| CAS Number | 461-58-5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | NH2(NH)CNHCN |
| Molecular Weight | 84.08 |
| InChI Key | QGBSISYHAICWAH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -1.2 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
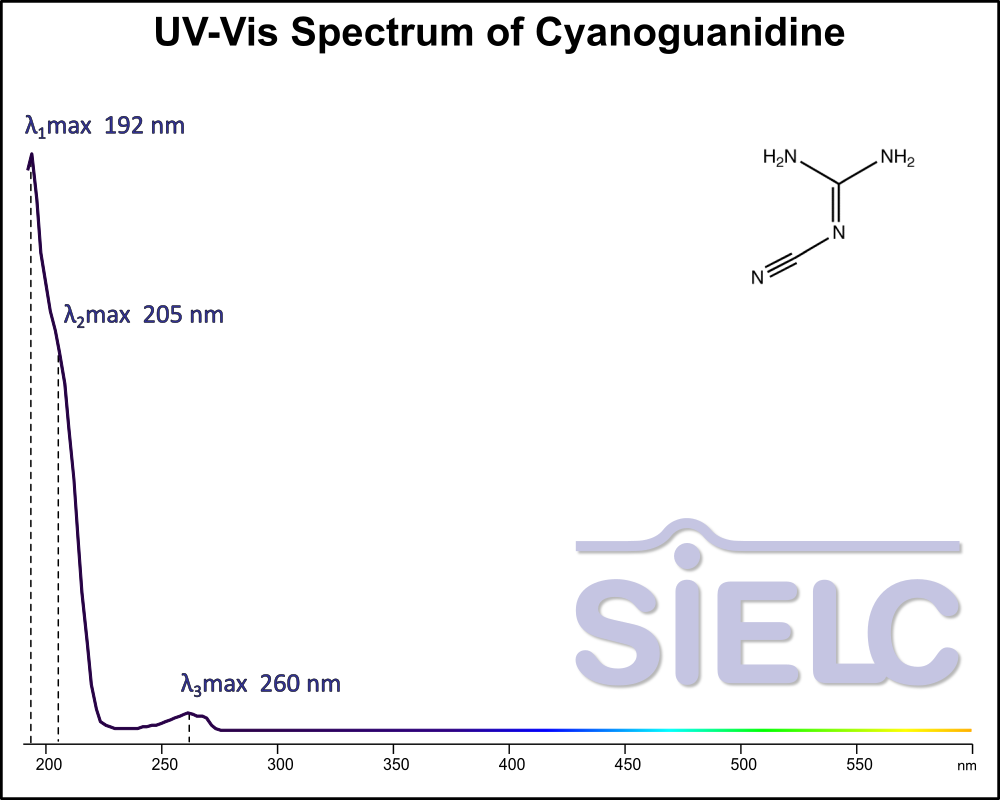
Uv-Vis Spectrum of Cyanoguanidine
January 30, 2026
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Dicyandiamide check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

HPLC Method for Analysis of Cyanamide, Dicyandiamide and Urea on Primesep S Column with Varies Mobile Phases
May 1, 2023
Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
HPLC Method for Analysis of Cyanamide, Dicyandiamide, Urea on Primesep S Column by SIELC Technologies
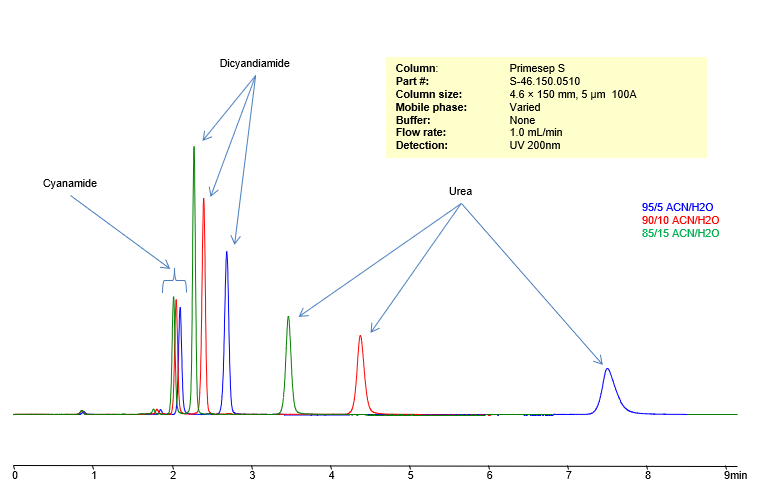
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Cyanamide, Dicyandiamide, Urea
Cyanamide (H2CN2) is a highly reactive and toxic compound used in the production of fertilizers, pharmaceuticals, and other chemicals. It can be used as a soil fumigant to control pests and weeds.
