| CAS Number | 68-35-9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H10N4O2S |
| Molecular Weight | 260.28 |
| InChI Key | SEEPANYCNGTZFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -0.1 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
UV-Vis Spectrum of Sulfadiazine
July 19, 2024
Access the UV-Vis Spectrum SIELC Library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

HPLC Separation of Antibiotics on Newcrom A Column
June 11, 2020
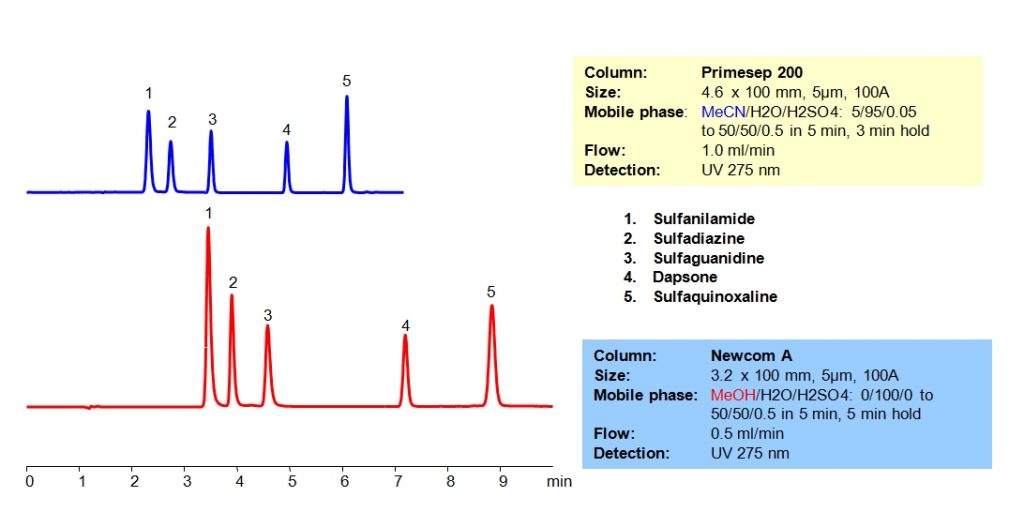
HPLC Method for Sulfanilamide, Sulfadiazine, Dapsone, Sulfaguanidine, Sulphaquinoxaline on Newcrom A by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Sulfanilamide, Sulfadiazine, Dapsone, Sulfaguanidine, Sulphaquinoxaline.
Antibiotics are widely used for treatment and prevention of bacterial infections.
Sulfanilamide is a sulfonamide antibacterial drug with the chemical formula C6H8N2O2S. It’s height of use was during World War II to treat and prevent the spread of infections among the Allies. Due to later discovery of more effective antibiotics, it is no longer as widely used. You can find detailed UV spectra of Sulfanilamide and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
Sulfadiazine is a sulfonamide antibiotic with the chemical formula C10H10N4O2S. It is the treatment of choice for toxoplasmosis and is considered the second-line treatment against numerous other infections. It works by blocking the synthesis of folic acid in bacteria, which prevents cell reproduction. Sulfadiazine can be either taken orally or applied topically. You can find detailed UV spectra of Sulfadiazine and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
Sulfaguanidine is a sulfonamide antibiotic with the chemical formula C7H10N4O2S. It is a guanidine derivative of sulfanilamide that works through inhibiting the synthesis of folic acid in bacteria. Most often, it is used to treat Bacillary dysentery.
Dapsone is a sulfone antibiotic with anti-inflammatory properties. As a gel, it is sold under the brand name Aczone as acne treatment, but it can also be used as part of treatment for other skin conditions including leprosy and dermatitis herpetiformis. It’s chemical formula is C12H12N2O2S.
Sulfaquinoxaline is a sulfonamide antibiotic that is typically used in veterinary medicine. It is used to treat Coccidiosis in cattle and sheep, as well as a variety infections in poultry. It is deemed not suitable for human use. It’s chemical formula is C14H12N4O2S.
Various antibiotics, particularly those with a sulfanilamide structure, were separated in HPLC using mixed-mode columns with varying strengths of ion-pairing groups. Methanol can be used in the mobile phase on Newcrom A column. The antibiotics were resolved on both columns with a gradient mobile phase consisting of acetonitrile (ACN) or methanol (MeOH), water and sulfuric acid (H2SO4) buffer. UV detection at 275nm.
| Column | Newcrom A, 3.2 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeOH Gradient |
| Buffer | H2SO4 Gradient |
| Flow Rate | 0.5 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 275 nm |
| Class of Compounds | Drugs, Antibiotics |
| Analyzing Compounds | Sulfanilamide, Sulfadiazine, Dapsone, Sulfaguanidine, Sulphaquinoxaline |
Application Column
Newcrom A
Column Diameter: 3.2 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Sulfadiazine
Sulfaguanidine
Sulfanilamide
Sulphaquinoxaline

