| CAS Number | 27220-47-9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H15Cl3N2O |
| Molecular Weight | 381.680 |
| InChI Key | LEZWWPYKPKIXLL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 4.81 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
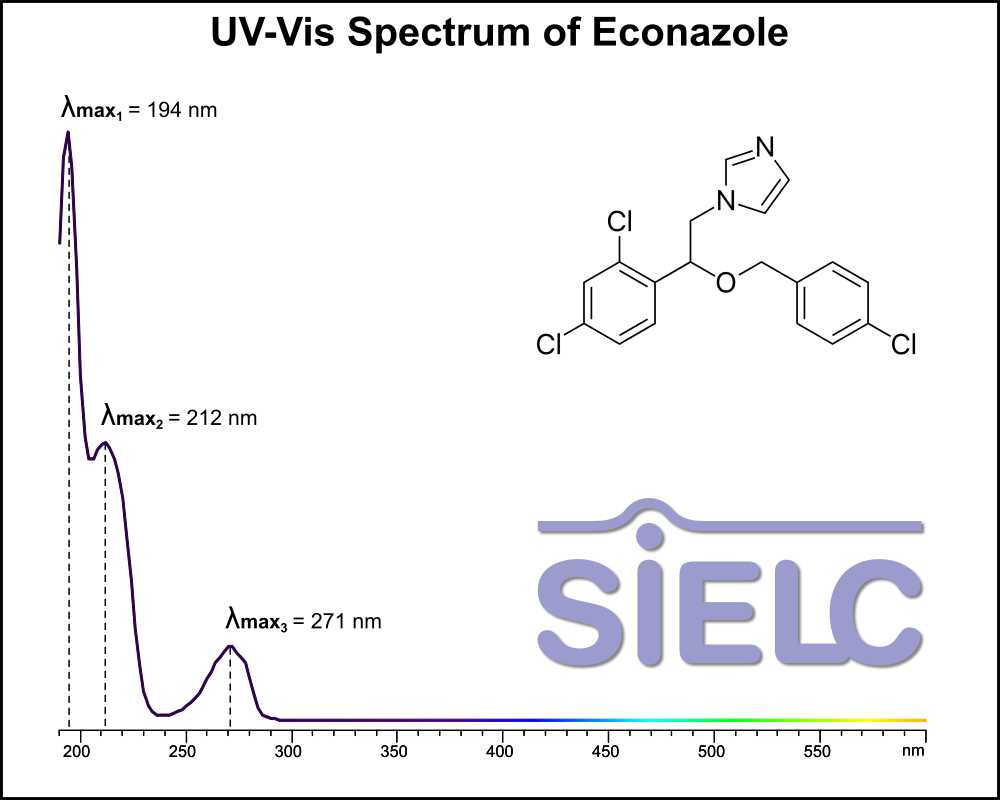
Uv-Vis Spectrum of Econazole
March 9, 2026
Access the UV-Vis Spectrum SIELC Library
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Econazole check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

HPLC Method for Separation of a Mixture of Antifungal Agents on Primesep B Column
September 20, 2023
HPLC Method for Analysis of Antifungal Agents on Primesep B by SIELC Technologies
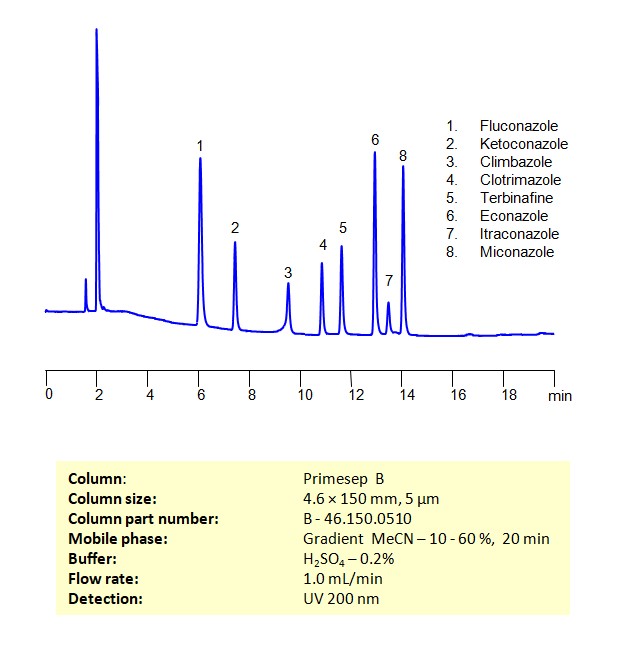
Separation and Analysis of Antifungal Agents on a Primesep B Column Using Gradient HPLC Method
Antifungal agents are drugs used to treat fungal infections. Depending on their mechanism of action and chemical structure, antifungal agents can be categorized into several classes. Here are some of the main classes and examples of antifungal agents:
- Fluconazole: A triazole antifungal mainly used for the treatment and prevention of superficial and systemic fungal infections.
