High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Procainamide, Procaine on BIST B+ by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
Procainamide and procaine are two different pharmaceutical compounds with distinct uses and properties.
Procainamide:
Class: Procainamide is an antiarrhythmic medication, belonging to the Class Ia antiarrhythmic drugs. It is used to treat certain types of abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) by stabilizing the cell membrane and reducing excitability in the heart muscle.
Mechanism of Action: Procainamide works by inhibiting sodium channels in cardiac cells, prolonging the action potential duration and refractory period, which helps in controlling irregular heartbeats.
Administration: It is typically administered intravenously or orally under medical supervision.
Medical Use: Procainamide is prescribed for conditions such as atrial and ventricular arrhythmias.
Procaine:
Class: Procaine is a local anesthetic drug, belonging to the amino ester group of local anesthetics.
Mechanism of Action: Procaine works by blocking nerve impulses and causing temporary loss of sensation in a specific area of the body.
Administration: It is usually administered through injection to induce local anesthesia. Procaine is commonly used for minor surgical procedures and dental work.
Medical Use: Procaine is employed for local anesthesia, providing pain relief in various medical and dental settings.
Procainamide is primarily used for cardiac conditions, while procaine is utilized as a local anesthetic for pain management during medical and dental procedures. While both compounds have a shared ancestry in PABA and contain amine groups, the specific functional groups (amide vs. ester) and their positions in the molecules contribute to their distinct pharmacological properties. It’s a good observation that small structural changes can lead to significant differences in the pharmacological actions of compounds.
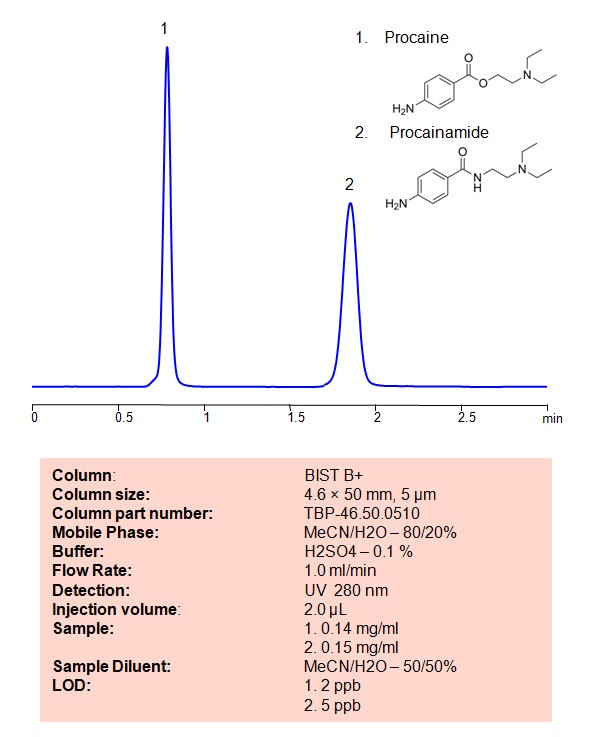
Procainamide and procaine can be retained, separated and analyzed on a BIST B+ mixed-mode stationary phase column using an analytical method with a simple mobile phase of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN) , and a sulfuric acid as a buffer. This analysis method can be detected using UV at 280 nm.
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analyses of Procainamide, Procaine
Condition
| Column | BIST B+, 4.6 x 50 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 80/20% |
| Buffe | H2SO4 -0.1% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 280 nm |
| Sample | 1. 0.14 mg/ml 2. 0.15 mg/ml |
| LOD * | 1. 2 ppb 2. 5 ppb |
| Injection volume | 2 µl |
*LOD was determined for this combination of instrument, method, and analyte, and it can vary from one laboratory to another even when the same general type of analysis is being performed
Description
| Class of Compounds | Drug |
| Analyzing Compounds | Procainamide, Procaine |
Application Column
BIST B+
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 50 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Procaine





