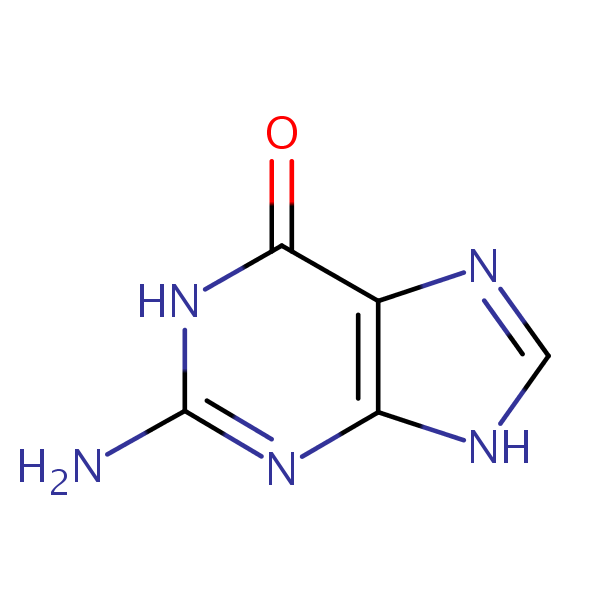
| CAS Number | 73-40-5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C5H5N5O |
| Molecular Weight | 151.129 |
| InChI Key | UYTPUPDQBNUYGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -0.910 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
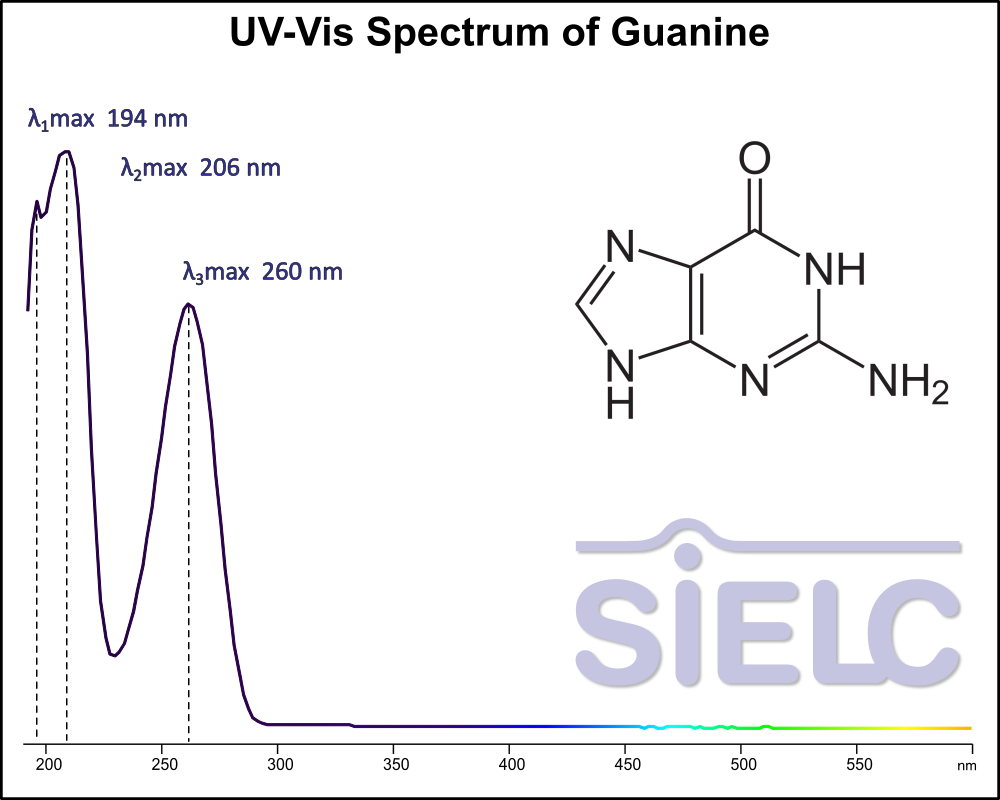
Uv-Vis Spectrum of Guanine
February 3, 2026
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Guanine check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

HPLC Separation of Uracil, Thymine, Hypoxanthine and Guanine on Newcrom AH
October 31, 2023
HPLC Method for Analysis of Uracil, Thymine, Hypoxanthine, Guanine on Newcrom AH Column by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
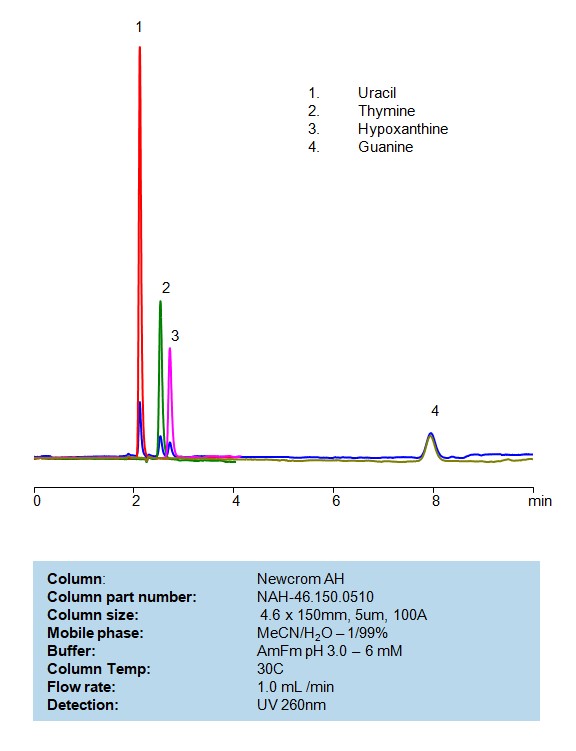
Uracil, Thymine, Hypoxanthine, and Guanine are all nitrogenous bases, each playing distinct roles in the biochemistry of nucleic acids.
Uracil (U):
- Found in: RNA
- Pairs with: Adenine (A)
- Structure: Pyrimidine
- Role: Uracil replaces thymine in RNA. In DNA, adenine pairs with thymine, but in RNA, adenine pairs with uracil.
Thymine (T):
- Found in: DNA
- Pairs with: Adenine (A)
- Structure: Pyrimidine
- Role: Thymine is specific to DNA, distinguishing it from RNA. It’s the base that pairs with adenine through two hydrogen bonds.
Hypoxanthine:
- A naturally occurring purine derivative. It’s not directly a base in standard DNA or RNA, but it plays a significant role in the metabolism of purines.
- It is the base form of the nucleoside inosine, which can be found in certain tRNAs and plays a role in wobble base pairing.
- Hypoxanthine is also an intermediate in the purine degradation pathway, leading to the production of uric acid.
Guanine (G):
- Found in: Both DNA and RNA
- Pairs with: Cytosine (C)
- Structure: Purine
- Role: Guanine is one of the four main nucleobases in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. It forms three hydrogen bonds with cytosine, contributing to the stability of the nucleic acid structures.
These nitrogenous bases are crucial for the structure, replication, and function of nucleic acids. Understanding their properties and interactions is fundamental to molecular biology and genetics.
Nucleotides can be retained and analyzed on a mixed-mode Newcrom AH column with a mobile phase consisting of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN), and ammonium formate. This analytical method can detect compounds with high resolution and peak symmetry using UV detection at 260 nm
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analyses of Uracil, Thymine, Hypoxanthine and Guanine
Condition
| Column | Newcrom AH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 1% |
| Buffer | Ammonium formate pH 3.0- 6 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Peak Retention Time | 2.21, 2.38, 2.81, 7.92 min |
| Detection | 260 nm |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Nucleotides |
| Analyzing Compounds | Uracil, Thymine, Hypoxanthine, Guanine |
Application Column
Newcrom AH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Hypoxanthine
Thymine
Uracil

Ionic Modifier Effect on Selectivity of Separation of Deoxyguanosine, Guanine and Guanosine on BIST B+
December 5, 2022
Ionic Modifier Effect on Selectivity of Separation of Deoxyguanosine, Guanine, Guanosine on BIST B+ by SIELC Technologies.
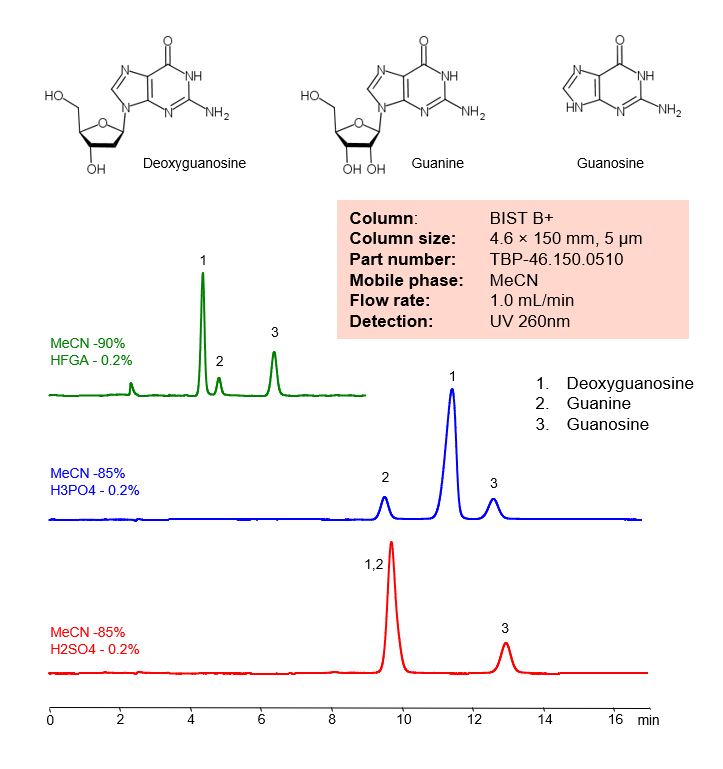
Deoxyguanosine is a deoxyribonucleoside with the chemical formula C10H13N5O4. It is a vital part of what makes up DNA.
Guanine, also noted as G and Gua, has the chemical formula C5H5N5O. By forming three hydrogen bonds with the Cytosine, it creates a base pair. It’s name comes from the Spanish term “guano”, meaning bird or bat dropping, as that is said to have been how it was first discovered. Outside of DNA, Guanine that is harvested from fish scales, is occasionally used in cosmetics for it’s luster.
Guanosine is a purine nucleoside with the chemical formula C10H13N5O5. It can be phosphorylated into many other forms, which play vital roles in biochemical possesses like synthesis of nucleic acids, proteins, photosynthesis, and more. It is also required for RNA splicing.
Deoxyguanosine, Guanine, Guanosine can be retained and analyzed using the BIST B+ stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water and acetonitrile (MeCN). Detection is performed using UV.
Condition
| Column | BIST B+, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN |
| Buffer | H3PO4, H2SO4, HFGA (Hexafluoroglutaric acid) – 0.2%, |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 260 nm |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Nucleosides |
| Analyzing Compounds | Deoxyguanosine, Guanine, Guanosine |
Application Column
BIST B+
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Guanine
Guanosine

HPLC Method for Analysis of Deoxyguanosine, Guanine and Guanosine on BIST B+
December 5, 2022
HPLC Method for Analysis of Deoxyguanosine, Guanine and Guanosine on BIST B+ by SIELC Technologies.
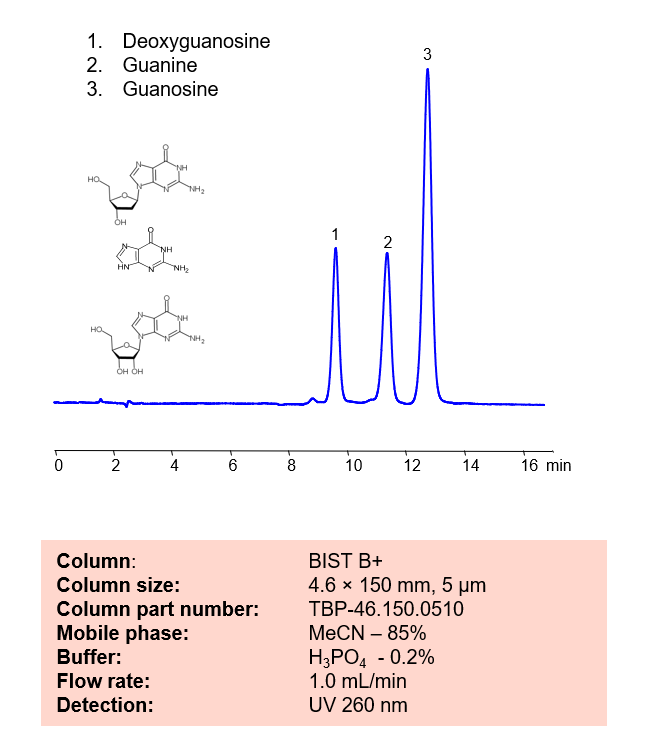
Deoxyguanosine is a deoxyribonucleoside with the chemical formula C10H13N5O4. It is a vital part of what makes up DNA.
Guanine, also noted as G and Gua, has the chemical formula C5H5N5O. By forming three hydrogen bonds with the Cytosine, it creates a base pair. It’s name comes from the Spanish term “guano”, meaning bird or bat dropping, as that is said to have been how it was first discovered. Outside of DNA, Guanine that is harvested from fish scales, is occasionally used in cosmetics for it’s luster.
Guanosine is a purine nucleoside with the chemical formula C10H13N5O5. It can be phosphorylated into many other forms, which play vital roles in biochemical possesses like synthesis of nucleic acids, proteins, photosynthesis, and more. It is also required for RNA splicing.
Guanine, Guanosine, Deoxyguanosine can be retained and analyzed using the BIST B+ stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water and acetonitrile (MeCN). Detection is performed using UV.
Condition
| Column | BIST B+, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 85% |
| Buffer | H3PO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 260 nm |
| Peak Retention Time | 9.6, 11.2, 12.8 min |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Nucleosides |
| Analyzing Compounds | Guanine, Guanosine, Deoxyguanosine |
Application Column
BIST B+
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Guanine
Guanosine

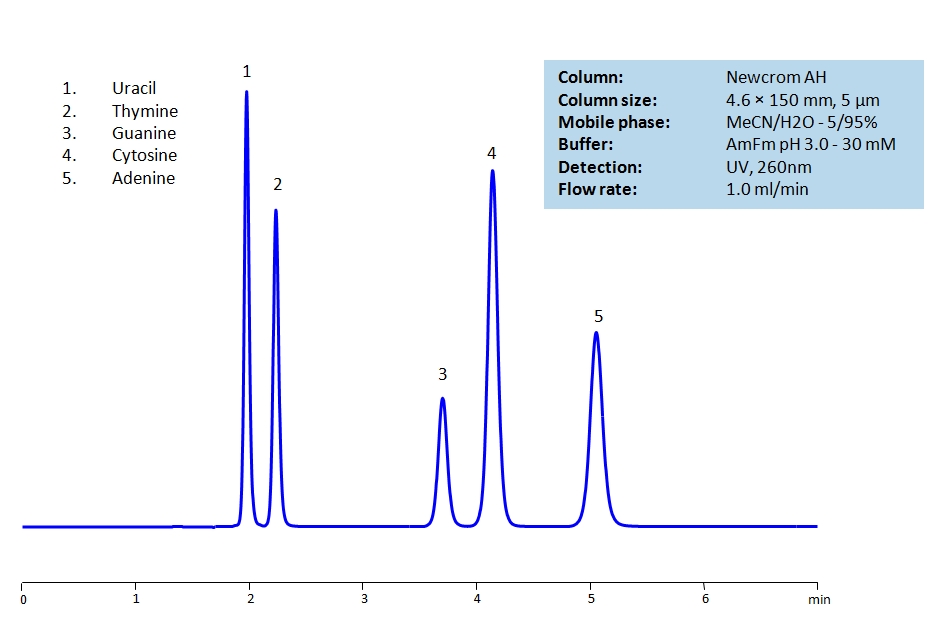
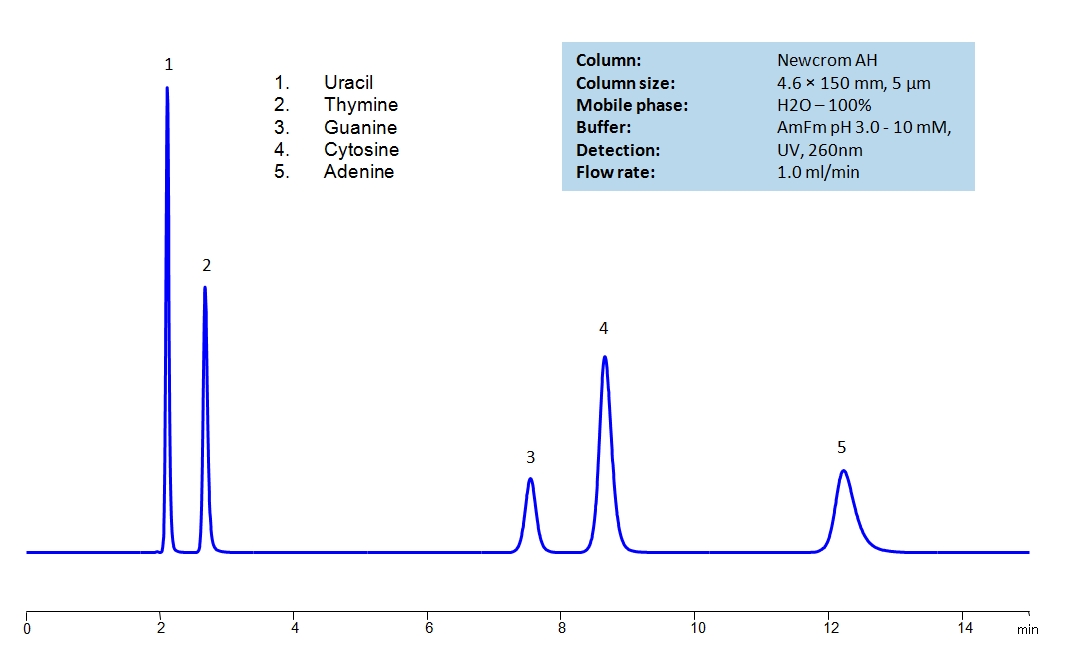
HPLC Separation of Uracil, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine, Adenine on Newcrom AH
April 14, 2020
HPLC Method for Uracil, Thymine, Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine on Newcrom AH by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Uracil, Thymine, Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine.
| Column | Newcrom AH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 5/95% |
| Buffer | AmFm pH 3.0- 30 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 260 nm, MS-compatible mobile phase |
| Column | Newcrom AH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | H2O – 100% |
| Buffer | AmFm pH 3.0- 10 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 260 nm, MS-compatible mobile phase |
Uracil, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine and Adenine are the nucleobases found in RNA and DNA.
Uracil, also noted as U and Ura, has C4H4N2O2 chemical formula. It is a derivative of pyrimidine that is rarely found in DNA, working more often in RNA in transcription by binding to adenine through hydrogen bonds. You can find detailed UV spectra of Uracil and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
Thymine, also noted as T and Thy, has the chemical formula C5H6N2O2. It is a a pyrimidine nucleobase that may be produced through methylation of uracil. In DNA, it creates a double hydrogen bond to Adenine to hold together the structure of DNA.
Guanine, also noted as G and Gua, has the chemical formula C5H5N5O. By forming three hydrogen bonds with the Cytosine, it creates a base pair. It’s name comes from the Spanish term “guano”, meaning bird or bat dropping, as that is said to have been how it was first discovered. Outside of DNA, Guanine that is harvested from fish scales, is occasionally used in cosmetics for it’s luster.
Cytosine, also noted as C and Cyt, has the chemical formula C4H5N3O. In DNA, it pairs with Guanine to create a base pair. In RNA, it is synonymous with Uracil, being an interchangeable third base. Not only that, due to it’s instability, it can change into Uracil through spontaneous deamination.
Adenine, also noted as A and Ade, has the chemical formula C5H5N5. Besides DNA and RNA, Adenine can also be found in Adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is a nucleotide triphosphate that provides energy in cells required for bodily functions. In DNA, it partners with Thymine via two hydrogen bonds, while in RNA it bonds to Uracil for protein synthesis.
The nucleobases are difficult to separate on reverse-phase columns due to their polar, hydrophilic and ionic nature. Using the Newcrom AH mixed-mode column, the nucleobases can be easily separated isocratically using low organic mobile phase (5% acetonitrile) or pure water, if organic mobile phase is undesirable, with ammonium formate buffer, making the method both UV and Mass Spec compatible.
Application Column
Newcrom AH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Cytosine
Guanine
Thymine
Uracil

HPLC Application for Separation of Nucleotide Bases Uracil, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine, Adenine on Primesep 200 Column
December 6, 2007
Nucleotide bases are parts of DNA and RNA. Adenine and guanine are purine-bases; uracil, thymine and cytosine are pyrimidine-bases. In the view of chromatography these compounds are very polar and similar in properties. It is hard to obtain base line HPLC separation on traditional C18 as peaks of nucleotide bases co-elute even at low organic concentration. In this application nucleobases are well retained and separated on Primesep 200 mixed-mode column. Compounds are retained by weak reverse phase and weak ion-exchange mechanisms. This HPLC method can utilize UV, ELSD, and LC/MS detection.
| Column | Primesep 200, 4.6*250 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 10/90% |
| Buffer | TFA – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 0.5 ml/min, 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 270 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Hormone |
| Analyzing Compounds | Uracil, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine, Adenine |
Application Column
Primesep 200
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsCytosine
Guanine
Purines
Pyrimidines
Uracil

Separation of Nucleic Bases
September 24, 2003
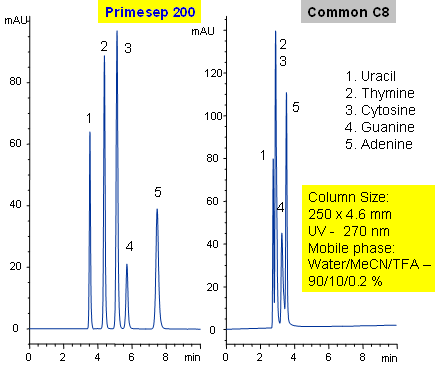
Primesep 200 separates with baseline resolution nucleic bases (uracil, thymine, cytosine, guanine, and adenine) by a combination of cation exchange and reversed phase. Uracil typically does not retain on reversed-phase column and is often used as an unretained void volume marker for C18 and C8 columns. Primesep 200 has an embedded anionic functional group which helps retain polar compounds polar and ion-exchange mechanisms. Excellent peak shape results with a mass spec compatible mobile phase of water, acetonitrile (MeCN, ACN) and trifluoracetic acid (TFA) with UV detection at 270 nm.
| Column | Primesep 200, 4.6*250 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 10/90% |
| Buffer | TFA – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 0.5 ml/min, 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 270 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Hormone |
| Analyzing Compounds | Uracil, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine, Adenine |
Application Column
Primesep 200
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsCytosine
Guanine
Nucleic Bases
Thymine
Uracil