| CAS Number | 79-11-8 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C2H3ClO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 94.490 |
| InChI Key | FOCAUTSVDIKZOP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 0.22 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
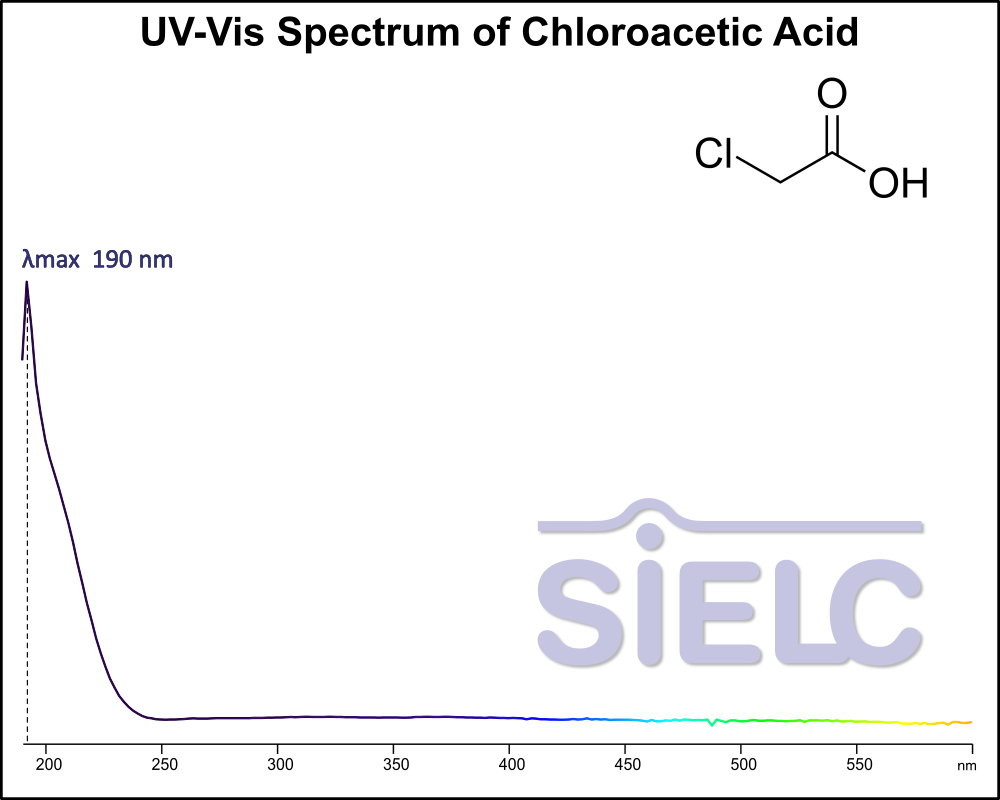
UV-Vis Spectrum of Chloroacetic Acid
December 24, 2025
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Chloroacetic acid check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

HPLC Method for Analysis of Chloroacetic acid, Dichloroacetic acid and Trichloroacetic acid on BIST™ A+ Column
July 7, 2022
Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
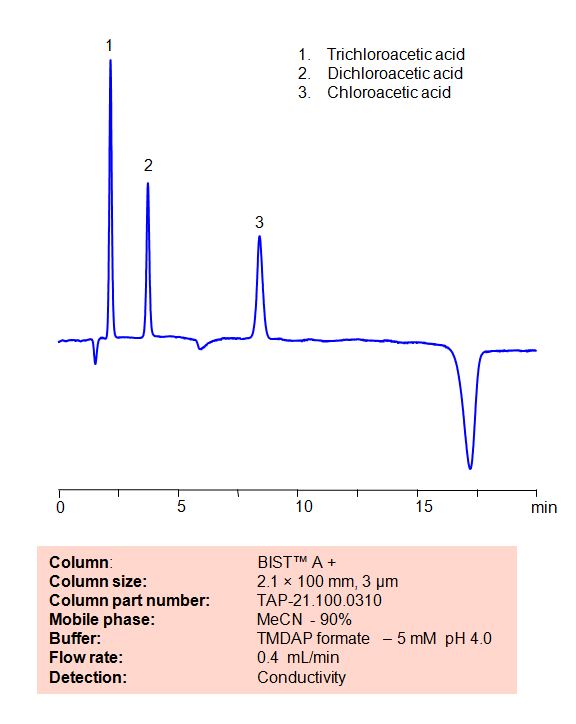
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Chloroacetic acid, Dichloroacetic acid and Trichloroacetic acid
Chloroacetic acid is a popular building block in organic syntheses. Dichloroacetic acid and Trichloroacetic acid are frequently used in cosmetic treatments to remove tattos and in chemical peels, as well as topical medication for the ablation of warts. Using SIELC’s newly introduced BIST™ method, a mixture of these three aicds can be separated on a negatively-charged, cation-exchange BIST™ A+ column, contrary to conventional chromatographic wisdom. There are two keys to this retention method: 1) a multi-charged, positive buffer, such as N,N,N’,N’-Tetramethyl-1,3-propanediamine (TMDAP), which acts as a bridge, linking the negatively-charged anion analytes to the negatively-charged column surface and 2) a mobile phase consisting mostly of organic solvent (such as MeCN) to minimize the formation of a solvation layer around the charged analytes. Other positively-charged buffers that can generate BIST™ include Calcium acetate and Magnesium acetate. Using this new and unique analysis method, these anions can be separated, retained, and detected with a Conductivity Detector.
