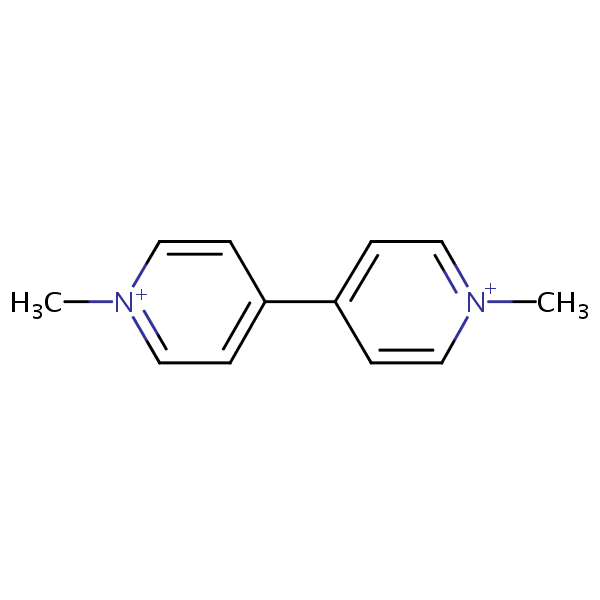
| CAS Number | 4685-14-7 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H14N2 |
| Molecular Weight | 186.258 |
| InChI Key | INFDPOAKFNIJBF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -2.77 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
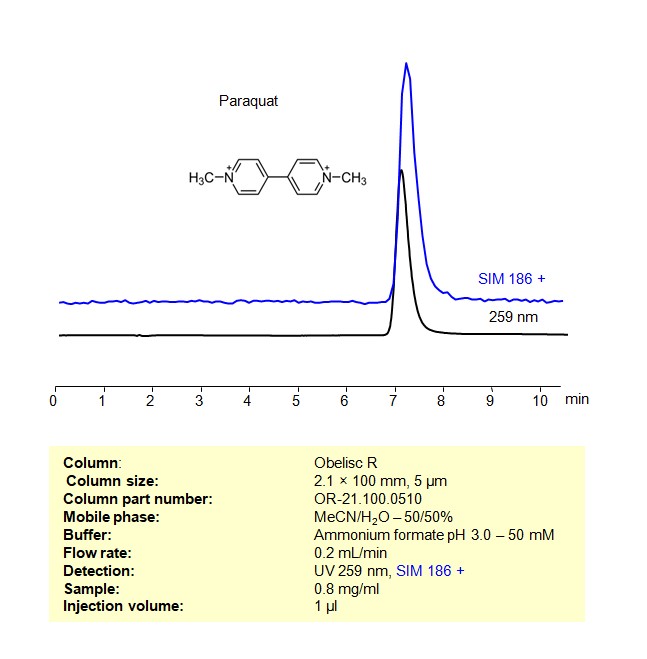
HPLC – MS Method for Analysis of Paraquat on Obelisc R Column
December 22, 2023
HPLC Method for Analysis of Paraquat on Obelisc R by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Paraquat
Paraquat is a widely used, non-selective herbicide known for its high efficacy in controlling a wide range of weeds. It has been an important tool in agriculture since its introduction in the mid-20th century. However, its use is accompanied by significant safety concerns due to its high toxicity.
Paraquat can be retained and analyzed on a Obelisc R mixed-mode stationary phase column using an isocratic analytical method with a simple mobile phase of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN), and a ammonium format as a buffer. This analysis method can be detected an Evaporative Light Scattering Detector (ELSD), or any other evaporative detection method (CAD, ESI-MS)
| Column | Obelisc R, 2.1 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 50%, |
| Buffer | Ammonium Formate pH 3.0-50 mM |
| Flow Rate | 0.2 ml/min |
| Detection | SIM 186 +, UV 259 nm |
| Spray Voltage: | 1.5 kV |
| Nebulizing gas: | 1.5 L/min |
| Drying gas: | 15 L/min |
| DL temp: | 250 ˚C |
| Heat Block: | 400 ˚C |
| Class of Compounds | Pesticides |
| Analyzing Compounds | Paraquat |
Application Column
Obelisc R
Column Diameter: 2.1 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A

HPLC Method for Analysis of Paraquat and Diquat on BIST B+ Column
November 30, 2022
HPLC Method for Analysis of Paraquat and Diquat on BIST B+ by SIELC Technologies.
Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
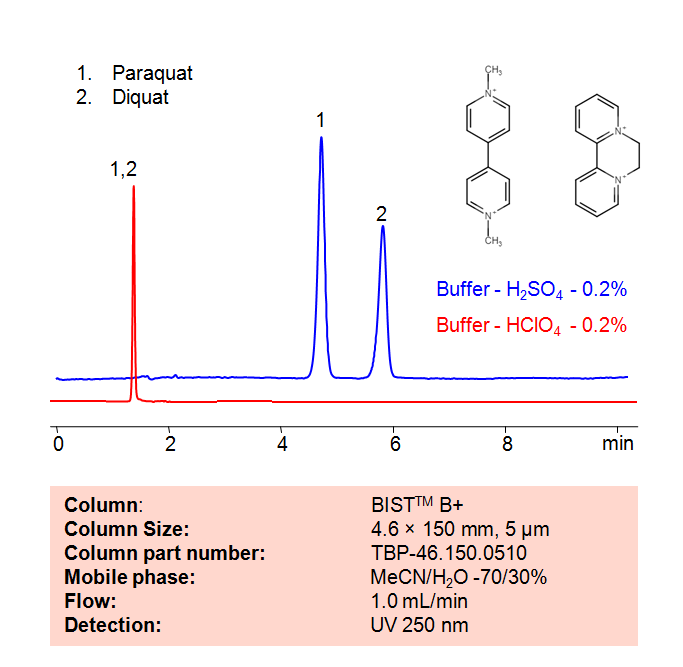
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analyses of Paraquat and Diquat
Paraquat and Diquat are two of the most popular herbicides on the market. With fairly similar structures and interactions with typical ion-exchange columns, they are usually extremely difficult to separate. Using SIELC’s newly introduced BIST™ method, Paraquat and Diquat, which protonate in water, can be retained on a positively-charged anion-exchange BIST™ B column. There are two keys to this retention method: 1) a multi-charged, negative buffer, such as Sulfuric acid (H2SO4), which acts as a bridge, linking the positively-charged herbicide analytes to the positively-charged column surface and 2) a mobile phase consisting mostly of organic solvent (such as MeCN) to minimize the formation of a solvation layer around the charged analytes. What allows these two compounds to be separated using BIST™ is the slight difference in charge position between the two analytes. Since the analytes interact so close to the surface, the minor difference in charge distribution is magnified and therefore significantly affects each analyte’s retention ability. Using this new and unique analysis method, Paraquat and Diquat can be retained and UV detected at 250 nm.
Condition
| Column | BIST B+, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 70% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 250 nm |
| Peak Retention Time | 4.7, 5.9 min |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Herbicides |
| Analyzing Compounds | Paraquat and Diquat |
Application Column
BIST B
BIST™ columns offer a unique and effective way to achieve separations that were traditionally challenging or even impossible with other HPLC columns. With the use of a special mobile phase, these ion exchange columns provide very strong retention for analytes with the same charge polarity as the stationary phase, unlocking new chromatography applications. What makes BIST™ columns stand out is their proprietary surface chemistry, which results in superior selectivity, resolution, and sensitivity. These columns offer a simple, efficient solution for a variety of analytical challenges, making them an excellent choice for researchers and analysts across many different fields. To learn more about the technology that powers BIST™ columns and to explore related applications, check out https://BIST.LC.
Select optionsBIST B+
BIST™ columns offer a unique and effective way to achieve separations that were traditionally challenging or even impossible with other HPLC columns. With the use of a special mobile phase, these ion exchange columns provide very strong retention for analytes with the same charge polarity as the stationary phase, unlocking new chromatography applications. What makes BIST™ columns stand out is their proprietary surface chemistry, which results in superior selectivity, resolution, and sensitivity. These columns offer a simple, efficient solution for a variety of analytical challenges, making them an excellent choice for researchers and analysts across many different fields. To learn more about the technology that powers BIST™ columns and to explore related applications, check out https://BIST.LC.
