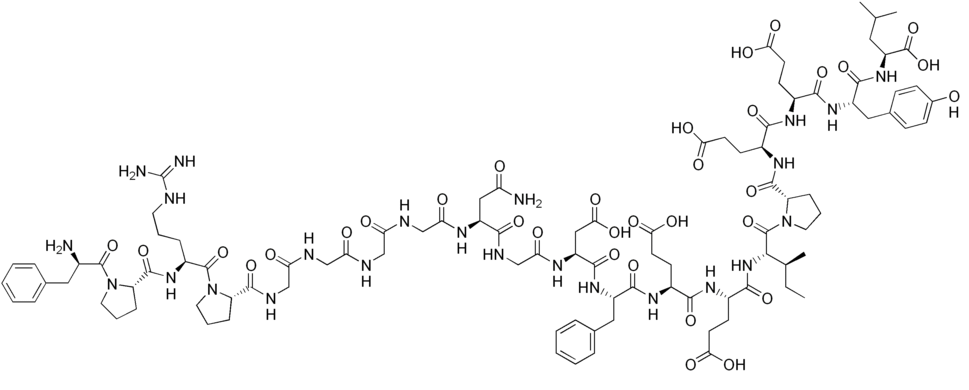
| CAS Number | 128270-60-0 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C98H138N24O33 |
| Molecular Weight | 2180.317 |
| InChI Key | OIRCOABEOLEUMC-GEJPAHFPSA-N |
| LogP | -0.0816 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
HPLC Method for Analysis of Bivalirudin and Asp9 – bivalirudin on BIST A+
November 30, 2022
HPLC Method for Bivalirudin on BIST A+ by SIELC Technologies
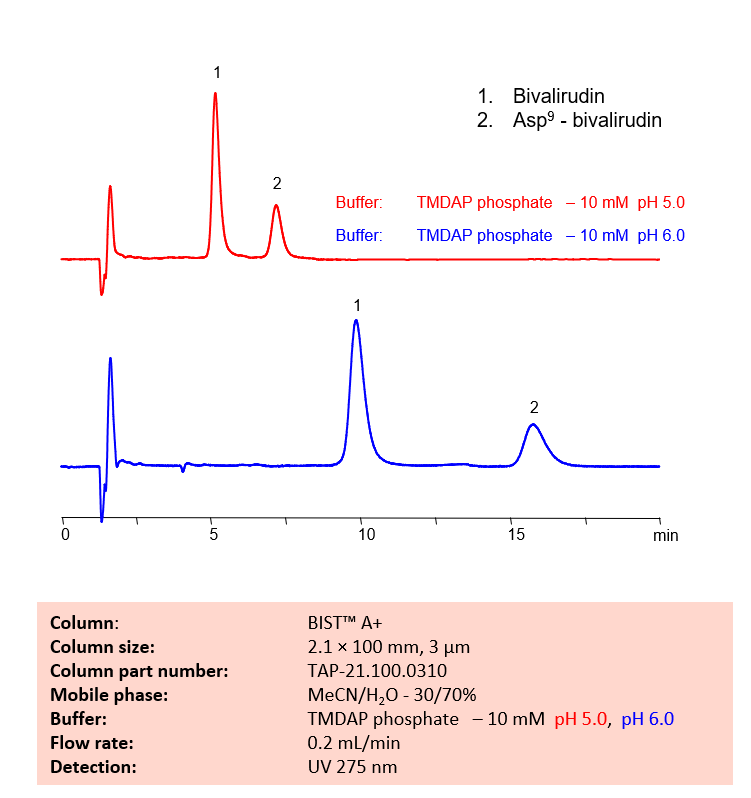
Bivalirudin is a short, 21-amino-acid peptide with the chemical formula C98H138N24O33. It has 2 basic and 6 acidic groups. It is sold as a direct thrombin inhibitor (DTI), which is used as an anticoagulant.
Asp9-bivalirudin is a process impurity and can be a result of the degradation of the drug bivalirudin. It has the chemical formula C98H137N23O34.
SIELC’s new BIST™ mode can retain and separate Bivalirudin and its degradant with a TMDAP phosphate buffer, and the respective retention times can be controlled by altering the pH of the buffer.
Condition
| Column | BIST A+, 2.1 x 100 mm, 3 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 30% |
| Buffer | TMDAP phosphate – 5 mM pH 5.0, pH 6.0 |
| Flow Rate | 0.2 mL/min |
| Detection | UV 275 nm |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Drugs, Anticoagulant |
| Analyzing Compounds | Bivalirudin |
Application Column
BIST A+
Column Diameter: 2.1 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 3 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

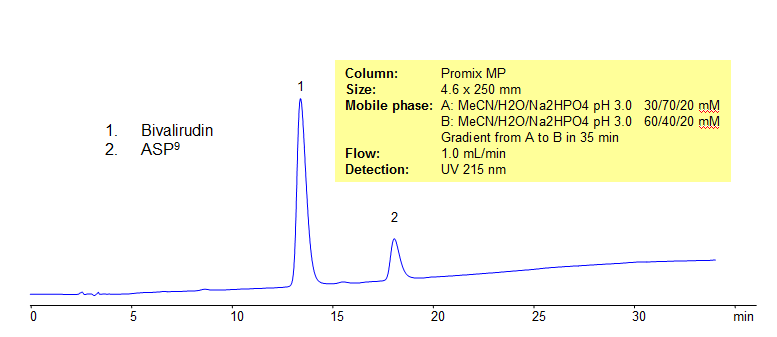
HPLC Analysis of Bivalirudin on Promix MP colum
February 20, 2016
Bivalirudin is a short 21 amino acids peptide. It has 2 basic and 6 acidic groups. It is a naturally occurred an anticoagulant. Asp9 – bivalirudin is a process impurity and can be a result of degradation of bivalirudin drug.
| Column | Promix MP, 4.6×250 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN – 30-60%, 35 min |
| Buffer | Na2HPO4 pH 3.0- 20 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 215 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Blood thinners |
| Analyzing Compounds | Bivalirudin |
Application Column
Promix MP
The Promix family of mixed-mode columns presents an innovative chromatography technology for the efficient resolution of peptides and proteins. This technology hinges on a unique blend of hydrophobic and ionic interactions, facilitated by a novel separation medium: a ligand bonded to a silica support, chemically combined with hydrophobic and ionic functional groups. This phase provides unparalleled selectivity and peak capacity. By independently adjusting the quantities of buffer and organic modifier, a virtually infinite number of separation conditions can be achieved, rendering it suitable for a wide array of biomolecules.
Select options