Condition
| Column | BIST™ A+, 2.1×100 mm, 3 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 90% |
| Buffer | TMDAP ( N,N,N’,N’-Tetramethyl-1,3-diaminopropane) formate – 5 mM pH 4.0 |
| Flow Rate | 0.4 ml/min |
| Detection | Conductivity |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Acid, Carboxylic acid, Haloacetic acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Chloroacetic acid, Dichloroacetic acid and Trichloroacetic acid |
Application Column
BIST A+
BIST™ columns offer a unique and effective way to achieve separations that were traditionally challenging or even impossible with other HPLC columns. With the use of a special mobile phase, these ion exchange columns provide very strong retention for analytes with the same charge polarity as the stationary phase, unlocking new chromatography applications. What makes BIST™ columns stand out is their proprietary surface chemistry, which results in superior selectivity, resolution, and sensitivity. These columns offer a simple, efficient solution for a variety of analytical challenges, making them an excellent choice for researchers and analysts across many different fields. To learn more about the technology that powers BIST™ columns and to explore related applications, check out https://BIST.LC.
Select optionsDichloroacetic acid
Trichloroacetic acid

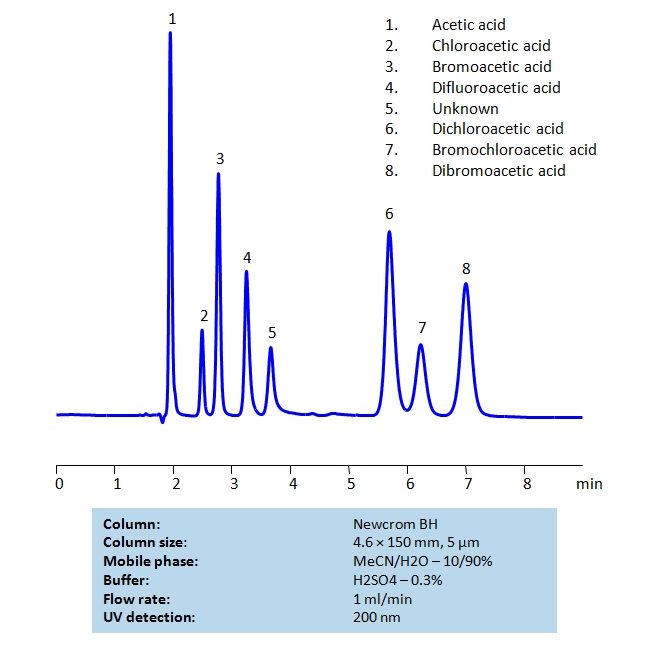
HPLC Separation of Bromoacetic and Chloroacetic Acids on Newcrom BH Column
June 17, 2020
HPLC Method for Difluoroacetic acid, Dichloroacetic acid, Dibromoacetic acid, Acetic Acid, Bromoacetic acid, Chloroacetic acid, Bromochloroacetic acid on Newcrom BH by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Difluoroacetic acid, Dichloroacetic acid, Dibromoacetic acid, Acetic Acid, Bromoacetic acid, Chloroacetic acid, Bromochloroacetic acid.