HPLC Separation of Antibiotics on Primesep 200 Column
June 6, 2020
HPLC Method for Sulfanilamide, Sulfadiazine, Sulfaguanidine, Dapsone on Primesep 200 by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Sulfanilamide, Sulfadiazine, Sulfaguanidine, Dapsone.
Sulfanilamide is a sulfonamide antibacterial drug with the chemical formula C6H8N2O2S. It’s height of use was during World War II to treat and prevent the spread of infections among the Allies. Due to later discovery of more effective antibiotics, it is no longer as widely used. You can find detailed UV spectra of Sulfanilamide and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
Sulfadiazine is a sulfonamide antibiotic with the chemical formula C10H10N4O2S. It is the treatment of choice for toxoplasmosis and is considered the second-line treatment against numerous other infections. It works by blocking the synthesis of folic acid in bacteria, which prevents cell reproduction. Sulfadiazine can be either taken orally or applied topically. You can find detailed UV spectra of Sulfadiazine and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
Sulfaguanidine is a sulfonamide antibiotic with the chemical formula C7H10N4O2S. It is a guanidine derivative of sulfanilamide that works through inhibiting the synthesis of folic acid in bacteria. Most often, it is used to treat Bacillary dysentery.
Dapsone is a sulfone antibiotic with anti-inflammatory properties. As a gel, it is sold under the brand name Aczone as acne treatment, but it can also be used as part of treatment for other skin conditions including leprosy and dermatitis herpetiformis. It’s chemical formula is C12H12N2O2S.
Sulfaquinoxaline is a sulfonamide antibiotic that is typically used in veterinary medicine. It is used to treat Coccidiosis in cattle and sheep, as well as a variety infections in poultry. It is deemed not suitable for human use. It’s chemical formula is C14H12N4O2S.
Antibiotics are widely used for treatment and prevention of bacterial infections. Various antibiotics, particularly those with a sulfanilamide structure, were separated in HPLC using mixed-mode columns with varying strengths of ion-pairing groups. Primesep 200 has weak acidic ion-exchange pairing groups while Newcrom A has strong acidic ion-exchange groups. In addition, methanol can be used in the mobile phase on Newcrom A column. The antibiotics were resolved on both columns with a gradient mobile phase consisting of acetonitrile (ACN) or methanol (MeOH), water and sulfuric acid (H2SO4) buffer. UV detection at 275nm.
| Column | Primesep 200, 4.6 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN Gradient |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.5% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 275 nm |
| Class of Compounds | Drugs, Antibiotics |
| Analyzing Compounds | Sulfanilamide, Sulfadiazine, Sulfaguanidine, Dapsone |
Application Column
Primesep 200
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Sulfadiazine
Sulfaguanidine
Sulfanilamide

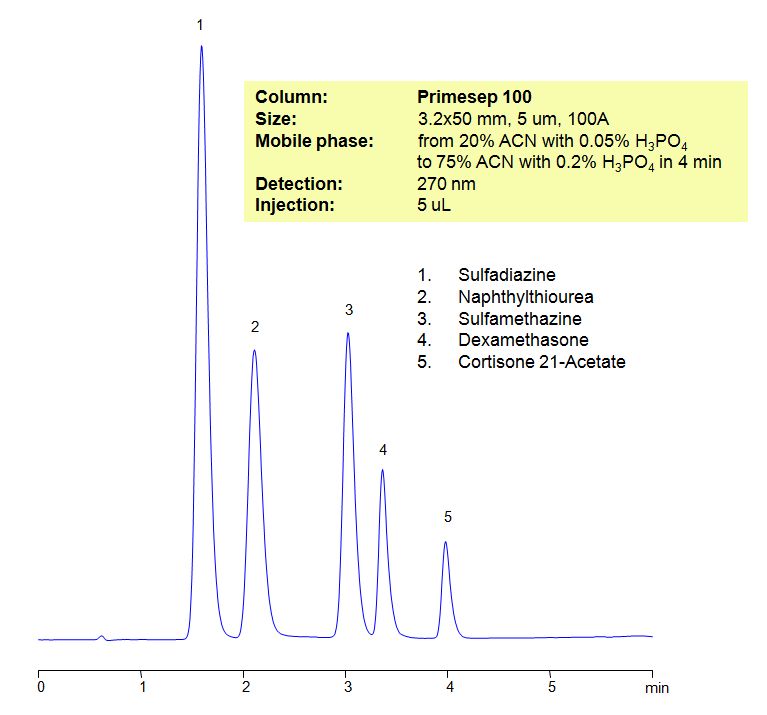
HPLC Method for Analysis of Sulfadiazine, Naphthylthiourea, Sulfamethazine, Dexamethasone, Cortisone 21-Acetate
July 11, 2017
Sulfadiazine is an antibiotic used to prevent rheumatic fever, chancroid, chlamydia and infections by Haemophilus influenzae. There are side effects to the use of the drug which include, but not limited to: nausea, headache, rash, depression.
| Column | Primesep 100, 3.2×50 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN – 20-75%, 4 min |
| Buffer | Gradient H3PO4 – 0.05-0.2%, 4 min |
| Flow Rate | 0.5 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 270 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Sulfadiazine, Naphthylthiourea, Sulfamethazine, Dexamethasone, Cortisone 21-Acetate |
Application Column
Primesep 100
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsDexamethasone
Naphthylthiourea
Sulfadiazine
Sulfamethazine