Select optionsParaquat

HPLC Method for Simultaneous Determination of -Quat Herbicides on Obelisc R Column
September 22, 2022
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Chlormequat, Mepiquat, Paraquat, Diquat
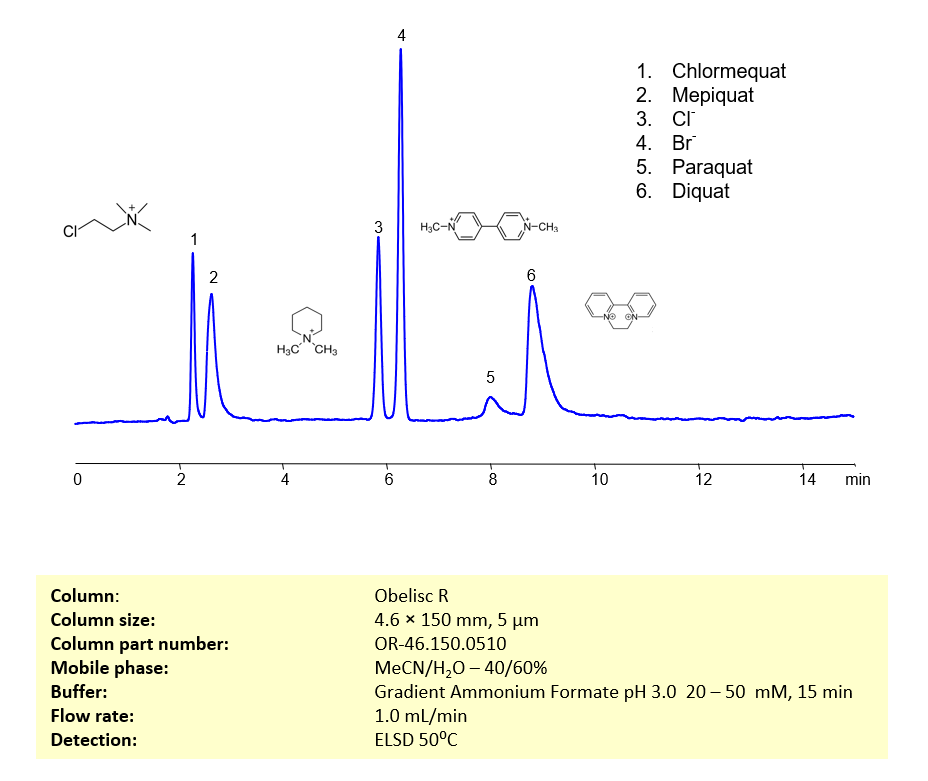
| Column | Obelisc R, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 40% |
| Buffer | Ammonium Formate pH 3.0 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD 50C |
| Class of Compounds | Herbicides |
| Analyzing Compounds |
Chlormequat, Mepiquat, Cl-, Br-, Paraquat, Diquat |
Application Column
Obelisc R
SIELC has developed the Obelisc™ columns, which are mixed-mode and utilize Liquid Separation Cell technology (LiSC™). These cost-effective columns are the first of their kind to be commercially available and can replace multiple HPLC columns, including reversed-phase (RP), AQ-type reversed-phase, polar-embedded group RP columns, normal-phase, cation-exchange, anion-exchange, ion-exclusion, and HILIC (Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography) columns. By controlling just three orthogonal method parameters - buffer concentration, buffer pH, and organic modifier concentration - users can adjust the column properties with pinpoint precision to separate complex mixtures.
Select optionsDiquat
Mepiquat
Paraquat

Separation of Herbicides Paraquat, Diquat and Glyphosate in One Run with LC/MS Compatible Conditions
December 5, 2013
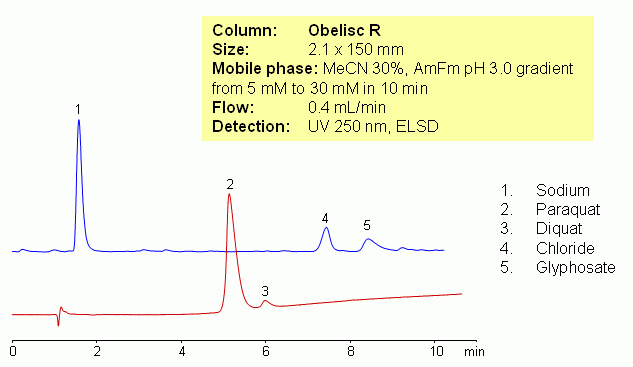
There is a need to separate different herbicides and pesticides in one run with LC/MS compatible conditions. Paraquat, diquat and glyphosate were separated on reversed-phase tri-modal cation- and anion-exchange column (Obelisc R) and on HILIC/ion-exchange columns (Obelisc N). Method explores unique properties of mixed-mode stationary phase which retains and separates cations like paraquat and diquat and anions/zwitter-ions like glyphosate in one run. Since columns are compatible with 100% organic and 100% water, a wide range of gradients can be used for analysis as well as isocratic conditions where it is desired. Method can be used for quantitation of these compounds in various matrices (soil, ground water, crops, food, etc.)
