| CAS Number | 652157-52-3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H15N3O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 245.235 |
| InChI Key | HXBGOHZLZCFWLH-OERIEOFYSA-N |
| LogP | -1.84 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
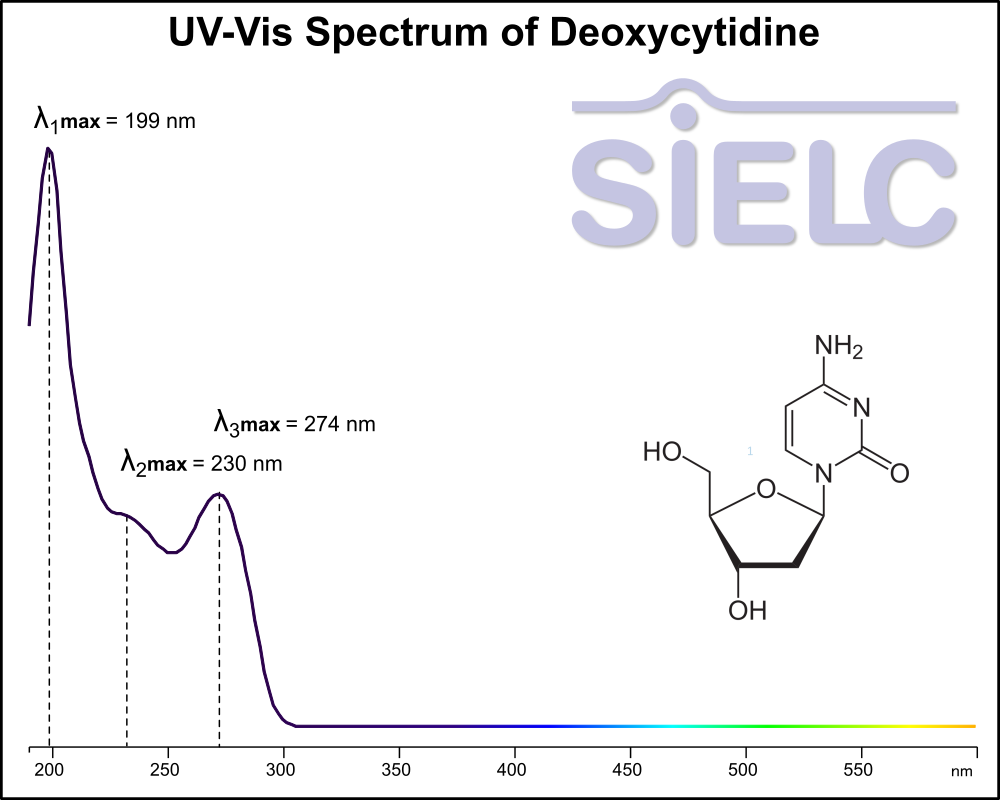
Uv-Vis Spectrum of Deoxycytidine
February 6, 2026
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Deoxycytidine check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

HPLC Method for Separation of Cytosine, Deoxycytidine and Cytidine on BIST B+ Column
November 28, 2022
HPLC Method for Separation of Cytosine, Deoxycytidine, Cytidine on BIST B+ by SIELC Technologies.
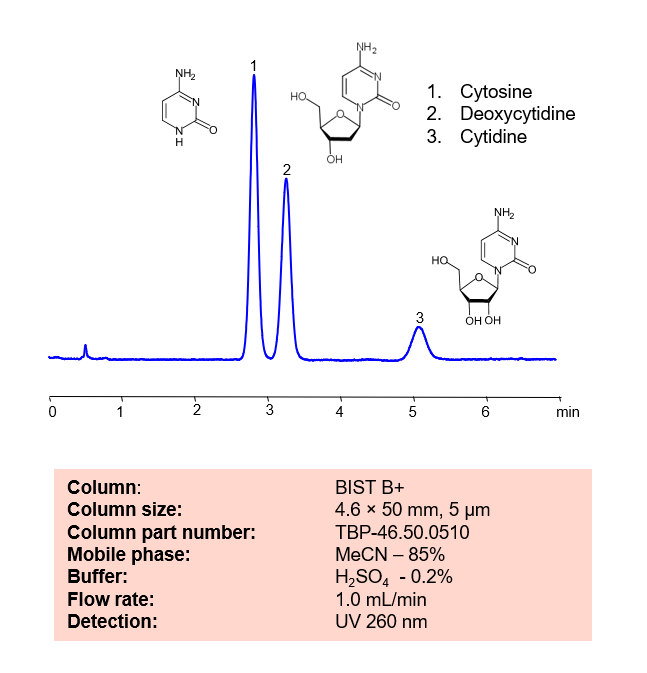
Cytosine, also noted as C and Cyt, has the chemical formula C4H5N3O. In DNA, it pairs with Guanine to create a base pair. In RNA, it is synonymous with Uracil, being an interchangeable third base. Not only that, due to it’s instability, it can change into Uracil through spontaneous deamination.
Deoxycytidine is a deoxyribonucleoside with the chemical formula C9H13N3O4. It is a precursor for 5-aza-2′-cytidine, which is a treatment for myelodysplastic syndrome. It works through interfering with the methylation of the P15/INK4B gene. It can also be used as a biomarker for tumor diagnosis.
Cytidine, also noted as C or Cyd, is a nucleoside molecule with the chemical formula C9H13N3O5. It is primarily found in foods with high RNA contents, such as organ meets, brewer’s yeast, and beer. During digestion, Cyd is broken down into ribosyl pyrimidines.
Cytosine, Deoxycytidine, Cytidine can be retained and analyzed using the BIST B+ stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water and acetonitrile (MeCN) with a sulfuric acid buffer. Detection is performed using UV.
Condition
| Column | BIST B+, 4.6 x 50 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 85% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 260 nm |
| Peak Retention Time | 2.8, 3.2, 5.1 min |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Nucleosides |
| Analyzing Compounds | Cytosine, Deoxycytidine, Cytidine |
Application Column
BIST B+
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 50 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Cytosine
Deoxycytidine