Dicyandiamide (C2H4N4) is a white crystalline solid that is often used as a slow-release fertilizer. It is also used in the production of pharmaceuticals, dyes, and resins. Dicyandiamide can also be used as a nitrification inhibitor in agriculture to reduce the loss of nitrogen from the soil.
Urea (CO(NH2)2) is a white crystalline solid that is widely used as a fertilizer due to its high nitrogen content. It is also used in the production of plastics, resins, and adhesives. Urea is also used in the manufacturing of animal feed, and as a raw material in the production of many industrial chemicals. In addition, it is also used as a component in certain skin creams and cosmetics due to its moisturizing properties.
Using a Primesep S normal-phase column and a mobile phase consisting of water and Acetonitrile (MeCN) with no buffer, Cyanamide, Dicyandiamide and Urea can be retained, separated, and analyzed. This analysis method can be UV detected at 200 nm.
Condition
| Column | Primesep S, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN |
| Buffer | No |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200 nm |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Amide, Urea |
| Analyzing Compounds | Cyanamide, Dicyandiamide, Urea |
Application Column
Primesep S
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Dicyandiamide
Urea

HPLC Method for Analysis of Cyanamide, Dicyandiamide and Urea on Primesep S Column
April 28, 2023
Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
HPLC Method for Analysis of Cyanamide, Dicyandiamide, Urea on Primesep S Column by SIELC Technologies
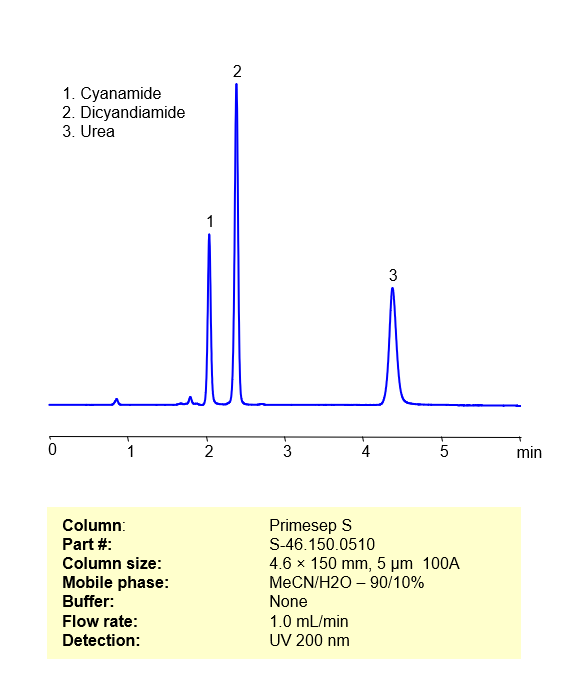
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Cyanamide, Dicyandiamide, Urea
Cyanamide (H2CN2) is a highly reactive and toxic compound used in the production of fertilizers, pharmaceuticals, and other chemicals. It can be used as a soil fumigant to control pests and weeds.
Dicyandiamide (C2H4N4) is a white crystalline solid that is often used as a slow-release fertilizer. It is also used in the production of pharmaceuticals, dyes, and resins. Dicyandiamide can also be used as a nitrification inhibitor in agriculture to reduce the loss of nitrogen from the soil.
Urea (CO(NH2)2) is a white crystalline solid that is widely used as a fertilizer due to its high nitrogen content. It is also used in the production of plastics, resins, and adhesives. Urea is also used in the manufacturing of animal feed, and as a raw material in the production of many industrial chemicals. In addition, it is also used as a component in certain skin creams and cosmetics due to its moisturizing properties.
Using a Primesep S normal-phase column and a mobile phase consisting of water and Acetonitrile (MeCN) with no buffer, Cyanamide, Dicyandiamide and Urea can be retained, separated, and analyzed. This analysis method can be UV detected at 200 nm.
