| CAS Number | 144-62-7 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C2H2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 90.03 |
| InChI Key | MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -0.3 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
HPLC Method for Analysis of Oxalic Acid on Newcrom BH Column
December 9, 2025
HPLC Method for Oxalic Acid on Newcrom BH by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Oxalic Acid.
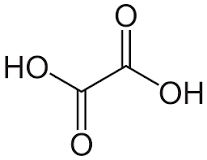
Oxalic Acid is an organic acid with the chemical formula C2H2O4. It is considered the simplest dicarboxylic acid, with it’s name being derrived from the genus of the plant from which it was isolated, Oxalis. It is primarily used as a bleaching agent in cleaning solutions, rust removal, and teeth whitening. Oxalic acid has an oral lowest published lethal dose of 600 mg/kg. You can find detailed UV spectra of Oxalic Acid and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
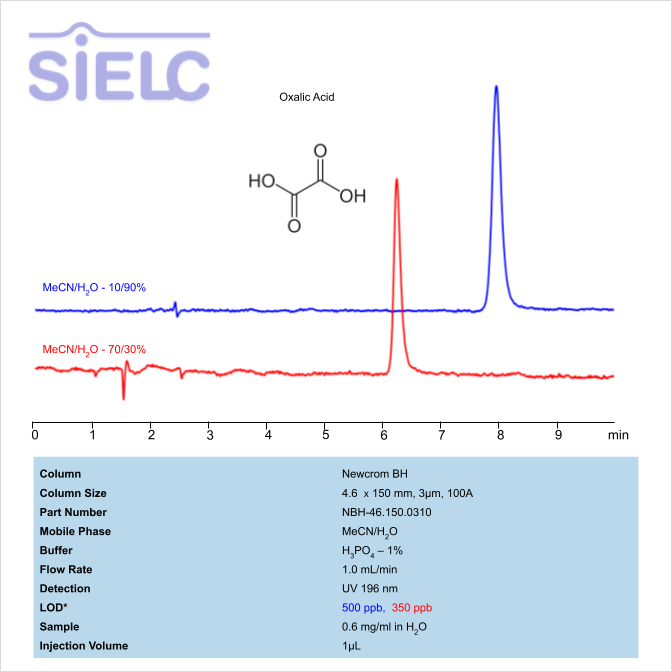
Multi-charged molecules, such as oxaloacetate and oxalate, generally have a tendency to exhibit poor peak shape on reverse-phase HPLC columns, where they show significant tailing. Oxalic Acid can be retained with great peak shape on a Newcrom BH mixed-mode column. Oxalic acid can be measured at low UV. Using a Newcrom BH mixed-mode column and a mobile phase consisting of acetonitrile (ACN) and water with sulfuric acid (H2SO4) buffer, oxaloacetic acid and oxalic acid can be retained, separated, and UV detected at 200 nm with precise resolution.
