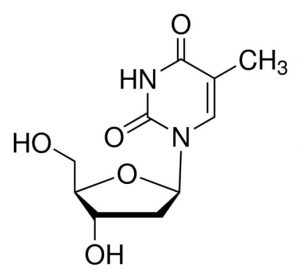
| CAS Number | 50-89-5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H14N2O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 242.231 |
| InChI Key | IQFYYKKMVGJFEH-XLPZGREQSA-N |
| LogP | -0.930 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
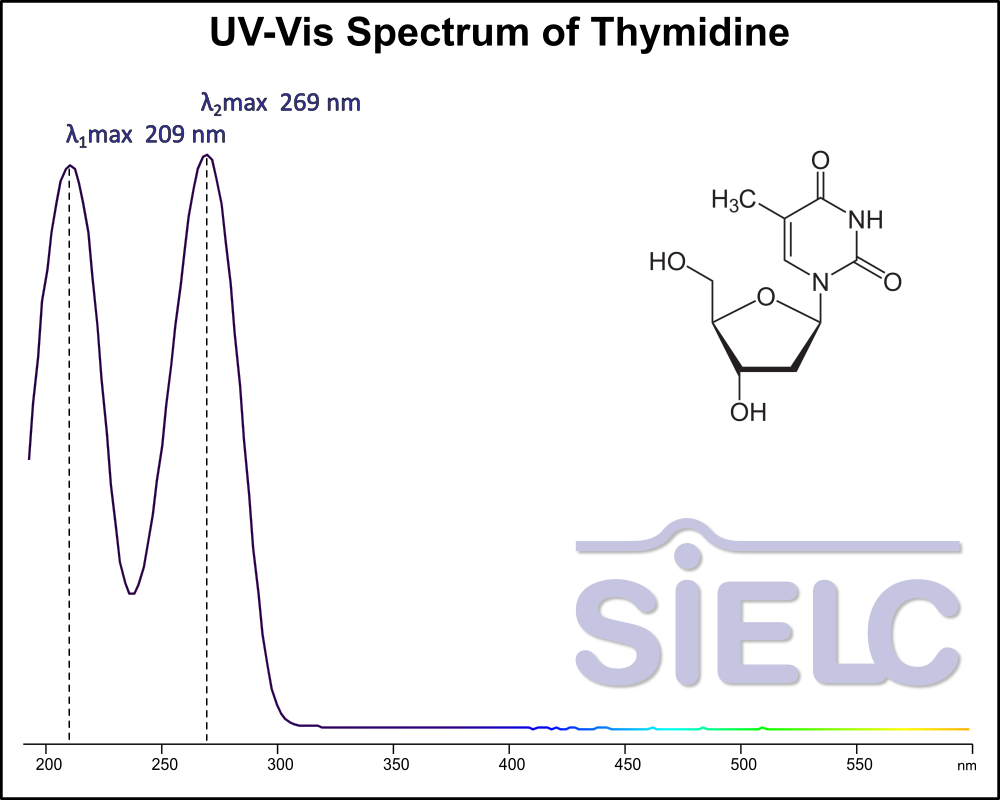
Uv-Vis Spectrum of Thymidine
February 2, 2026
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Thymidine check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

HPLC Separation of Nucleosides and Deoxynucleosides
July 23, 2012
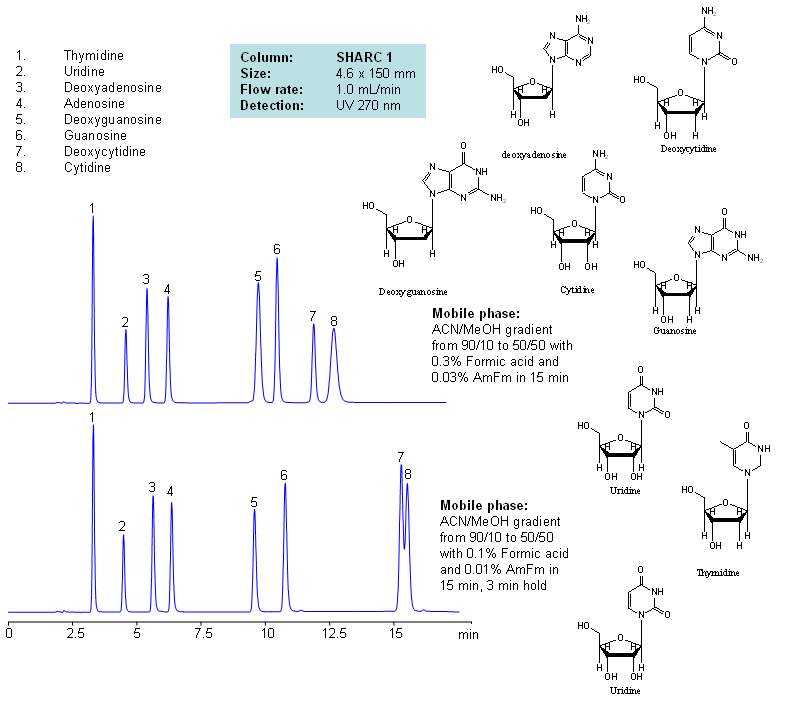
| Column | Sharc 1, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/MeOH |
| Buffer | AmFm, Formic acid |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 270 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | Thymidine, Uridine, Deoxyadenosine, Adenosine, Deoxyguanosine, Guanosine, Deoxycytidine, Cytidine |
Application Column
SHARC 1
The SHARC™ family of innovative columns represents the first commercially available columns primarily utilizing separation based on hydrogen bonding. SHARC stands for Specific Hydrogen-bond Adsorption Resolution Column. Hydrogen bonding involves an interaction or attraction between a bound hydrogen atom and molecules containing electronegative atoms, such as oxygen, nitrogen, and fluorine.