- Ketoconazole: An imidazole antifungal used to treat a wide variety of fungal infections, though its oral use has become less common due to potential side effects. It’s still frequently used topically.
- Climbazole: An imidazole antifungal primarily used in hair care products to treat dandruff.
- Clotrimazole: An imidazole antifungal used to treat various fungal infections including vaginal yeast infections, oral thrush, and ringworm.
- Itraconazole: A triazole antifungal used primarily to treat a variety of systemic fungal infections.
- Terbinafine: This compound belongs to the allylamine class. It’s mainly used to treat fungal infections of the nails and skin, like athlete’s foot and ringworm.
- Econazole: An imidazole antifungal used mainly for skin infections such as athlete’s foot and ringworm.
- Miconazole: An imidazole antifungal with a broad spectrum of activity. It’s used for a variety of skin infections and also as a vaginal cream for yeast infections.
- Triclosan: This is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent. While it has some antifungal activity, it’s more commonly known for its antibacterial properties. Due to concerns regarding its safety and potential contribution to antibiotic resistance, its use in hand soaps and some other personal care products has been phased out in several regions.
Of these, fluconazole, itraconazole, ketoconazole, climbazole, clotrimazole, econazole, and miconazole belong to the azole class, which primarily acts by inhibiting the fungal enzyme lanosterol 14α-demethylase. This enzyme is crucial for ergosterol synthesis, a vital component of fungal cell membranes. Terbinafine, on the other hand, inhibits squalene epoxidase, another enzyme important in ergosterol synthesis. Triclosan works through a different mechanism, targeting bacterial and fungal fatty acid synthesis.
Antifungal Agents can be separated, retained, and analyzed on a Primesep B mix mode phase column using an gradient analytical method with a simple mobile phase of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN), and sulfuric acid as a buffer. This analysis method can be detected in the UV 200 nm.
| Column | Primesep B, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN – 10-60%, 20 min |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 200 nm |
| Class of Compounds | Antifungal Agents |
| Analyzing Compounds | Fluconazole, Ketoconazole, Climbazole, Clotrimazole, Itraconazole, Terbinafine, Econazole, Miconazole |
Application Column
Primesep B
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Clotrimazole
Econazole
Fluconazole
Itraconazole
Ketoconazole
Miconazole
Terbinafine

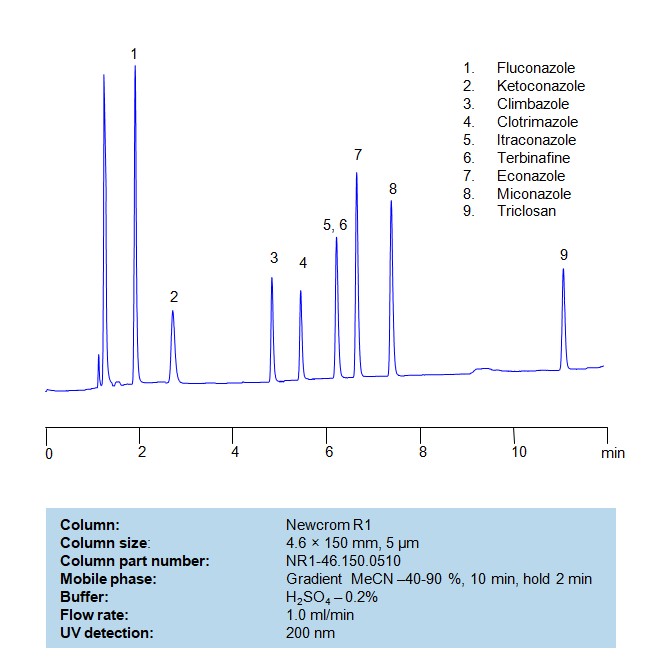
HPLC Method for Separation of a Mixture of Antifungal Agents on Newcrom R1 Column
September 20, 2023
HPLC Method for Analysis of Antifungal Agents on Newcrom R1 by SIELC Technologies
Separation and Analysis of Antifungal Agents on a Newcrom R1 Reverse Phase Column Using Gradient HPLC Method
Antifungal agents are drugs used to treat fungal infections. Depending on their mechanism of action and chemical structure, antifungal agents can be categorized into several classes. Here are some of the main classes and examples of antifungal agents:
- Fluconazole: A triazole antifungal mainly used for the treatment and prevention of superficial and systemic fungal infections.
- Ketoconazole: An imidazole antifungal used to treat a wide variety of fungal infections, though its oral use has become less common due to potential side effects. It’s still frequently used topically.
- Climbazole: An imidazole antifungal primarily used in hair care products to treat dandruff.
- Clotrimazole: An imidazole antifungal used to treat various fungal infections including vaginal yeast infections, oral thrush, and ringworm.
- Itraconazole: A triazole antifungal used primarily to treat a variety of systemic fungal infections.
- Terbinafine: This compound belongs to the allylamine class. It’s mainly used to treat fungal infections of the nails and skin, like athlete’s foot and ringworm.
- Econazole: An imidazole antifungal used mainly for skin infections such as athlete’s foot and ringworm.
- Miconazole: An imidazole antifungal with a broad spectrum of activity. It’s used for a variety of skin infections and also as a vaginal cream for yeast infections.
- Triclosan: This is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent. While it has some antifungal activity, it’s more commonly known for its antibacterial properties. Due to concerns regarding its safety and potential contribution to antibiotic resistance, its use in hand soaps and some other personal care products has been phased out in several regions.
Of these, fluconazole, itraconazole, ketoconazole, climbazole, clotrimazole, econazole, and miconazole belong to the azole class, which primarily acts by inhibiting the fungal enzyme lanosterol 14α-demethylase. This enzyme is crucial for ergosterol synthesis, a vital component of fungal cell membranes. Terbinafine, on the other hand, inhibits squalene epoxidase, another enzyme important in ergosterol synthesis. Triclosan works through a different mechanism, targeting bacterial and fungal fatty acid synthesis.
Antifungal agents can be separated, retained, and analyzed on a Newcrom R1 reverse phase column using an gradient analytical method with a simple mobile phase of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN), and sulfuric acid as a buffer. This analysis method can be detected in the UV 200 nm.
