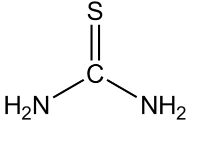
| CAS Number | 62-56-6 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | CH4N2S |
| Molecular Weight | 76.120 |
| InChI Key | UMGDCJDMYOKAJW-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -1.08 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
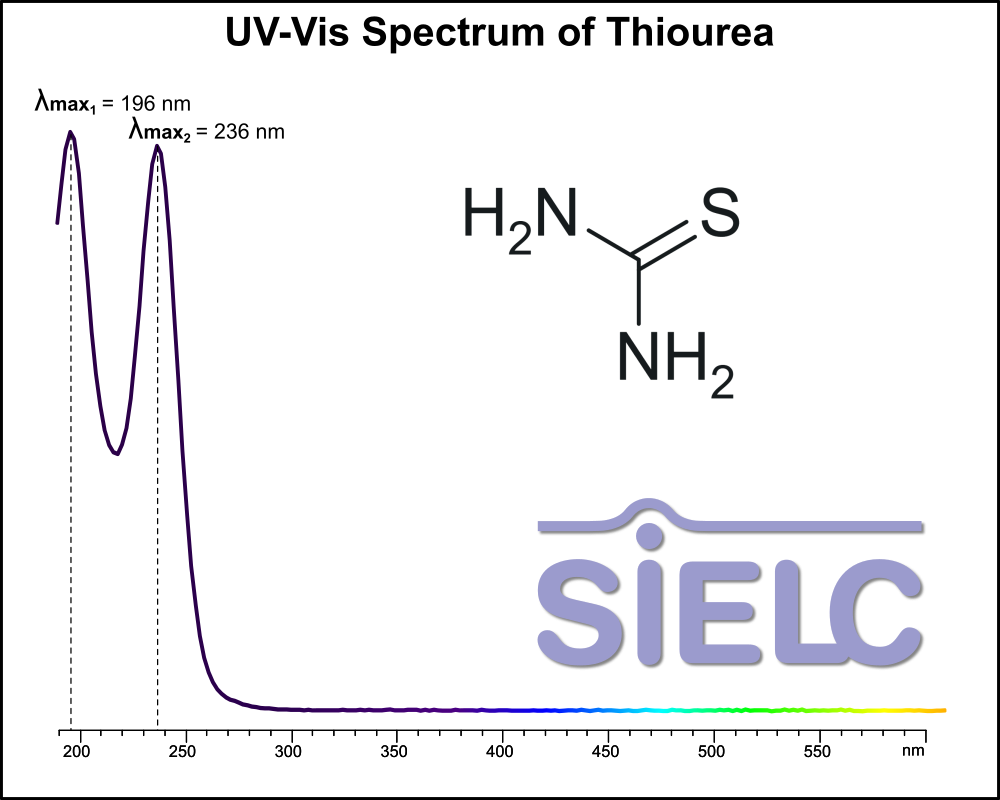
UV-Vis Spectrum of Thiourea
July 11, 2025
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Thiourea check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

HPLC Method for Separation of Thiourea, Thiouracil (TU), Methylthiouracil (MTU) and Propylthiouracil (PTU) on Primesep P
August 4, 2023
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
HPLC Method for Separation of Thiourea, Thiouracil, Methylthiouracil, Propylthiouracil on Primesep P Column by SIELC Technologies
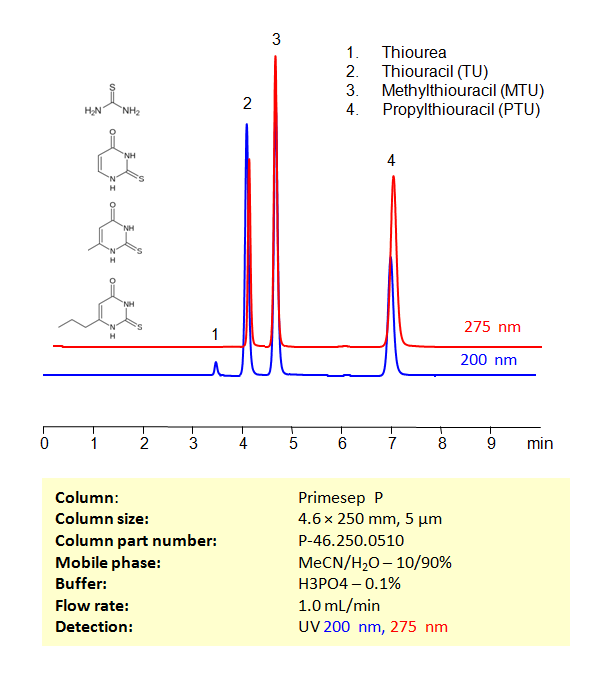
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Thiourea, Thiouracil, Methylthiouracil, Propylthiouracil
Thiourea, Thiouracil (TU), Methylthiouracil (MTU), and Propylthiouracil (PTU) are organic compounds that belong to the class of thioureas, which are characterized by the presence of a thiocarbonyl functional group (C=S).