Select optionsCytidine
Deoxyadenosine
Deoxycytidine
Deoxyguanosine
Guanosine
Thymidine
Uridine

HPLC Separation of Thymidine, Uridine, Adenosine, Guanosine, and Cytidine Using the Hydrogen Bonding Method
June 15, 2012
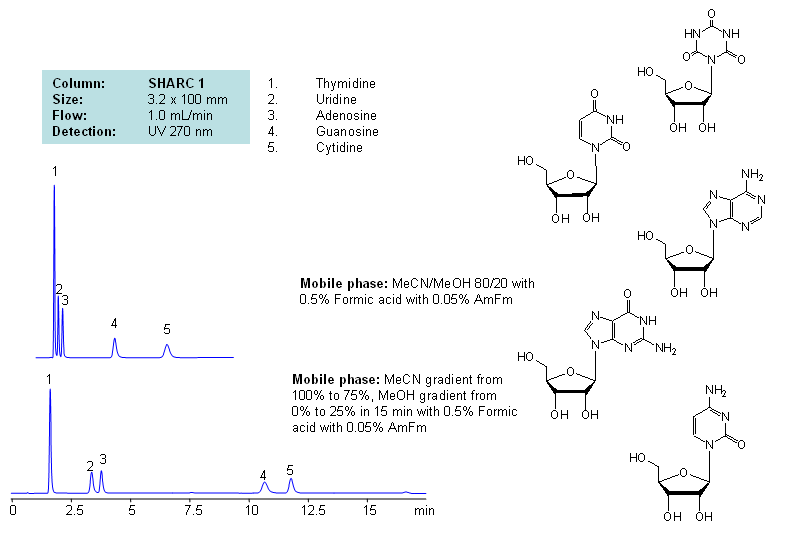
Application Notes: Nucleosides are glycosylamines consisting of nucleobase linked to ribose or deoxyribose sugar and are building blocks for DNA and RNA. These compounds are very polar and contain groups available for hydrogen bonding interaction. Thymidine, uridine, adenosine, guanosine and cytidine were separated using a hydrogen-bonding method. There is a strong correlation between the retention time and mobile phase composition. The strength of hydrogen-bonding interaction increases as the number of hydroxyls in the analytes increase. Additionally the order of elution for compounds depends on the ratio of the mobile phases: acetonitrile and methanol. Our method is compatible with LC/MS and preparative chromatography.
Application Columns: SHARC 1, 3.2×100 mm, 5 um, 100A, To learn more about SHARC 1 columns click here. To order this column click here. To see more chromatographic separations check our web site.
Application Compounds: Thymidine, uridine, adenosine, guanosine and cytidine
| Column | Sharc 1, 3.2×100 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/MeOH |
| Buffer | AmFm, Formic acid |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 270 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | Thymidine, Uridine, Adenosine, Guanosine, Cytidine |
Application Column
SHARC 1
The SHARC™ family of innovative columns represents the first commercially available columns primarily utilizing separation based on hydrogen bonding. SHARC stands for Specific Hydrogen-bond Adsorption Resolution Column. Hydrogen bonding involves an interaction or attraction between a bound hydrogen atom and molecules containing electronegative atoms, such as oxygen, nitrogen, and fluorine.
Select optionsCytidine
Guanosine
Thymidine
Uridine