Acetic acid and its various chloro- and bromo- forms are widely used in organic chemistry. Their similar structure makes the acids difficult to retain and separate on reverse-phase HPLC columns. By using Newcrom BH mixed-mode column which also has ion-exchange properties, the separation can be achieved with a simple isocratic method and relatively short time with a mobile phase of acetonitrile (ACN), water and sulfuric acid (H2SO4) buffer. UV detection at 200nm.
| Column | Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 10/90% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.3% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200nm |
| Class of Compounds | Acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Difluoroacetic acid, Dichloroacetic acid, Dibromoacetic acid, Acetic Acid, Bromoacetic acid, Chloroacetic acid, Bromochloroacetic acid |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Bromoacetic acid
Bromochloroacetic acid
Chloroacetic acid
Dibromoacetic acid
Dichloroacetic acid
Difluoroacetic acid

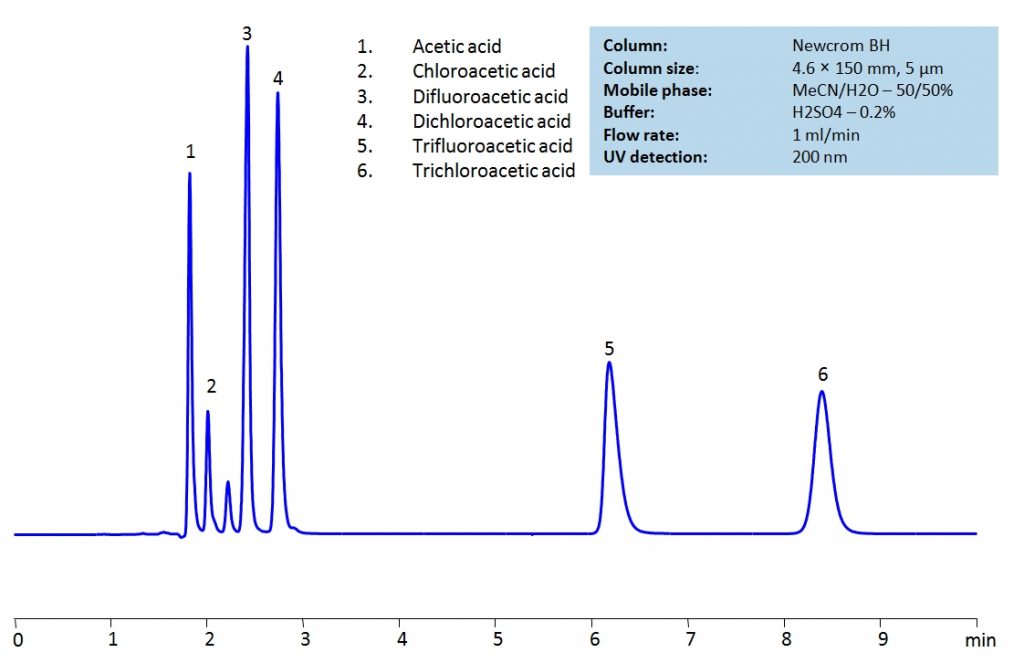
HPLC Separation of Acetic acid, Chloroacetic acid, Dichloroacetic acid, Trifluoroacetic acid, Trichloroacetic acid
May 20, 2020
HPLC Method for TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid), Acetic Acid, Chloroacetic acid, Dichloroacetic acid, Trichloroacetic acid, Difluoroacetic acid on Newcrom BH by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid), Acetic Acid, Chloroacetic acid, Dichloroacetic acid, Trichloroacetic acid, Difluoroacetic acid.