Each of these compounds has different properties and uses due to the different structures and substitution patterns on the thiourea core. They are all important molecules in both the field of chemistry and medicine.
Propylthiouracil (PTU) is a medication primarily used to treat hyperthyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone. It belongs to a class of drugs called thioureas and specifically to a subgroup known as thioamides.
PTU works by reducing the amount of thyroid hormone produced by the thyroid gland. It inhibits the enzyme thyroid peroxidase, preventing the iodination of tyrosine residues in thyroglobulin and the coupling of these iodotyrosine residues, which are key steps in the synthesis of thyroid hormones.
Additionally, PTU has a unique property among thioamides – it also inhibits the peripheral conversion of thyroxine (T4) to triiodothyronine (T3), the more potent form of thyroid hormone.
The drug is usually taken orally and it’s often used for Graves’ disease, an autoimmune disorder that is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. However, like all medications, PTU has potential side effects. The most serious one is liver damage, which can be fatal. Because of this, PTU is typically used when other treatments cannot be used, either because of allergies, during early pregnancy, or in preparation for thyroidectomy.
Methylthiouracil (MTU) is a thioamide drug, similar to propylthiouracil (PTU), and is used in the treatment of hyperthyroidism. The drug works by inhibiting the synthesis of thyroid hormones, thereby reducing the excessive production of these hormones seen in conditions such as Graves’ disease.
The compound is a derivative of thiouracil, with a methyl group attached to the molecule. Its chemical formula is C5H6N2S.
While MTU can be effective in managing hyperthyroidism, like other thioamide drugs, it also has the potential for serious side effects. The most notable is agranulocytosis, a potentially life-threatening decrease in the number of white blood cells. This side effect, although rare, requires immediate medical attention. More common side effects can include rash, fever, joint pain, and gastrointestinal issues. Because of the risk of side effects, patients on MTU are usually closely monitored by their healthcare provider.
Thiourea is a versatile chemical compound with the formula (NH2)2CS. It is structurally similar to urea, except that the oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur atom. It is a white crystalline solid when pure.
Thiourea is used in a variety of applications. It is a reagent in organic synthesis, often used in the toning of silver-gelatin photography prints, as a component of hair preparations and bleaches, and as a radioprotective agent in cancer therapy.
In agriculture, thiourea is used as a soil treatment agent to promote germination and stimulate flowering and fruiting.
Using a Primesep P Mixed-mode phase column and a mobile phase consisting of water and Acetonitrile (MeCN) with Phosphoric acid as a buffer, Thiourea, Thiouracil (TU), Methylthiouracil (MTU) And Propylthiouracil (PTU) can be retained, separated, and analyzed. This analysis method can be UV detected at 200 nm.
Condition
| Column | Primesep P, 4.6 x 250 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN -10% |
| Buffer | H3PO4 – 0.1% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200, 275 nm |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Amide, Urea |
| Analyzing Compounds | Thiourea, Thiouracil, Methylthiouracil, Propylthiouracil |
Application Column
Primesep P
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 250 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Propylthiouracil
Thiouracil
Thiourea

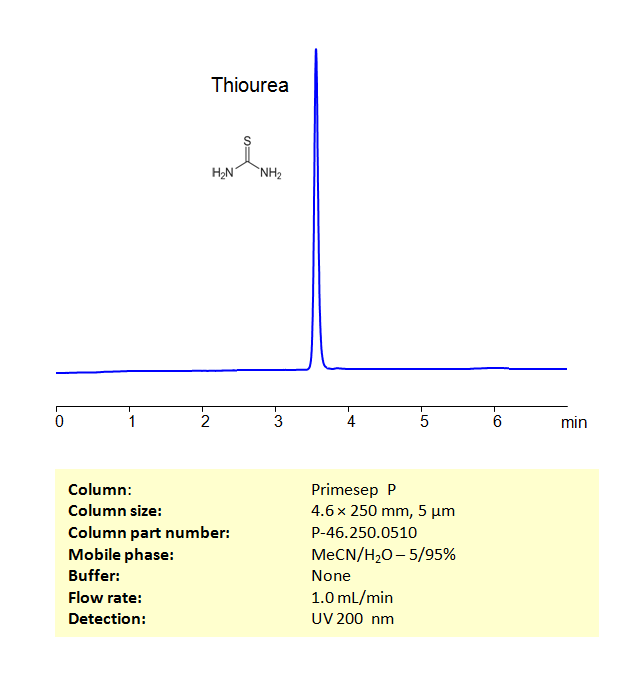
HPLC Method for Analysis of Thiourea on Primesep P Column
July 25, 2023
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
HPLC Method for Analysis of Thiourea on Primesep P by SIELC Technologies
Thiourea is a versatile chemical compound with the formula (NH2)2CS. It is structurally similar to urea, except that the oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur atom. It is a white crystalline solid when pure.
