Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
HPLC Method for Separation of Thiourea, Thiouracil, Methylthiouracil, Propylthiouracil on Primesep P Column by SIELC Technologies
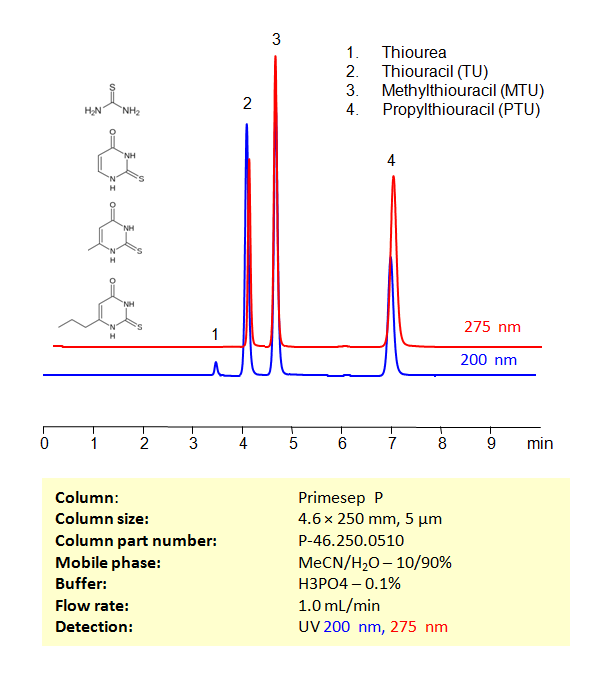
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Thiourea, Thiouracil, Methylthiouracil, Propylthiouracil
Thiourea, Thiouracil (TU), Methylthiouracil (MTU), and Propylthiouracil (PTU) are organic compounds that belong to the class of thioureas, which are characterized by the presence of a thiocarbonyl functional group (C=S).
Each of these compounds has different properties and uses due to the different structures and substitution patterns on the thiourea core. They are all important molecules in both the field of chemistry and medicine.
Propylthiouracil (PTU) is a medication primarily used to treat hyperthyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone. It belongs to a class of drugs called thioureas and specifically to a subgroup known as thioamides.
PTU works by reducing the amount of thyroid hormone produced by the thyroid gland. It inhibits the enzyme thyroid peroxidase, preventing the iodination of tyrosine residues in thyroglobulin and the coupling of these iodotyrosine residues, which are key steps in the synthesis of thyroid hormones.
Additionally, PTU has a unique property among thioamides – it also inhibits the peripheral conversion of thyroxine (T4) to triiodothyronine (T3), the more potent form of thyroid hormone.
The drug is usually taken orally and it’s often used for Graves’ disease, an autoimmune disorder that is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. However, like all medications, PTU has potential side effects. The most serious one is liver damage, which can be fatal. Because of this, PTU is typically used when other treatments cannot be used, either because of allergies, during early pregnancy, or in preparation for thyroidectomy.
Methylthiouracil (MTU) is a thioamide drug, similar to propylthiouracil (PTU), and is used in the treatment of hyperthyroidism. The drug works by inhibiting the synthesis of thyroid hormones, thereby reducing the excessive production of these hormones seen in conditions such as Graves’ disease.
The compound is a derivative of thiouracil, with a methyl group attached to the molecule. Its chemical formula is C5H6N2S.
While MTU can be effective in managing hyperthyroidism, like other thioamide drugs, it also has the potential for serious side effects. The most notable is agranulocytosis, a potentially life-threatening decrease in the number of white blood cells. This side effect, although rare, requires immediate medical attention. More common side effects can include rash, fever, joint pain, and gastrointestinal issues. Because of the risk of side effects, patients on MTU are usually closely monitored by their healthcare provider.
Thiourea is a versatile chemical compound with the formula (NH2)2CS. It is structurally similar to urea, except that the oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur atom. It is a white crystalline solid when pure.
Thiourea is used in a variety of applications. It is a reagent in organic synthesis, often used in the toning of silver-gelatin photography prints, as a component of hair preparations and bleaches, and as a radioprotective agent in cancer therapy.
In agriculture, thiourea is used as a soil treatment agent to promote germination and stimulate flowering and fruiting.
Using a Primesep P Mixed-mode phase column and a mobile phase consisting of water and Acetonitrile (MeCN) with Phosphoric acid as a buffer, Thiourea, Thiouracil (TU), Methylthiouracil (MTU) And Propylthiouracil (PTU) can be retained, separated, and analyzed. This analysis method can be UV detected at 200 nm.
Condition
| Column | Primesep P, 4.6 x 250 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN -10% |
| Buffer | H3PO4 – 0.1% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200, 275 nm |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Amide, Urea |
| Analyzing Compounds | Thiourea, Thiouracil, Methylthiouracil, Propylthiouracil |
Application Column
Primesep P
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 250 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Propylthiouracil
Thiouracil
Thiourea