| Column | Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 3 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | H3PO4- 1% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 196 nm |
| Class of Compounds | Acids |
| Analyzing Compounds | Oxalic Acid |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 3 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

UV-Vis Spectrum of Oxalic Acid
December 4, 2025
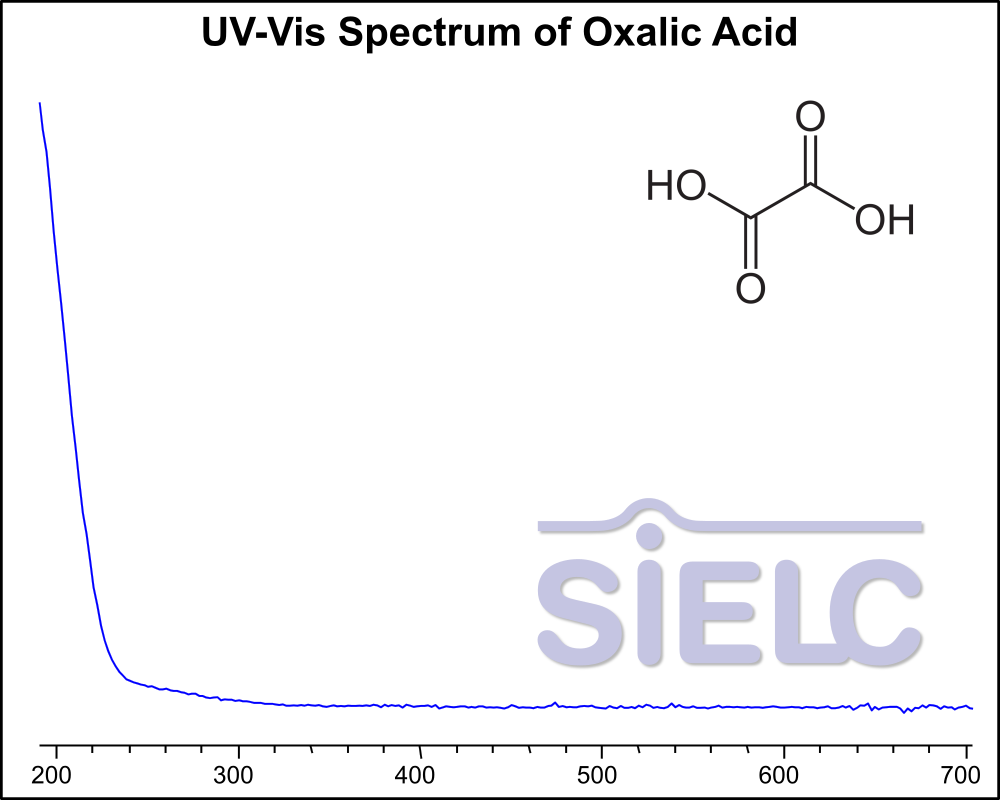
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Oxalic Acid check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

HPLC Method for Analysis of Dicarbon Carboxylic Acids on Newcrom BH Column
June 6, 2023
HPLC Method for Analysis of Oxalic Acid, Glycolic acid, Acetic Acid, Glyoxylic acid on Newcrom BH by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
- Glyoxylic Acid (CHO-COOH): This is the smallest α-keto acid. It is a yellowish solid that occurs naturally and is useful industrially. It participates in many biochemical reactions. Its reduced form, D-lactic acid, can be found in various microorganisms.
- Glycolic Acid (HOCH2COOH): This is the smallest α-hydroxy acid (AHA). It’s derived from sugar cane and is a colorless, odorless, and hygroscopic crystalline solid. It is used in various skin-care products because of its capability to penetrate skin.
- Acetic Acid (CH3COOH): It is a simple carboxylic acid. It’s an important chemical reagent and industrial chemical, primarily used in the production of cellulose acetate for photographic film and polyvinyl acetate for wood glue, as well as synthetic fibers and fabrics. It gives vinegar its sour taste and pungent smell.
- Oxalic Acid (C2H2O4): This is a colorless crystalline solid that forms a colorless solution in water. It occurs naturally in many foods, but too much can lead to kidney stones. It’s used in many different industrial processes, including rust removal, bleaching, and as a reducing agent in developing photographic film.
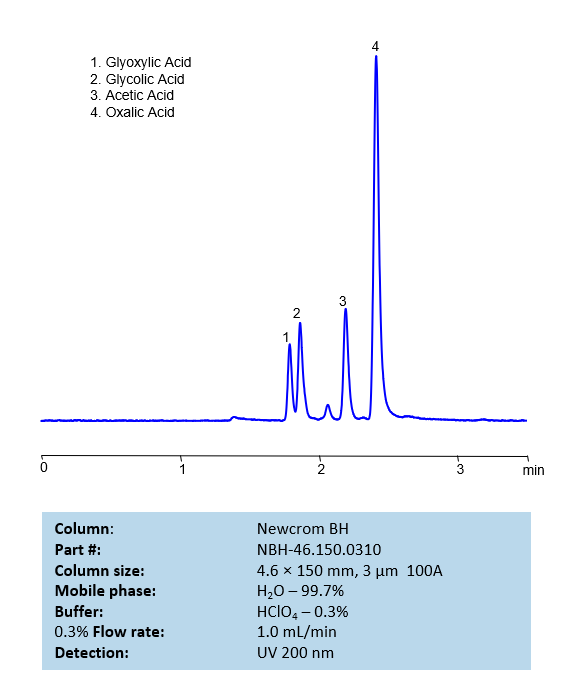
These four acids be separate and analyzed on a reverse-phase Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 3 µm, 100 A, dual ended column with a mobile phase consisting of water and perchloric acid as a buffer modifier. This analysis method can be UV detected at 200 nm.