Condition
| Column | Primesep S, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 90% |
| Buffer | No |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200 nm |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Amide, Urea |
| Analyzing Compounds | Cyanamide, Dicyandiamide, Urea |
Application Column
Primesep S
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Dicyandiamide
Urea

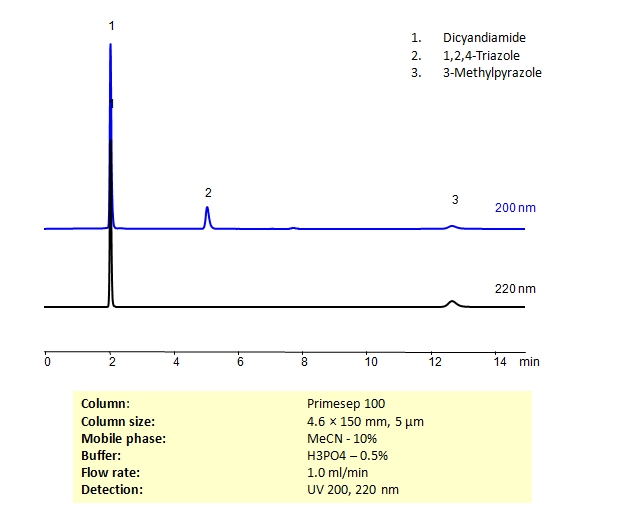
HPLC Separation of Dicyandiamide, 1,2,4-Triazole, 3-Methylpyrazole on Primesep 100 Column
December 20, 2019
HPLC Method for Dicyandiamide, 1,2,4-Triazole, 3-Methylpyrazole on Primesep 100 by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Dicyandiamide, 1,2,4-Triazole, 3-Methylpyrazole
Dicyandiamide, or cyanoguanidine, is used as a curing agent for epoxy resins. 1,2,4-triazole, is a heterocycle used primarily as an antifungal but has other uses in the pharmaceutical industry as well. 3-methylpyrazole is used in nitrogen fertilizers. All three compounds are structurally similar and can be separated in HPLC using Primesep 100 reverse-phase (RP) mixed-mode cation-exchange (CX) column using acetonitrile (ACN) and water mobile phase with phosphoric acid buffer and UV detected at 200nm and 220nm.
| Column | Primesep 100, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 10% |
| Buffer | H3PO4 – 0.5% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200, 220 nm |
| Class of Compounds | Heterocycle, Amine, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Dicyandiamide, 1,2,4-Triazole, 3-Methylpyrazole |
Application Column
Primesep 100
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
3-Methylpyrazole
Dicyandiamide

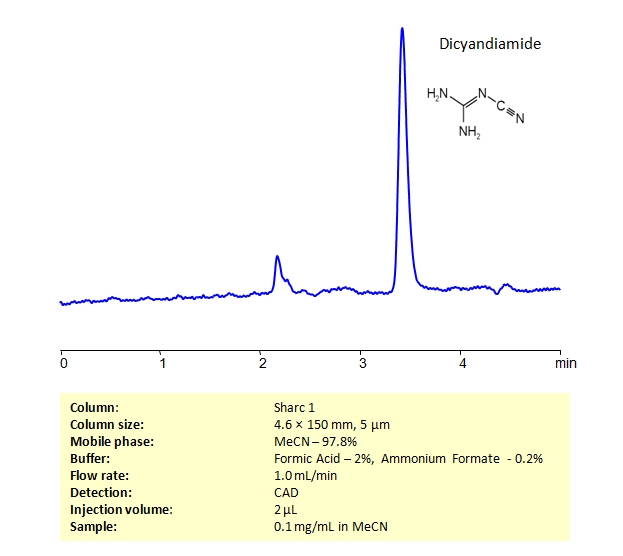
HPLC Determination of Dicyandiamide on Sharc 1 Column
November 22, 2019
HPLC Method for Dicyandiamide on SHARC 1 by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Dicyandiamide
Dicyandiamide, also known as cyanoguanidine, has a C₂H₄N₄ chemical formula. It is a white crystalline powder that has a variety of uses from agricultural to mechanical. Though, typically it is found in fertilizers as a nitrification inhibitor. It slows down nitrogen release and and reduces losses from soil.
Dicyandiamide can be retained and analyzed using the SHARC 1 stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water and acetonitrile (MeCN) with a triethanolamine buffer. Detection is performed using CAD.
| Column | SHARC 1, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 97.8% |
| Buffer | AmFm 0.2%, Formic Acid – 2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | CAD (Corona) MS- compatible mobile phase |
| Class of Compounds | Amide, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Dicyandiamide |
Application Column
SHARC 1
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended