| CAS Number | 59-46-1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C13H20N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 236.316 |
| InChI Key | MFDFERRIHVXMIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 2.14 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
UV-Vis Spectrum of Procaine
July 12, 2024
Access the UV-Vis Spectrum SIELC Library
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Procaine, Procaine hydrochloride check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
Procaine hydrochloride

HPLC MS Method for Analysis of Procaine on Primesep 200 Column
February 12, 2024
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Procaine on Primesep 200 by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode SIELC Technologies
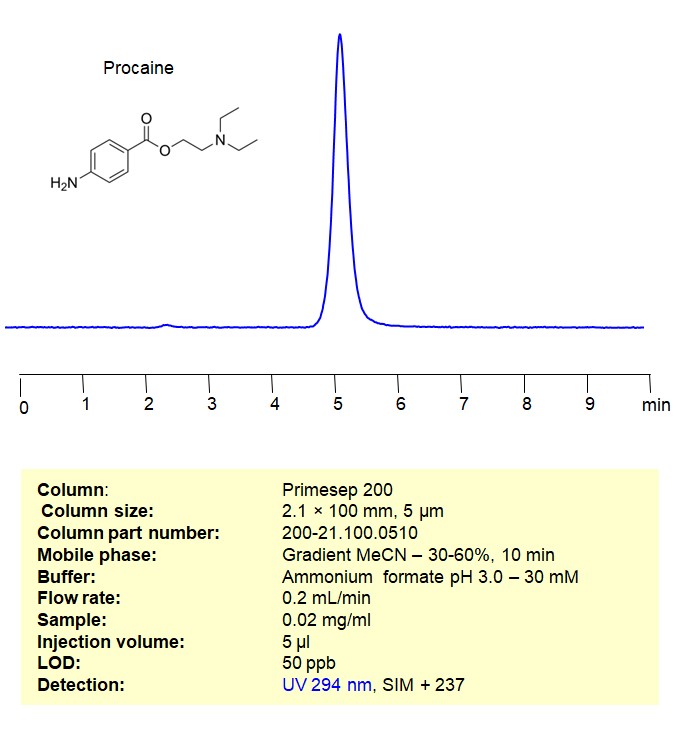
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Procaine
Procaine is a local anesthetic drug that belongs to the class of amino esters. It is often used to numb specific areas of the body during medical procedures or minor surgeries. Procaine works by blocking nerve signals in the body, leading to a temporary loss of sensation in the treated area.
Some common uses of procaine include dental procedures, minor skin surgeries, and as an ingredient in certain formulations for pain relief. It is often combined with other medications, such as benzyl alcohol, to enhance its stability and effectiveness.
Procaine can be retained and analyzed using a Primesep 200 mixed-mode stationary phase column. The analysis employs an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase comprising water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and ammonium formate as a buffer. This method allows for detection using UV at 294 nm
| Column | Primesep 200, 10 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN 30-60%, 10 min |
| Buffer | AmFm pH 3.0 – 30 mM |
| Flow Rate | 0.2 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 294 nm, SIM + 237 |
| Samples | 0.02 mg/ml |
| Injection volume | 5 µl |
| LOD* | 200 ppb |
| Class of Compounds | Amide |
| Analyzing Compounds | Procaine |
Application Column
Primesep 200
Column Diameter: 10 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
UV Detection

HPLC Method for Separation of Procainamide and Procaine on BIST B+ Column Column
February 12, 2024
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Procainamide, Procaine on BIST B+ by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
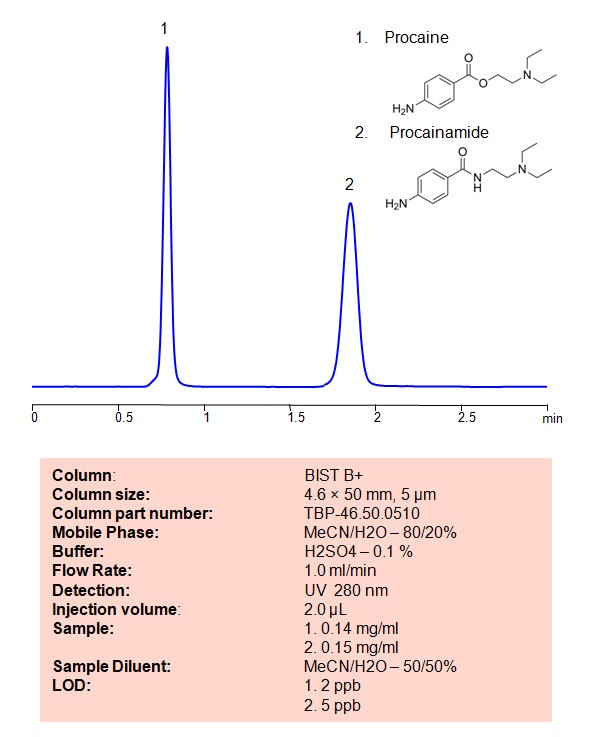
Procainamide and procaine are two different pharmaceutical compounds with distinct uses and properties.
Procainamide:
Class: Procainamide is an antiarrhythmic medication, belonging to the Class Ia antiarrhythmic drugs. It is used to treat certain types of abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) by stabilizing the cell membrane and reducing excitability in the heart muscle.
Mechanism of Action: Procainamide works by inhibiting sodium channels in cardiac cells, prolonging the action potential duration and refractory period, which helps in controlling irregular heartbeats.
Administration: It is typically administered intravenously or orally under medical supervision.
Medical Use: Procainamide is prescribed for conditions such as atrial and ventricular arrhythmias.
Procaine:
Class: Procaine is a local anesthetic drug, belonging to the amino ester group of local anesthetics.
Mechanism of Action: Procaine works by blocking nerve impulses and causing temporary loss of sensation in a specific area of the body.
Administration: It is usually administered through injection to induce local anesthesia. Procaine is commonly used for minor surgical procedures and dental work.
Medical Use: Procaine is employed for local anesthesia, providing pain relief in various medical and dental settings.
Procainamide is primarily used for cardiac conditions, while procaine is utilized as a local anesthetic for pain management during medical and dental procedures. While both compounds have a shared ancestry in PABA and contain amine groups, the specific functional groups (amide vs. ester) and their positions in the molecules contribute to their distinct pharmacological properties. It’s a good observation that small structural changes can lead to significant differences in the pharmacological actions of compounds.
Procainamide and procaine can be retained, separated and analyzed on a BIST B+ mixed-mode stationary phase column using an analytical method with a simple mobile phase of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN) , and a sulfuric acid as a buffer. This analysis method can be detected using UV at 280 nm.
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analyses of Procainamide, Procaine
Condition
| Column | BIST B+, 4.6 x 50 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 80/20% |
| Buffe | H2SO4 -0.1% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 280 nm |
| Sample | 1. 0.14 mg/ml 2. 0.15 mg/ml |
| LOD * | 1. 2 ppb 2. 5 ppb |
| Injection volume | 2 µl |
*LOD was determined for this combination of instrument, method, and analyte, and it can vary from one laboratory to another even when the same general type of analysis is being performed
Description
| Class of Compounds | Drug |
| Analyzing Compounds | Procainamide, Procaine |
Application Column
BIST B+
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 50 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Procaine

HPLC Method for Separation of Procainamide and Procaine on Newcrom A Column
February 6, 2024
HPLC Method for Analysis of Procainamide, Procaine on Newcrom A by SIELC Technologies
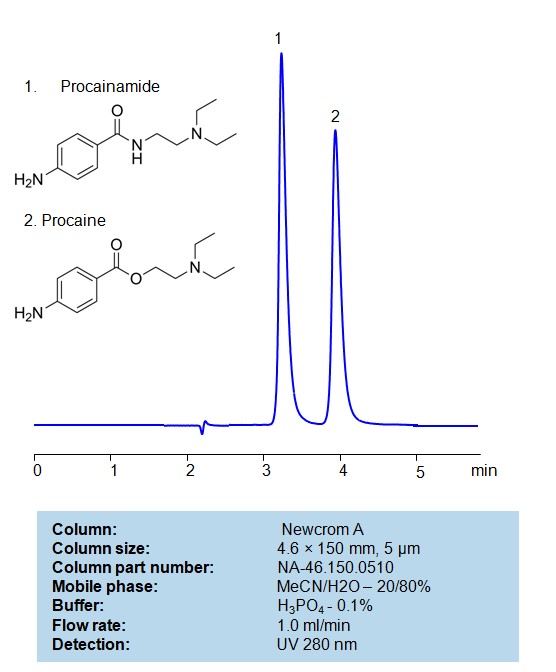
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Procainamide, Procaine
Procainamide and procaine are two different pharmaceutical compounds with distinct uses and properties.