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Oxalic Acid, Glycolic acid, Acetic Acid, Glyoxylic acid
Condition
| Column | Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 3 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | H2O -99.7% |
| Buffer | HClO4 – 0.3 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200 nm |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Dicarbon Carboxylic Acids |
| Analyzing Compounds | Oxalic Acid, Glycolic acid, Acetic Acid, Glyoxylic acid |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 3 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Glycolic acid
Glyoxylic acid
Oxalic Acid

HPLC Method for Analysis of Maleic acid, Ascorbic acid, Nicotinic acid, Fumaric acid and Oxalic acid on BIST™ A+ Column
July 8, 2022
Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
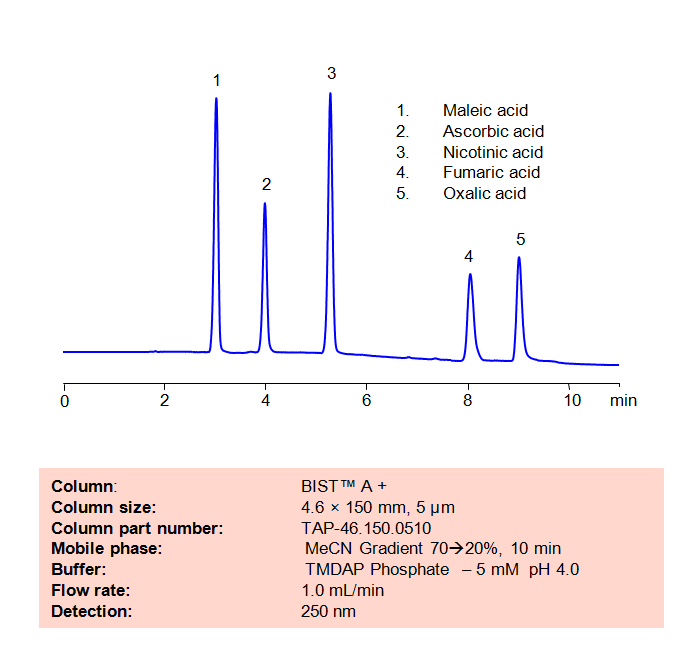
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Maleic acid, Ascorbic acid, Nicotinic acid, Fumaric acid and Oxalic acid
The maleate ion from Maleic acid is a popular ingredient as the maleate salt in several different drugs, including Methergine, Pyrilamine, and Carfenazine, among others. Nicotinic acid, also known as Niacin or Vitamin B3, is an essential nutrient for the human body and is sometimes taken as a treatment for high cholesterol. Aconitic acid is a key intermediary in the citric acid cycle, and is also used a flavoring agent and in the production of rubbers and plastics. Fumaric acid is a popular preservative and food additive with a fruit-like taste. Using SIELC’s newly introduced BIST™ method, a mixture of these organic acids can be separated on a negatively-charged, cation-exchange BIST™ A+ column, contrary to conventional chromatographic wisdom. There are two keys to this retention method: 1) a multi-charged, positive buffer, such as N,N,N’,N’-Tetramethyl-1,3-propanediamine (TMDAP), which acts as a bridge, linking the negatively-charged anion analytes to the negatively-charged column surface and 2) a mobile phase consisting mostly of organic solvent (such as MeCN) to minimize the formation of a solvation layer around the charged analytes. Other positively-charged buffers that can generate BIST™ include Calcium acetate and Magnesium acetate. Using this new and unique analysis method, these organic acids can be separated, retained, and detected through ELSD. This method is also compatible with Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) and CAD.
Condition
| Column | BIST™ A+, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN Gradient |
| Buffer | TMDAP ( N,N,N’,N’-Tetramethyl-1,3-diaminopropane) phosphate – 5 mM pH 4.0 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 250 nm |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Acids, Organic acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Maleic acid, Ascorbic acid, Nicotinic acid, Fumaric acid and Oxalic acid |
Application Column
BIST A+
BIST™ columns offer a unique and effective way to achieve separations that were traditionally challenging or even impossible with other HPLC columns. With the use of a special mobile phase, these ion exchange columns provide very strong retention for analytes with the same charge polarity as the stationary phase, unlocking new chromatography applications. What makes BIST™ columns stand out is their proprietary surface chemistry, which results in superior selectivity, resolution, and sensitivity. These columns offer a simple, efficient solution for a variety of analytical challenges, making them an excellent choice for researchers and analysts across many different fields. To learn more about the technology that powers BIST™ columns and to explore related applications, check out https://BIST.LC.
Select optionsFumaric Acid
Maleic Acid
Nicotinic Acid/Niacin (3-pyridinecarboxylic acid)
Oxalic Acid

HPLC Method for Determination of Oxalic acid on Newcrom BH
November 5, 2021
HPLC Method for Oxalic Acid on Newcrom BH by SIELC Technologies
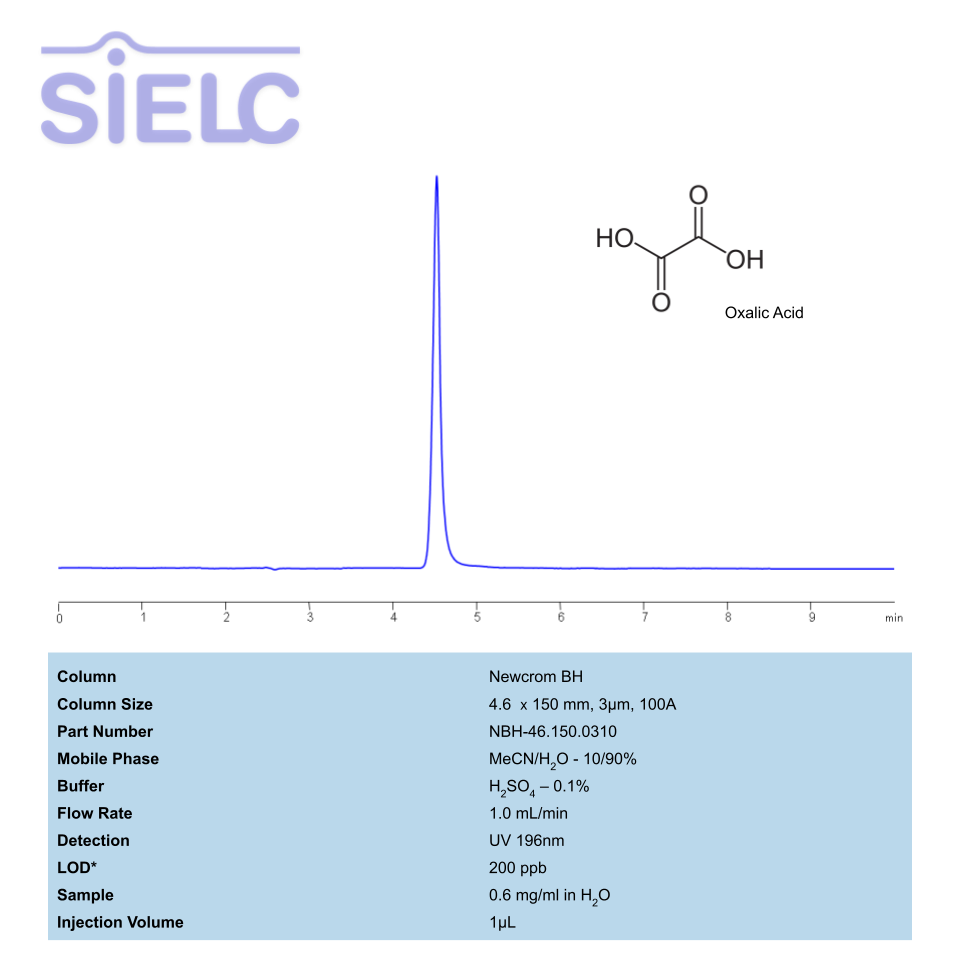
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Oxalic Acid.