| Column | Obelisc R, 2.1×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 30% |
| Buffer | Gradient AmFm pH 3.0 – 5-30 mM, 10 min |
| Flow Rate | 0.4 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 250 nm, ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Insecticide, Herbicide, Fungicide, Hydrophobic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Paraquat, Diquat, Glyphosate |
Application Column
Obelisc N
SIELC has developed the Obelisc™ columns, which are mixed-mode and utilize Liquid Separation Cell technology (LiSC™). These cost-effective columns are the first of their kind to be commercially available and can replace multiple HPLC columns, including reversed-phase (RP), AQ-type reversed-phase, polar-embedded group RP columns, normal-phase, cation-exchange, anion-exchange, ion-exclusion, and HILIC (Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography) columns. By controlling just three orthogonal method parameters - buffer concentration, buffer pH, and organic modifier concentration - users can adjust the column properties with pinpoint precision to separate complex mixtures.
Select optionsObelisc R
SIELC has developed the Obelisc™ columns, which are mixed-mode and utilize Liquid Separation Cell technology (LiSC™). These cost-effective columns are the first of their kind to be commercially available and can replace multiple HPLC columns, including reversed-phase (RP), AQ-type reversed-phase, polar-embedded group RP columns, normal-phase, cation-exchange, anion-exchange, ion-exclusion, and HILIC (Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography) columns. By controlling just three orthogonal method parameters - buffer concentration, buffer pH, and organic modifier concentration - users can adjust the column properties with pinpoint precision to separate complex mixtures.
Select optionsGlyphosate
Paraquat
UV Detection

Paraquat and Diquat Separation in Non-aqueous Mobile Phase
July 10, 2013
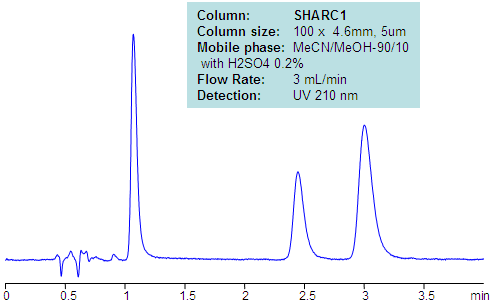
Paraquat, diquat and glyphosate were separated on reversed-phase tri-modal cation- and anion-exchange column (Obelisc R) and on HILIC/ion-exchange columns (Obelisc N). Method explores unique properties of mixed-mode stationary phase which retains and separates cations like paraquat and diquat and anions/zwitter-ions like glyphosate in one run. Since columns are compatible with 100% organic and 100% water, a wide range of gradients can be used for analysis as well as isocratic conditions where it is desired. Method can be used for quantitation of these compounds in various matrices (soil, ground water, crops, food, etc.)
| Column | Sharc 1, 4.6×100 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/MeOH – 90/10% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.2 |
| Flow Rate | 3 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 210 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Insecticide, Herbicide, Fungicide, Hydrophobic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Paraquat, Diquat |
Application Column
Paraquat

Separation of Paraquat, Diguat, and Glyphosate on Obelisc R Column
July 3, 2013
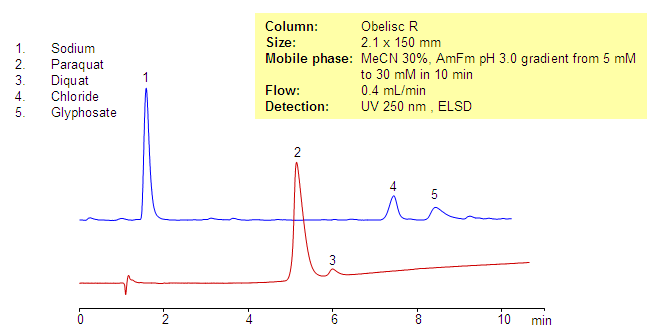
Paraquat, diquat and glyphosate are three of most widely used herbicides in the world. Paraquat and diquat are very polar and very basic quaternary amines. Glyphosate is an aminophosphonic analog of glycine. It is very polar and acidic at most of the pH of the mobile phase. Since glyphosate and the quats have opposite charges no ion-pairing method can be developed for the mixture of basic and acidic herbicides. All three herbicides were separated on the Obelisc R tri-modal column. Paraquat and diquat are retained by a cation-exchange mechanism, and glyphosate is retained by weak reversed-phase and strong anion-exchange mechanisms. This method can be used for analysis of common herbicides in fruits, vegetables, ground water, drinking water and other matrices. Method is LC/MS compatible and can be used to determine trace levels of herbicides.