| Column | Newcrom R1, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN – 40-90%, 10 min, hold 2 min |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 200 nm |
| Class of Compounds | Antifungal Agents |
| Analyzing Compounds | Fluconazole, Ketoconazole, Climbazole, Clotrimazole, Itraconazole, Terbinafine, Econazole, Miconazole, Triclosan |
Application Column
Newcrom R1
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Clotrimazole
Econazole
Fluconazole
Itraconazole
Ketoconazole
Miconazole
Terbinafine
Triclosan

HPLC Method for Analysis of Econazole on Primesep 200 Column
September 7, 2023
HPLC Method for Analysis of Econazole on Primesep 200 by SIELC Technologies
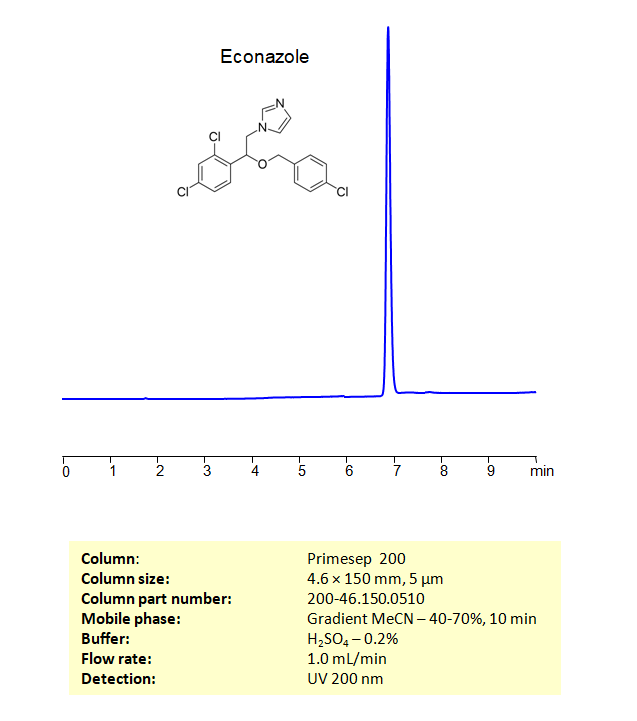
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Econazole
Econazole is an antifungal medication primarily used to treat a variety of fungal skin infections. It belongs to the imidazole class of antifungal agents. Here are some key points about econazole:
Mechanism of Action:
Like other imidazole antifungals, econazole works by inhibiting the enzyme responsible for producing ergosterol, a key component of the fungal cell membrane. A lack of ergosterol disrupts the integrity of the fungal cell membrane, leading to the death of the fungus.
Econazole can be retained, and analyzed on a Primesep 200 mixed-mode stationary phase column using an isocratic analytical method with a simple mobile phase of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN), and a sulfuric acid as a buffer. This analysis method can be detected in the UV 200 nm.
| Column | Primesep 200, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN – 40-70%, 10 min |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 200 nm |
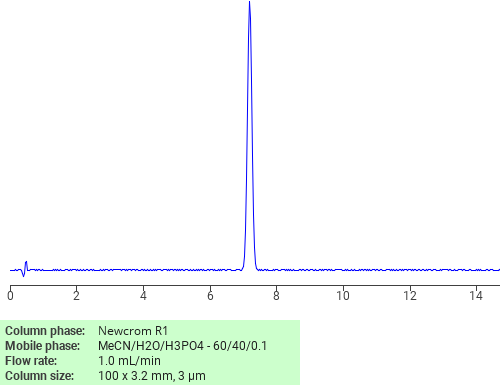
| Peak Retention Time | 6.89 min |
| Class of Compounds | Allylamines |
| Analyzing Compounds | Econazole |
Application Column
Primesep 200
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

Separation of Econazole on Newcrom R1 HPLC column
February 16, 2018
Econazole can be analyzed by this reverse phase (RP) HPLC method with simple conditions. The mobile phase contains an acetonitrile (MeCN), water, and phosphoric acid. For Mass-Spec (MS) compatible applications the phosphoric acid needs to be replaced with formic acid. Smaller 3 µm particles columns available for fast UPLC applications. This liquid chromatography method is scalable and can be used for isolation impurities in preparative separation. It also suitable for pharmacokinetics.
Application Column
Newcrom R1
The Newcrom columns are a family of reverse-phase-based columns. Newcrom A, AH, B, and BH are all mixed-mode columns with either positive or negative ion-pairing groups attached to either short (25 Å) or long (100 Å) ligand chains. Newcrom R1 is a special reverse-phase column with low silanol activity.
Select options