Thiourea is used in a variety of applications. It is a reagent in organic synthesis, often used in the toning of silver-gelatin photography prints, as a component of hair preparations and bleaches, and as a radioprotective agent in cancer therapy.
In agriculture, thiourea is used as a soil treatment agent to promote germination and stimulate flowering and fruiting.
Using a Primesep P Mixed-mode phase column and a mobile phase consisting of water and Acetonitrile (MeCN) with no buffer, thiourea can be retained and analyzed. This analysis method can be UV detected at 200 nm.
LOD was determined for this combination of instrument, method, and analyte, and it can vary from one laboratory to another even when the same general type of analysis is being performed.
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Thiourea
Condition
| Column | Primesep P, 4.6 x 250 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 5/95% |
| Buffer | None |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200 nm |
| Peak Retention Time | 3.56 min |
| Sample concentration | 0.02 mg/ml |
| Injection volume | 1 µl |
| LOD | UV 1 ppb |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Thioureas |
| Analyzing Compounds | Thiourea |
Application Column
Primesep P
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 250 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

HPLC Method for Separation of Thiourea and Dimethylthiourea (DMTU) on Primesep P Column
July 25, 2023
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
HPLC Method for Separation of Thiourea, Dimethylthiourea on Primesep P Column by SIELC Technologies
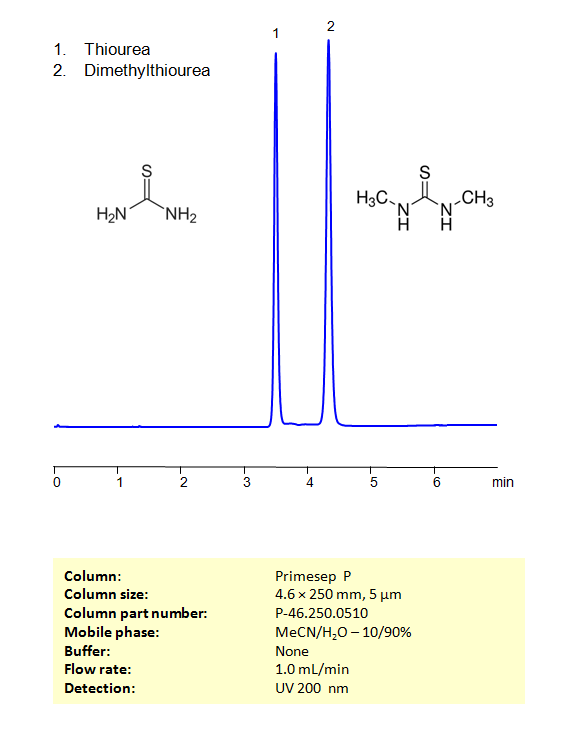
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Thiourea, Dimethylthiourea
Dimethylthiourea is an organic compound containing two methyl groups attached to a thiourea molecule. The chemical formula is (CH3)2NCSNH2. Like other thiourea derivatives, dimethylthiourea has a range of uses in various fields, including research and industrial applications.
In research, it’s often used due to its properties as a good hydrogen bond donor and acceptor, allowing it to participate in a variety of reactions. For example, it can be used as a reducing agent in some types of reactions. It also has some interesting properties in terms of its electrical conductivity and its ability to absorb certain types of radiation, which make it useful in some niche applications.
Thiourea is a versatile chemical compound with the formula (NH2)2CS. It is structurally similar to urea, except that the oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur atom. It is a white crystalline solid when pure.
Thiourea is used in a variety of applications. It is a reagent in organic synthesis, often used in the toning of silver-gelatin photography prints, as a component of hair preparations and bleaches, and as a radioprotective agent in cancer therapy.
In agriculture, thiourea is used as a soil treatment agent to promote germination and stimulate flowering and fruiting.
Using a Primesep P Mixed-mode phase column and a mobile phase consisting of water and Acetonitrile (MeCN) with no buffer, Thiourea and Dimethylthiourea can be retained, separated, and analyzed. This analysis method can be UV detected at 200 nm.