| Column | Obelisc R, 2.1×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 30% |
| Buffer | Gradient AmFm pH 3.0 – 5-30 mM, 10 min |
| Flow Rate | 0.4 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 250 nm, ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Insecticide, Herbicide, Fungicide, Hydrophobic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Paraquat, Diquat, Glyphosate |
Application Column
Obelisc R
SIELC has developed the Obelisc™ columns, which are mixed-mode and utilize Liquid Separation Cell technology (LiSC™). These cost-effective columns are the first of their kind to be commercially available and can replace multiple HPLC columns, including reversed-phase (RP), AQ-type reversed-phase, polar-embedded group RP columns, normal-phase, cation-exchange, anion-exchange, ion-exclusion, and HILIC (Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography) columns. By controlling just three orthogonal method parameters - buffer concentration, buffer pH, and organic modifier concentration - users can adjust the column properties with pinpoint precision to separate complex mixtures.
Select optionsDiquat
Glyphosate
Paraquat
Sodium
UV Detection

HPLC Separation of Mixture of Paraquat and Diquat
October 6, 2010
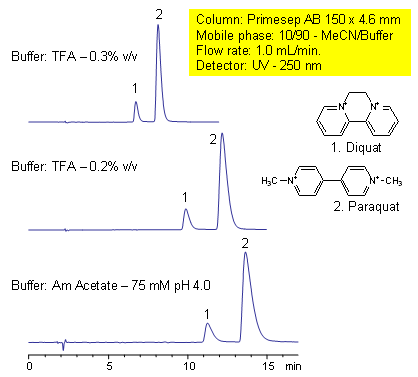
Paraquat and diquat are two of most widely used herbicides in the world. Both compounds are toxic for humans and animals. Presence of paraquat and diquat in water is regulated by EPA. Paraquat and diquat have two quaternary amines, making them very polar molecules. Paraquat and diquat also have similar formula. Due to low hydrophobicity and highly basic properties, they show limited retention on reversed-phase columns and produce very poor peak shape due to the residual silanol interactions. Primesep AB and Obelisc R column retain and separate these two compounds with perfect peak shape.
Application Column
Primesep AB
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Paraquat

HPLC Separation Paraquat and Diquat on Obelisc R
March 3, 2010
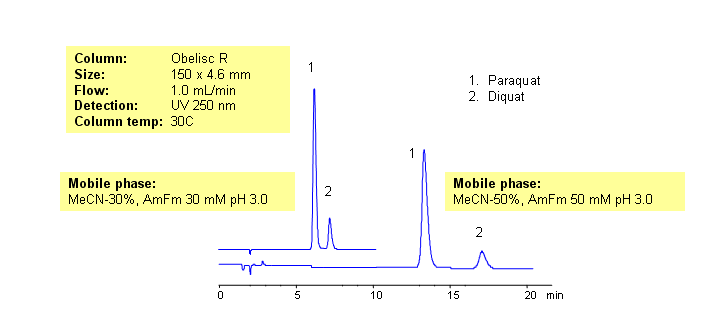
Paraquat and diquat are two of most widely used herbicides in the world. Both compounds are toxic for humans and animals. Presence of paraquat and diquat in water is regulated by EPA. Paraquat and diquat have two quaternary amines, making them very polar molecules. Paraquat and diquat also have similar formula. Due to low hydrophobicity and highly basic properties, they show limited retention on reversed-phase columns and produce very poor peak shape due to the residual silanol interactions. Obelisc R column retains and separates these two compounds with perfect peak shape. Method can be used for analysis of paraquat and diquat in soil, ground and drinking water, and other samples. Method allows to separate both compounds in one run without ion-pairing reagent.
Application Column
Obelisc R
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Paraquat