HPLC Separation of Nucleosides and Deoxynucleosides
July 23, 2012
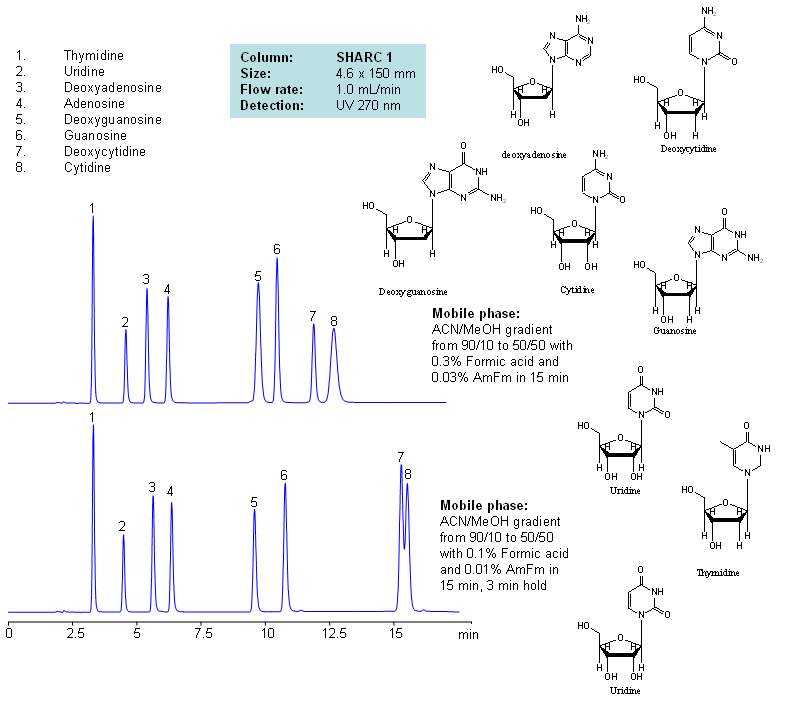
| Column | Sharc 1, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/MeOH |
| Buffer | AmFm, Formic acid |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 270 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | Thymidine, Uridine, Deoxyadenosine, Adenosine, Deoxyguanosine, Guanosine, Deoxycytidine, Cytidine |
Application Column
SHARC 1
The SHARC™ family of innovative columns represents the first commercially available columns primarily utilizing separation based on hydrogen bonding. SHARC stands for Specific Hydrogen-bond Adsorption Resolution Column. Hydrogen bonding involves an interaction or attraction between a bound hydrogen atom and molecules containing electronegative atoms, such as oxygen, nitrogen, and fluorine.
Select optionsCytidine
Deoxyadenosine
Deoxycytidine
Deoxyguanosine
Guanosine
Thymidine
Uridine

Separation of Deoxyribo Nucleosides
September 24, 2003
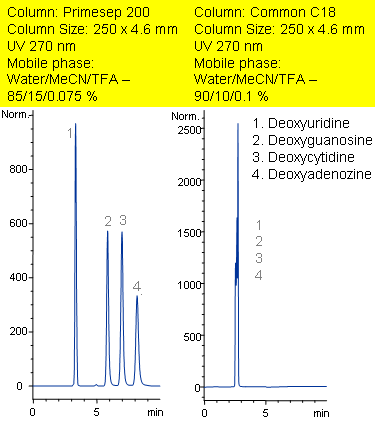
Primesep 200 separates with baseline resolution the nucleosides (deoxyuridine, deoxyguanosine, deoxycytidine, deoxyadenozine) by a combination of cation exchange and reversed phase. These compounds are not retained on a traditional C18 column. Primesep 200 has an embedded anionic functional group which helps retain polar compounds by polar and ion-exchange mechanisms. Excellent peak shape results with a mass spec compatible mobile phase of water, acetonitrile (MeCN, ACN) and trifluoracetic acid (TFA) with UV detection at 270 nm.
Application Column
Primesep 200
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 250 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Deoxycytidine
Deoxyguanosine
Deoxyuridine