Procainamide:
- Class: Procainamide is an antiarrhythmic medication, belonging to the Class Ia antiarrhythmic drugs. It is used to treat certain types of abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) by stabilizing the cell membrane and reducing excitability in the heart muscle.
- Mechanism of Action: Procainamide works by inhibiting sodium channels in cardiac cells, prolonging the action potential duration and refractory period, which helps in controlling irregular heartbeats.
- Administration: It is typically administered intravenously or orally under medical supervision.
- Medical Use: Procainamide is prescribed for conditions such as atrial and ventricular arrhythmias.
Procaine:
- Class: Procaine is a local anesthetic drug, belonging to the amino ester group of local anesthetics.
- Mechanism of Action: Procaine works by blocking nerve impulses and causing temporary loss of sensation in a specific area of the body.
- Administration: It is usually administered through injection to induce local anesthesia. Procaine is commonly used for minor surgical procedures and dental work.
- Medical Use: Procaine is employed for local anesthesia, providing pain relief in various medical and dental settings.
Procainamide is primarily used for cardiac conditions, while procaine is utilized as a local anesthetic for pain management during medical and dental procedures. While both compounds have a shared ancestry in PABA and contain amine groups, the specific functional groups (amide vs. ester) and their positions in the molecules contribute to their distinct pharmacological properties. It’s a good observation that small structural changes can lead to significant differences in the pharmacological actions of compounds.
Procainamide and Procaine can be retained, separated and analyzed using a Newcrom A mixed-mode stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and phosphoricacid as a buffer. Detection is achieved using UV 280 nm
| Column | Newcrom A, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O -20/80% |
| Buffer | H3PO4 – 0.1% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 280 nm |
| Class of Compounds | Drug |
| Analyzing Compounds | Procainamide, Procaine |
Application Column
Newcrom A
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Procaine

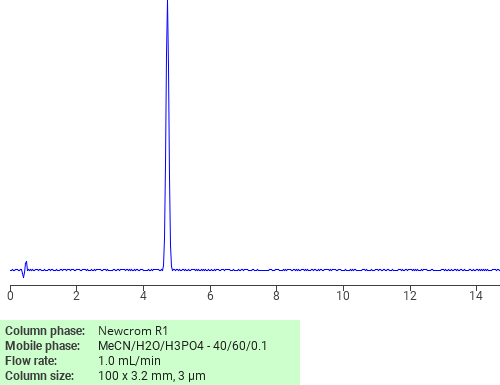
Separation of Procaine on Newcrom R1 HPLC column
May 16, 2018
Procaine can be analyzed by this reverse phase (RP) HPLC method with simple conditions. The mobile phase contains an acetonitrile (MeCN), water, and phosphoric acid. For Mass-Spec (MS) compatible applications the phosphoric acid needs to be replaced with formic acid. Smaller 3 µm particles columns available for fast UPLC applications. This liquid chromatography method is scalable and can be used for isolation impurities in preparative separation. It also suitable for pharmacokinetics.
Application Column
Newcrom R1
The Newcrom columns are a family of reverse-phase-based columns. Newcrom A, AH, B, and BH are all mixed-mode columns with either positive or negative ion-pairing groups attached to either short (25 Å) or long (100 Å) ligand chains. Newcrom R1 is a special reverse-phase column with low silanol activity.
Select options