Condition
| Column | Primesep P, 4.6 x 250 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN -10% |
| Buffer | No |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200 nm |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Amide, Urea |
| Analyzing Compounds | Thiourea, Dimethylthiourea |
Application Column
Primesep P
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 250 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Thiourea

HPLC Method for Separation of Urea and Thiourea on Primesep S Column
July 25, 2023
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
HPLC Method for Separation of Thiourea, Urea on Primesep S Column by SIELC Technologies
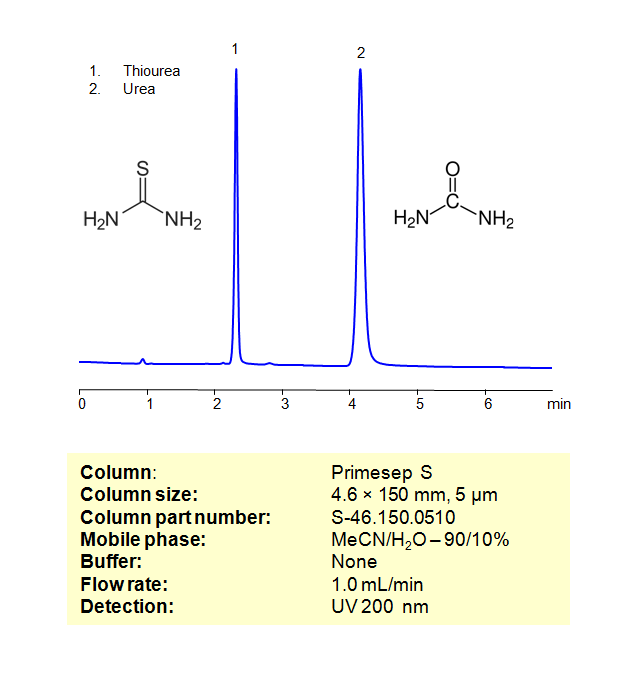
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Thiourea, Urea
Urea (CO(NH2)2) is a white crystalline solid that is widely used as a fertilizer due to its high nitrogen content. It is also used in the production of plastics, resins, and adhesives. Urea is also used in the manufacturing of animal feed, and as a raw material in the production of many industrial chemicals. In addition, it is also used as a component in certain skin creams and cosmetics due to its moisturizing properties.
Thiourea is a versatile chemical compound with the formula (NH2)2CS. It is structurally similar to urea, except that the oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur atom. It is a white crystalline solid when pure.
Thiourea is used in a variety of applications. It is a reagent in organic synthesis, often used in the toning of silver-gelatin photography prints, as a component of hair preparations and bleaches, and as a radioprotective agent in cancer therapy.
In agriculture, thiourea is used as a soil treatment agent to promote germination and stimulate flowering and fruiting.
Using a Primesep S normal-phase column and a mobile phase consisting of water and Acetonitrile (MeCN) with no buffer, Thiourea and Urea can be retained, separated, and analyzed. This analysis method can be UV detected at 200 nm.
Condition
| Column | Primesep S, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN -90% |
| Buffer | No |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200 nm |
Description
Application Column
Primesep S
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Urea

HILIC Retention of Polar Compounds on Primesep S
August 22, 2010
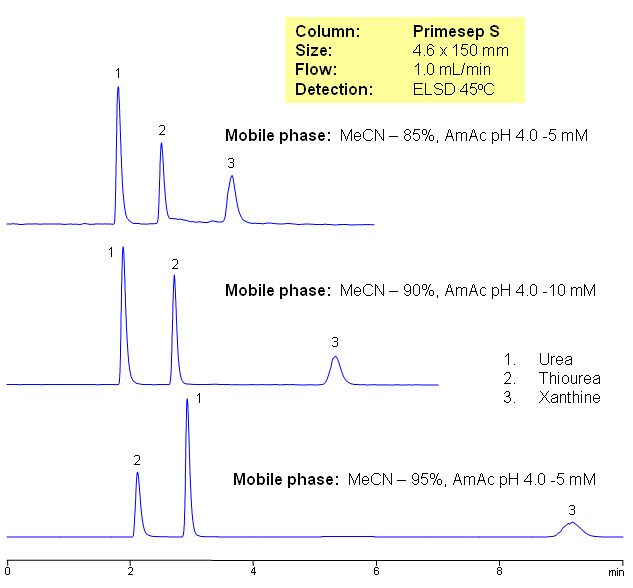
Three neutral polar compounds (urea, thiourea, and xanthine) are separated on a Primesep S HILIC cation-exchange column with LC/MS compatible mobile phase. The retention time is controlled by the amount of acetonitrile in the mobile phase.
Application Column
Primesep S
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsUrea
Xanthine