Oxalic Acid is an organic acid with the chemical formula C2H2O4. It is considered the simplest dicarboxylic acid, with it’s name being derrived from the genus of the plant from which it was isolated, Oxalis. It is primarily used as a bleaching agent in cleaning solutions, rust removal, and teeth whitening. Oxalic acid has an oral lowest published lethal dose of 600 mg/kg. You can find detailed UV spectra of Oxalic Acid and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
Multi-charged molecules, such as oxaloacetate and oxalate, generally have a tendency to exhibit poor peak shape on reverse-phase HPLC columns, where they show significant tailing. Oxalic Acid can be retained with great peak shape on a Newcrom BH mixed-mode column. Oxalic acid can be measured at low UV. Using a Newcrom BH mixed-mode column and a mobile phase consisting of acetonitrile (ACN) and water with sulfuric acid (H2SO4) buffer, oxaloacetic acid and oxalic acid can be retained, separated, and UV detected at 200 nm with precise resolution.
| Column | Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 3 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 10/90% |
| Buffer | H2SO4- 0.1% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 196 nm |
| Class of Compounds | Acids |
| Analyzing Compounds | Oxalic Acid |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 3 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

HPLC Determination of Oxalic Acid on Newcrom B Column
November 5, 2019
HPLC Method for Oxalic Acid on Newcrom B by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Oxalic Acid
Oxalic Acid. also known as ethanedioic acid is an organic acid. It occurs naturally in plants, but is also often found in industrial uses as a bleaching agent, rust remover, and cleaning agent. Industrial uses of it also extend into households, as it is easily accessible. Despite that, in large amounts, it can be toxic.
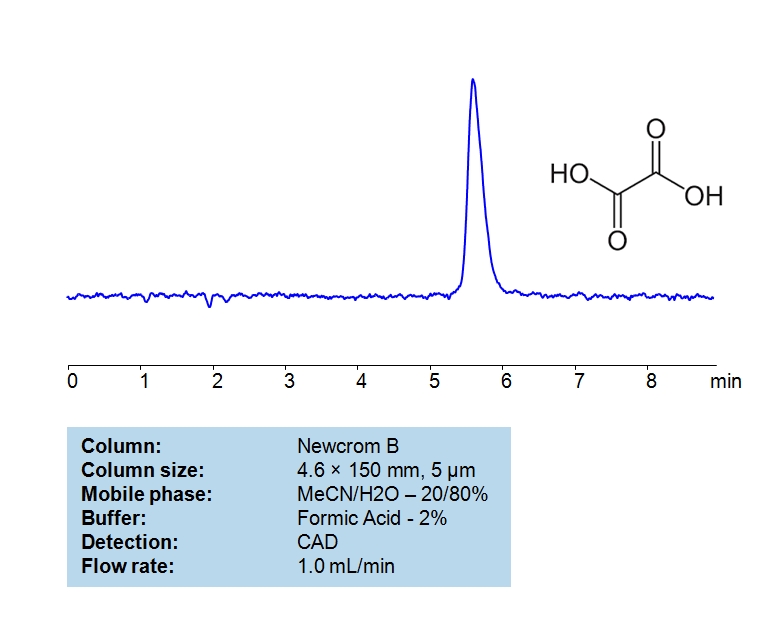
Oxalic Acid can be retained and analyzed using the Newcrom B stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water and acetonitrile (MeCN) with a formic acid buffer. Detection is performed using CAD.
| Column | Newcrom B, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 20/80% |
| Buffer | Formic Acid – 2.0 % |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | CAD (Corona) |
| Class of Compounds | Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Oxalic Acid |
Application Column
Newcrom B
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended