and deoxyadenosine, can be baseline separated in a short time using an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase of water, acetonitrile (MeCN, ACN), and ammonium formate (AmFm) buffer. Detection can be achieved with UV 260 nm, mass spectrometry (MS), evaporative light scattering detection (ELSD) and Charged aerosol detection (,.CAD).
| Column | Newcrom AH, 3.2×100 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 10/90% |
| Buffer | AmFm pH 3.0 – 10 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 260 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Nucleatide |
| Analyzing Compounds | Adenosine, Deoxyadenosine |
Application Column
Newcrom AH
The Newcrom columns are a family of reverse-phase-based columns. Newcrom A, AH, B, and BH are all mixed-mode columns with either positive or negative ion-pairing groups attached to either short (25 Å) or long (100 Å) ligand chains. Newcrom R1 is a special reverse-phase column with low silanol activity.
Select optionsDeoxyadenosine

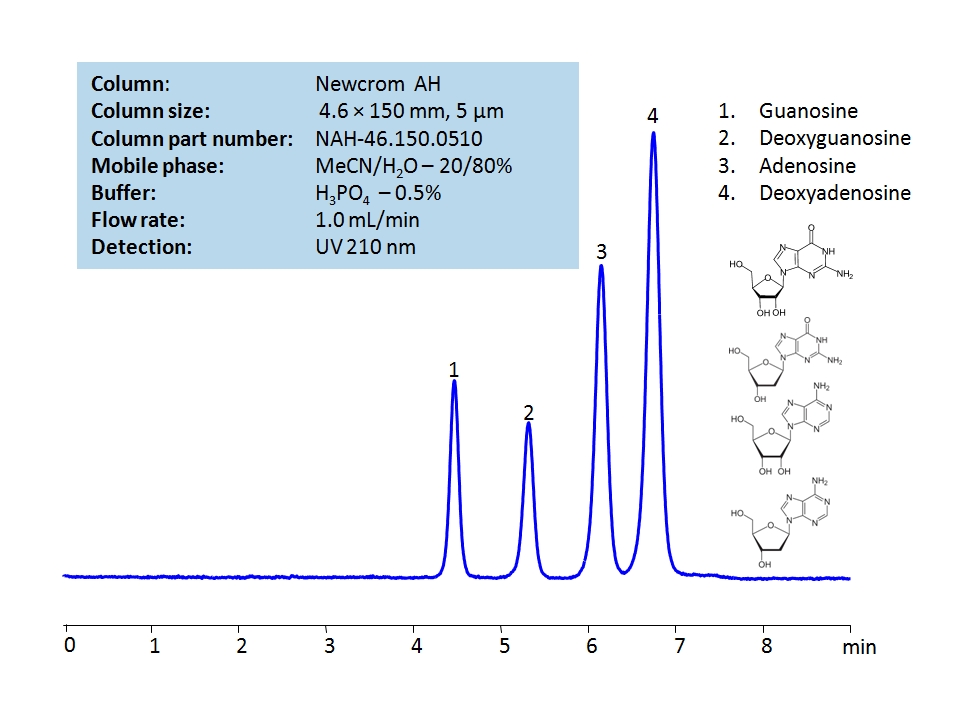
HPLC Separation of Guanosine, Deoxyguanosine, Adenosine, Deoxyadenosine on Newcrom AH Column
May 25, 2021
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
Nucleosides are the building blocks for DNA and RNA as well as other roles in biomechanical processes such as signal transduction. By using a Newcrom AH mixed-mode column with a cation-exchange mechanism, nucleosides: guanosine, deoxyguanosine, adenosine, and deoxyadenosine, can be baseline separated in a short time using an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase of water, acetonitrile (MeCN, ACN), and H3PO4 as a buffer. UV detection at 210 nm.
| Column | Newcrom AH, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 20/80% |
| Buffer | H3PO4 – 0.5% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 210 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Nucleoside, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Guanosine, Deoxyguanosine, Adenosine, Deoxyadenosine |
Application Column
Newcrom AH
The Newcrom columns are a family of reverse-phase-based columns. Newcrom A, AH, B, and BH are all mixed-mode columns with either positive or negative ion-pairing groups attached to either short (25 Å) or long (100 Å) ligand chains. Newcrom R1 is a special reverse-phase column with low silanol activity.
Select optionsDeoxyadenosine
Deoxyguanosine
Guanosine

HPLC Separation of Adenosine, Cordycepin and Adenine on Newcrom AH Column
April 8, 2020
Due to cordycepin having a very similar structure to adenosine, it has shown to have inhibitive properties on the COVID-19 coronavirus. However, due to their similar structures, the separation of the two sugars can be challenging. Both sugars can be separated isocratically in about six minutes on the Newcrom AH mixed-mode column, which has both hydrophobic and cationic exchange properties. The mobile phase consists of acetonitrile (ACN, MeCN) and water with ammonium formate as a buffer which makes it mass-spec (MS) compatible. It can also be UV detected at 260nm.
| Column | Newcrom AH, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 10/90% |
| Buffer | AmFm pH 3.0- 20 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 260 nm, MS-compatible mobile phase |
| Class of Compounds | Hydrophilic, Drug, Xanthine, Nucleobase |
| Analyzing Compounds | Adenosine, Cordycepin, Adenine |
Application Column
Newcrom AH
The Newcrom columns are a family of reverse-phase-based columns. Newcrom A, AH, B, and BH are all mixed-mode columns with either positive or negative ion-pairing groups attached to either short (25 Å) or long (100 Å) ligand chains. Newcrom R1 is a special reverse-phase column with low silanol activity.
Select optionsAdenosine
Cordycepin

Separation of Model Compounds in Reversed-Phase and Mixed-Mode
April 25, 2019
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
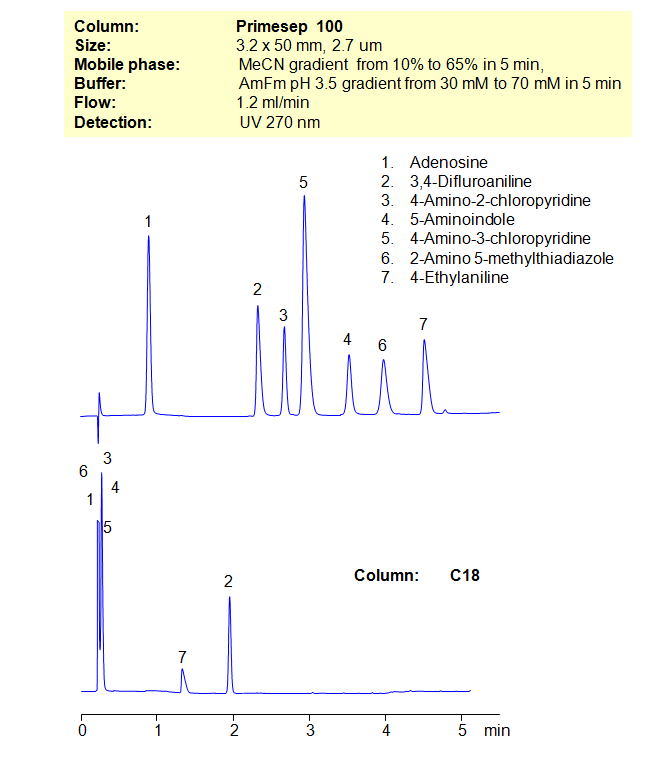
Many compounds are difficult, if not impossible, to separate on reverse-phase columns in HPLC. Other compounds cannot be separated on ion-exchange columns. That’s where the mixed-mode columns come in. By using a stationary phase with both hydrophobic and ion-exchange properties, allows the chromatographer to have additional controls over separation conditions. Here, we demonstrate the separation of compounds that can’t be achieved on a C18 column. By using both an organic gradient and buffer gradient of ammonium formate (AmFm), we can separate structurally similar compounds that can’t be separated on a reverse-phase column alone.
| Column | Primesep 100, 3,2×50 mm, 2,7 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN – 10-60%, 5 min |
| Buffer | Gradient AmFm pH 3.5- 30 – 70 mM, 5 min |
| Flow Rate | 1.2 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 270 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Basic, Hydrophilic, Hydrophobic, Ionizable. |
| Analyzing Compounds | Adenosine, 3,4-Difluroaniline, 4-Amino-2-chloropyridine, 5-Aminoindole, 4-Amino-3-chloropyridine, 2-Amino 5-methylthiadiazole, 4-Ethylaniline |
Application Column
Primesep 100
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select options2-Amino-5-methyl-thiazole
3,4-Difluoroaniline
4-Amino-2-Chloropyridine
4-Amino-3-Chloropyridine
4-Ethylaniline
5-Aminoindole
Adenosine

HPLC Separation of Nucleosides and Deoxynucleosides
July 23, 2012
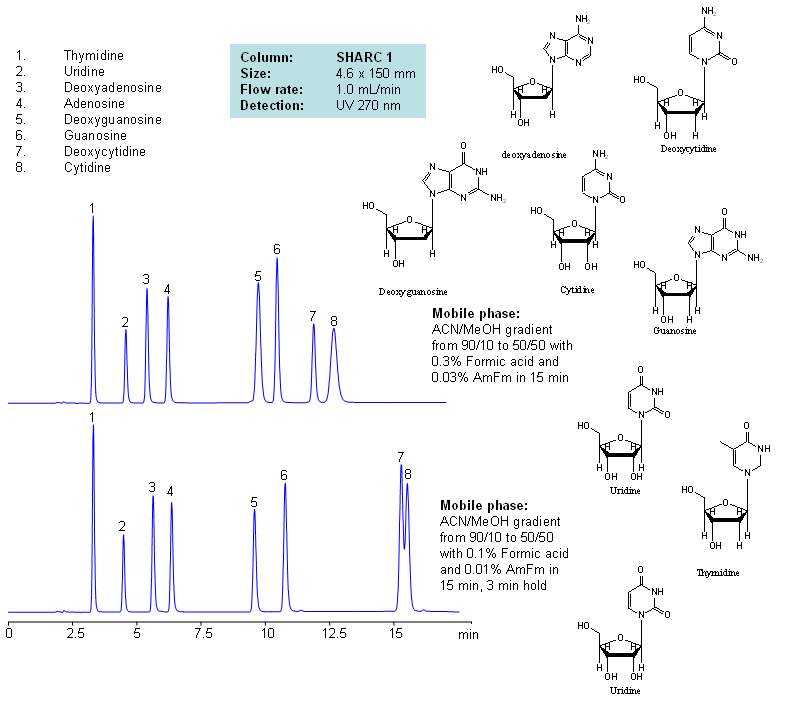
| Column | Sharc 1, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/MeOH |
| Buffer | AmFm, Formic acid |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 270 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | Thymidine, Uridine, Deoxyadenosine, Adenosine, Deoxyguanosine, Guanosine, Deoxycytidine, Cytidine |
Application Column
SHARC 1
The SHARC™ family of innovative columns represents the first commercially available columns primarily utilizing separation based on hydrogen bonding. SHARC stands for Specific Hydrogen-bond Adsorption Resolution Column. Hydrogen bonding involves an interaction or attraction between a bound hydrogen atom and molecules containing electronegative atoms, such as oxygen, nitrogen, and fluorine.
