| CAS Number | 68-94-0 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C5H4N4O |
| Molecular Weight | 136.114 |
| InChI Key | FDGQSTZJBFJUBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -0.750 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
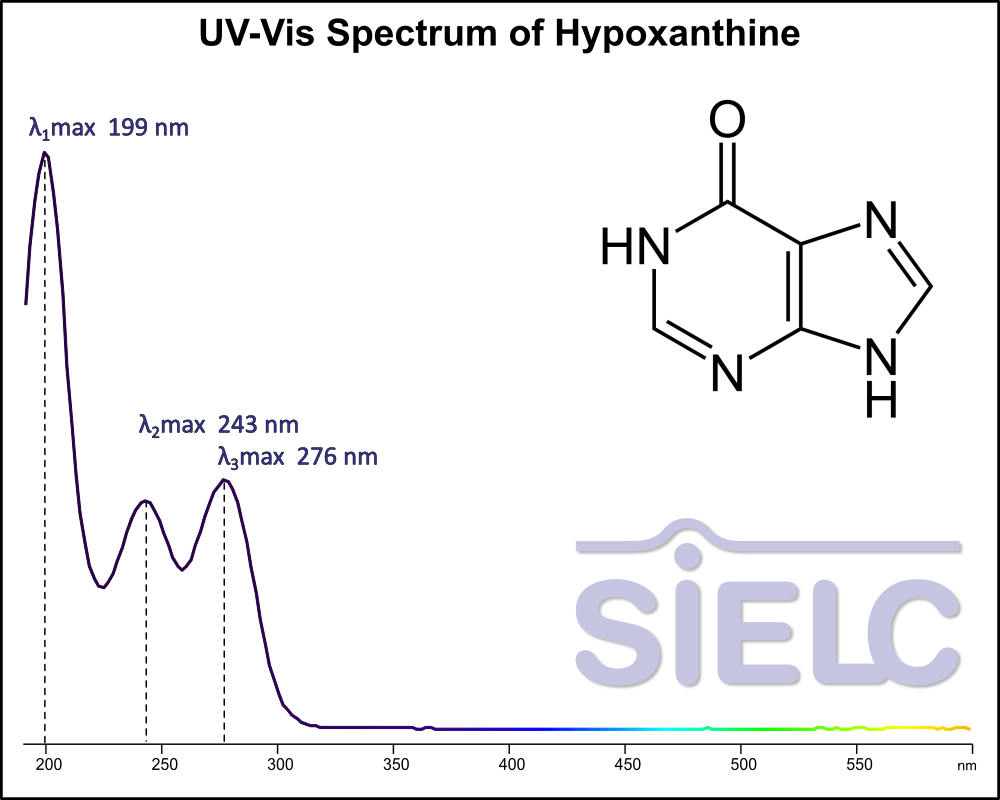
Uv-Vis Spectrum of Hypoxanthine
February 2, 2026
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Hypoxanthine check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

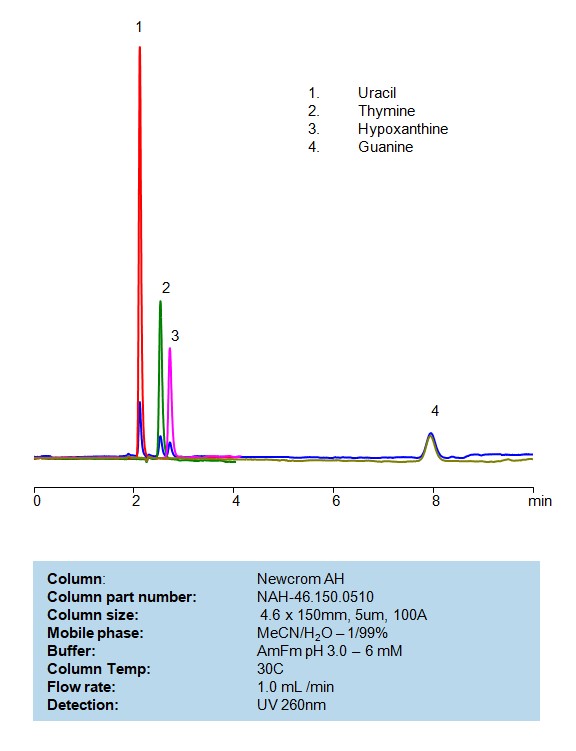
HPLC Separation of Uracil, Thymine, Hypoxanthine and Guanine on Newcrom AH
October 31, 2023
HPLC Method for Analysis of Uracil, Thymine, Hypoxanthine, Guanine on Newcrom AH Column by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
Uracil, Thymine, Hypoxanthine, and Guanine are all nitrogenous bases, each playing distinct roles in the biochemistry of nucleic acids.