Acetic Acid is the second simplest carboxylic acid with the chemical formula CH3COOH. It is well known for being the active ingredient in vinegar, leading to the belief that it is the earliest mass produced acid, dating back to 3BC. Outside of it’s use in food and household matters, it is also used in production of vinyl acetate and cellulose acetate.
Chloroacetic Acid, also known as monochloroacetic acid (MCA), is a very toxic acid with the chemical formula ClCH2CO2H. It is most often used in the production of other chemicals such as phenoxy herbicides, carboxymethyl cellulose, and carboxymethyl starch. It is considered extremely hazardous as it can cause burns on skin and eyes as well as be fatal if inhaled or swallowed.
Difluoroacetic Acid (DFA) is a dihalogenocarboxylic acid with the chemical formula CHF2COOH. As a solution, it quickly dissociates to form difluoroacetate ions.
Dichloroacetic Acid (DCA), also known as bichloroacetic acid (BCA), is a highly corrosive acid with the chemical formula C2H2Cl2O2. While it is used in personal care items and disinfectants, it is a known carcinogen. Despite that, research shows that it may be a plausible treatment for certain cancers.
Trifluoroacetic Acid (TFA) is a synthetic organofluorine acid with the chemical formula C2HF3O2. It is corrosive and toxic to aquatic life and mammals, causing severe irritation and burns to skin, eyes, and the respiratory tract. Not only that, TFA is also highly mobile and persistent, leading to high retention of it in soil and water. Determination of it’s threat level on the environmental and health levels are still ongoing.
Trichloroacetic Acid (TCA), also known as trichloroethanoic acid, is an analogue of acetic acid with the chemical formula C2HCl3O2. It is often used as a skin peeling treatment to exfoliate damaged skin and encourage collagen production. In laboratory research, it is used for precipitating proteins and to extract and prepare standards for ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) assays.
Acetic acid and its substitution derivatives, chloroacetic acid, dichloroacetic acid, trichloroacetic acid, difluoroacetic acid and trifluoroacetic acid, are heavily used as building blocks for more complex compounds in organic synthesis. All six acids can be isocratically separated in HPLC using Newcrom BH mixed-mode column with acetonitrile (ACN) and water mobile phase with sulfuric acid (H2SO4) as buffer and UV detected at 200nm.
| Column | Newcrom BH, 3.2 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 50/50% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200nm |
| Class of Compounds | Acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid), Acetic Acid, Chloroacetic acid, Dichloroacetic acid, Trichloroacetic acid, Difluoroacetic acid |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 3.2 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Chloroacetic acid
Dichloroacetic acid
Difluoroacetic acid
TFA (Trifluoroacetic Acid)
Trichloroacetic acid

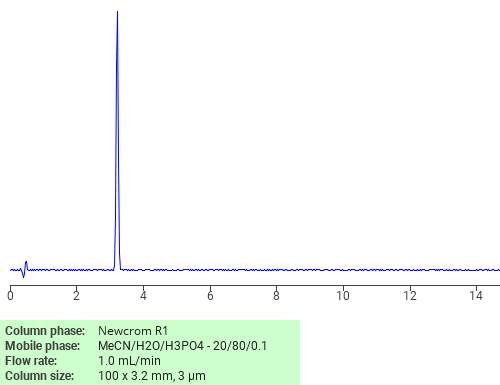
Separation of Chloroacetic acid on Newcrom R1 HPLC column
February 16, 2018
Chloroacetic acid can be analyzed by this reverse phase (RP) HPLC method with simple conditions. The mobile phase contains an acetonitrile (MeCN), water, and phosphoric acid. For Mass-Spec (MS) compatible applications the phosphoric acid needs to be replaced with formic acid. Smaller 3 µm particles columns available for fast UPLC applications. This liquid chromatography method is scalable and can be used for isolation impurities in preparative separation. It also suitable for pharmacokinetics.
Application Column
Newcrom R1
The Newcrom columns are a family of reverse-phase-based columns. Newcrom A, AH, B, and BH are all mixed-mode columns with either positive or negative ion-pairing groups attached to either short (25 Å) or long (100 Å) ligand chains. Newcrom R1 is a special reverse-phase column with low silanol activity.
Select options