Select optionsCytidine
Deoxyadenosine
Deoxycytidine
Deoxyguanosine
Guanosine
Thymidine
Uridine

HPLC Separation of Adenosine and Adenine Using the Hydrogen Bonding Method
June 18, 2012
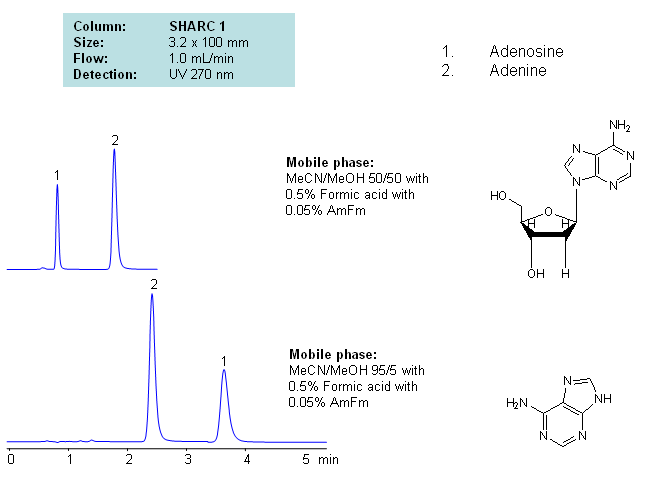
Application Notes: Nucleosides are glycosylamines consisting of a nucleobase linked to a ribose or a deoxyribose sugar. Nucleoside are building blocks for DNA and RNA. These compounds are very polar in nature and contain groups available for hydrogen bonding interactions. Method for separation of adenine and adenosine were developed using a hydrogen-bonding method. There is a strong correlation between retention time for adenine/adenosine and the mobile phase composition, which consists of acetonitrile and methanol. Order of elution for compounds depends on the amount of acetonitrile and methanol. Furthermore, ellution of adenine and adenosine can be reversed based on the composition of the mobile phase. Our method is compatible with LC/MS and preparative chromatography.
| Column | Sharc 1, 3.2×100 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/MeOH |
| Buffer | AmFm, Formic acid |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 270 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | Adenosine, Adenine |
Application Column
SHARC 1
The SHARC™ family of innovative columns represents the first commercially available columns primarily utilizing separation based on hydrogen bonding. SHARC stands for Specific Hydrogen-bond Adsorption Resolution Column. Hydrogen bonding involves an interaction or attraction between a bound hydrogen atom and molecules containing electronegative atoms, such as oxygen, nitrogen, and fluorine.
Select optionsAdenosine

HPLC Separation of Thymidine, Uridine, Adenosine, Guanosine, and Cytidine Using the Hydrogen Bonding Method
June 15, 2012
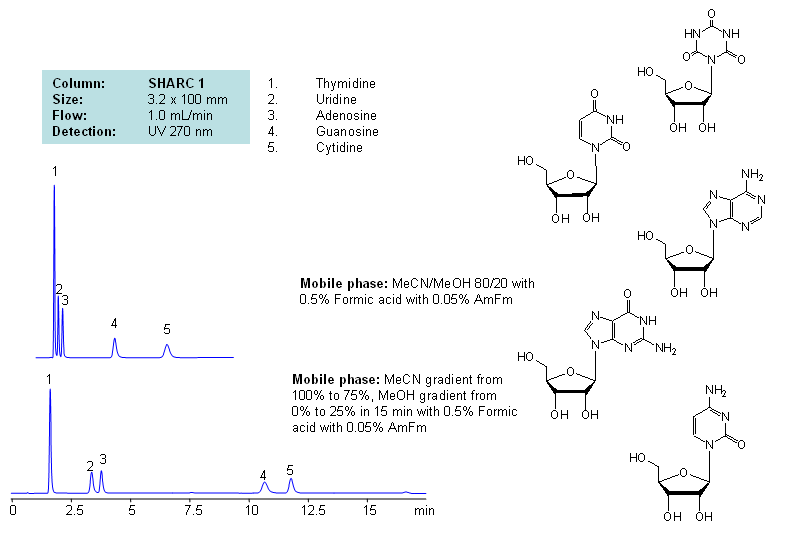
Application Notes: Nucleosides are glycosylamines consisting of nucleobase linked to ribose or deoxyribose sugar and are building blocks for DNA and RNA. These compounds are very polar and contain groups available for hydrogen bonding interaction. Thymidine, uridine, adenosine, guanosine and cytidine were separated using a hydrogen-bonding method. There is a strong correlation between the retention time and mobile phase composition. The strength of hydrogen-bonding interaction increases as the number of hydroxyls in the analytes increase. Additionally the order of elution for compounds depends on the ratio of the mobile phases: acetonitrile and methanol. Our method is compatible with LC/MS and preparative chromatography.