Uracil (U):
- Found in: RNA
- Pairs with: Adenine (A)
- Structure: Pyrimidine
- Role: Uracil replaces thymine in RNA. In DNA, adenine pairs with thymine, but in RNA, adenine pairs with uracil.
Thymine (T):
- Found in: DNA
- Pairs with: Adenine (A)
- Structure: Pyrimidine
- Role: Thymine is specific to DNA, distinguishing it from RNA. It’s the base that pairs with adenine through two hydrogen bonds.
Hypoxanthine:
- A naturally occurring purine derivative. It’s not directly a base in standard DNA or RNA, but it plays a significant role in the metabolism of purines.
- It is the base form of the nucleoside inosine, which can be found in certain tRNAs and plays a role in wobble base pairing.
- Hypoxanthine is also an intermediate in the purine degradation pathway, leading to the production of uric acid.
Guanine (G):
- Found in: Both DNA and RNA
- Pairs with: Cytosine (C)
- Structure: Purine
- Role: Guanine is one of the four main nucleobases in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. It forms three hydrogen bonds with cytosine, contributing to the stability of the nucleic acid structures.
These nitrogenous bases are crucial for the structure, replication, and function of nucleic acids. Understanding their properties and interactions is fundamental to molecular biology and genetics.
Nucleotides can be retained and analyzed on a mixed-mode Newcrom AH column with a mobile phase consisting of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN), and ammonium formate. This analytical method can detect compounds with high resolution and peak symmetry using UV detection at 260 nm
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analyses of Uracil, Thymine, Hypoxanthine and Guanine
Condition
| Column | Newcrom AH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 1% |
| Buffer | Ammonium formate pH 3.0- 6 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Peak Retention Time | 2.21, 2.38, 2.81, 7.92 min |
| Detection | 260 nm |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Nucleotides |
| Analyzing Compounds | Uracil, Thymine, Hypoxanthine, Guanine |
Application Column
Newcrom AH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Hypoxanthine
Thymine
Uracil

HPLC Method for Analysis mixture of Xanthines and Uric Acid BIST B+ by SIELC Technologies
November 16, 2022
HPLC Method for Analysis mixture of Caffeine, 1,3-Dimethyluric acid, Xanthine, Hypoxanthine, Uric acid by SIELC Technologies.
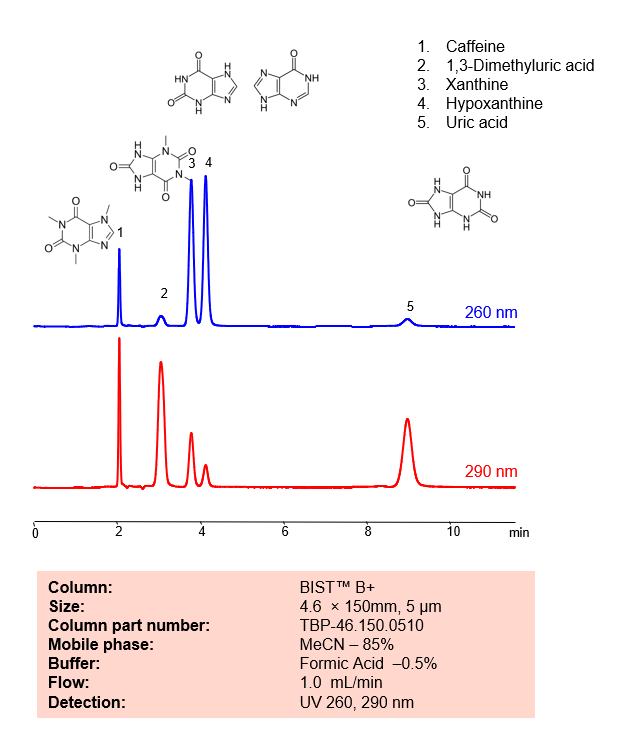
Xanthines and uric acid are related compounds in the body and both are involved in the metabolism of purines.