Application Columns: SHARC 1, 3.2×100 mm, 5 um, 100A, To learn more about SHARC 1 columns click here. To order this column click here. To see more chromatographic separations check our web site.
Application Compounds: Thymidine, uridine, adenosine, guanosine and cytidine
| Column | Sharc 1, 3.2×100 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/MeOH |
| Buffer | AmFm, Formic acid |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 270 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | Thymidine, Uridine, Adenosine, Guanosine, Cytidine |
Application Column
SHARC 1
The SHARC™ family of innovative columns represents the first commercially available columns primarily utilizing separation based on hydrogen bonding. SHARC stands for Specific Hydrogen-bond Adsorption Resolution Column. Hydrogen bonding involves an interaction or attraction between a bound hydrogen atom and molecules containing electronegative atoms, such as oxygen, nitrogen, and fluorine.
Select optionsCytidine
Guanosine
Thymidine
Uridine

HPLC Separation of Nucleic Bases at pH 4 and 5 on Obelisc N
March 3, 2007
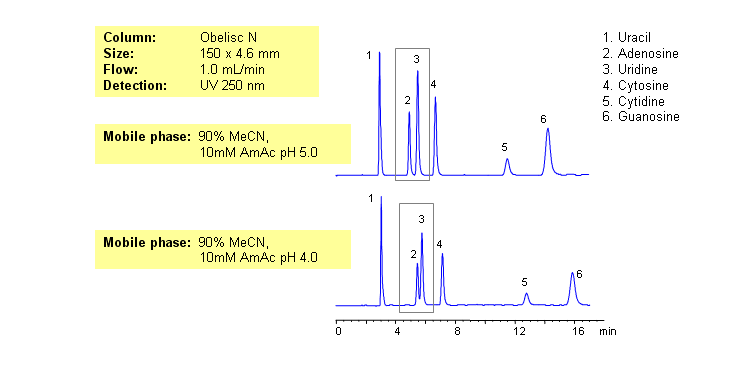
Nucleic bases are biological compounds found in genetic molecules (DNA, RNA). They can be separated on an Obelisc N column, which offers very polar characteristics and can be used with positively or negatively charged groups. Closely-eluted adenosine and uridine can be further separated by simply adjusting the pH of the mobile phase. Mobile phase is water and acetonitrile (MeCN, ACN) with Ammonium Acetate as buffer. UV detection at 250nm.
| Column | Obelisc N, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN -90% |
| Buffer | AmAc |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 250 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | Uracil, Uridine, Adenosine, Guanosine, Cytidine, Cytosine |
Application Column
Obelisc N
SIELC has developed the Obelisc™ columns, which are mixed-mode and utilize Liquid Separation Cell technology (LiSC™). These cost-effective columns are the first of their kind to be commercially available and can replace multiple HPLC columns, including reversed-phase (RP), AQ-type reversed-phase, polar-embedded group RP columns, normal-phase, cation-exchange, anion-exchange, ion-exclusion, and HILIC (Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography) columns. By controlling just three orthogonal method parameters - buffer concentration, buffer pH, and organic modifier concentration - users can adjust the column properties with pinpoint precision to separate complex mixtures.
Select optionsCytidine
Cytosine
Guanosine
Uracil
Uridine