Xanthines are a group of alkaloids that are widely distributed in plants, and also occur in the tissues and fluids of animals. They are known to stimulate the central nervous system and cardiac muscle, and also have diuretic effects.
In the body, xanthines are intermediates in the degradation of adenosine monophosphate to uric acid. This metabolic pathway starts with adenosine monophosphate (AMP), which is deaminated to form inosine monophosphate (IMP). IMP is then converted into a xanthine known as hypoxanthine. Hypoxanthine is then oxidized to xanthine, and finally, xanthine is further oxidized to uric acid. Both of the oxidation steps are catalyzed by the enzyme xanthine oxidase.
Caffeine is a natural stimulant and methylxanthine alkaloid. with the molecular formula C6H10N4O2. Caffeine can be found in a variety of plants, including tea, coffea, cocoa, kola nuts, and guarana. Ingestion of it can increase alertness and cognitive function. It can also cause worsening anxiety, heart palpitations, and headaches You can find detailed UV spectra of caffeine and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
1,3-Dimethyluric acid is an oxopurine with the chemical formula C7H8N4O3. It is a is a metabolite of caffeine and theophylline with antioxidant properties. It is used as a biomarker in urine for activity of the CYP1A2 enzyme.
Xanthine is a purine base with the chemical formula C5H4N4O2. It is a product on the pathway of purine degradation. Numerous stimulants are derived from xanthine.
Hypoxanthine is a naturally occurring purine derivative with the chemical formula C5H4N4O. It is a reaction intermediate in the metabolism of adenosine as well as a metabolite found in Escherichia coli.
Uric acid is a waste product that’s produced when the body breaks down purines, substances found in foods and drinks like liver, anchovies, mackerel, dried beans, peas, and beer. It is normally excreted from the body in urine. However, if the body produces too much uric acid or doesn’t excrete enough of it, it can build up in the blood and potentially lead to health problems such as gout and kidney stones
Caffeine, 1,3-Dimethyluric acid, Xanthine, Hypoxanthine, Uric acid can be retained, analyzed, and separated using an isocratic analytical method on a BIST B+ column. The simple mobile phase for this method comprises water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and formic acid as an ionic modifier. The analytical method can be monitored with UV detection at 260 nm, an Evaporative Light Scattering Detector (ELSD), or any other evaporative detection method such as Charged Aerosol Detection (CAD) or Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry (ESI-MS)
Condition
| Column | BIST B+, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 85% |
| Buffer | FA – 0.5% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 260, 290 nm |
| Peak Retention Time | 2.01, 3.02, 4.2, 9.09 min |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Acid, Xanthines |
| Analyzing Compounds | Caffeine, 1,3-Dimethyluric acid, Xanthine, Hypoxanthine, Uric acid |
Application Column
BIST B+
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Caffeine
Hypoxanthine
Uric acid
Xanthine

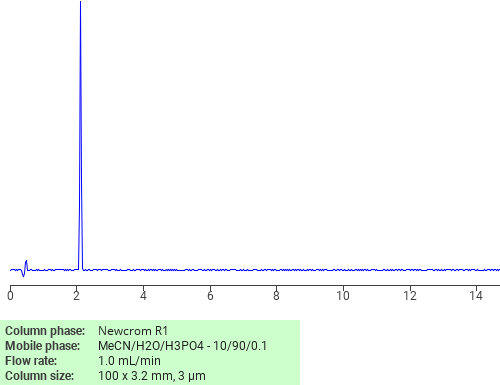
Separation of Hypoxanthine on Newcrom R1 HPLC column
May 16, 2018
Hypoxanthine can be analyzed by this reverse phase (RP) HPLC method with simple conditions. The mobile phase contains an acetonitrile (MeCN), water, and phosphoric acid. For Mass-Spec (MS) compatible applications the phosphoric acid needs to be replaced with formic acid. Smaller 3 µm particles columns available for fast UPLC applications. This liquid chromatography method is scalable and can be used for isolation impurities in preparative separation. It also suitable for pharmacokinetics.
Application Column
Newcrom R1
The Newcrom columns are a family of reverse-phase-based columns. Newcrom A, AH, B, and BH are all mixed-mode columns with either positive or negative ion-pairing groups attached to either short (25 Å) or long (100 Å) ligand chains. Newcrom R1 is a special reverse-phase column with low silanol activity.
Select options