| CAS Number | 67644-00-2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H16N2O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 244.24 |
| InChI Key | QLROSWPKSBORFJ-BQBZGAKWSA-N |
| LogP | -2.2 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
HPLC Method for Analysis of Polyglutamic Acid on BIST A
January 9, 2023
Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
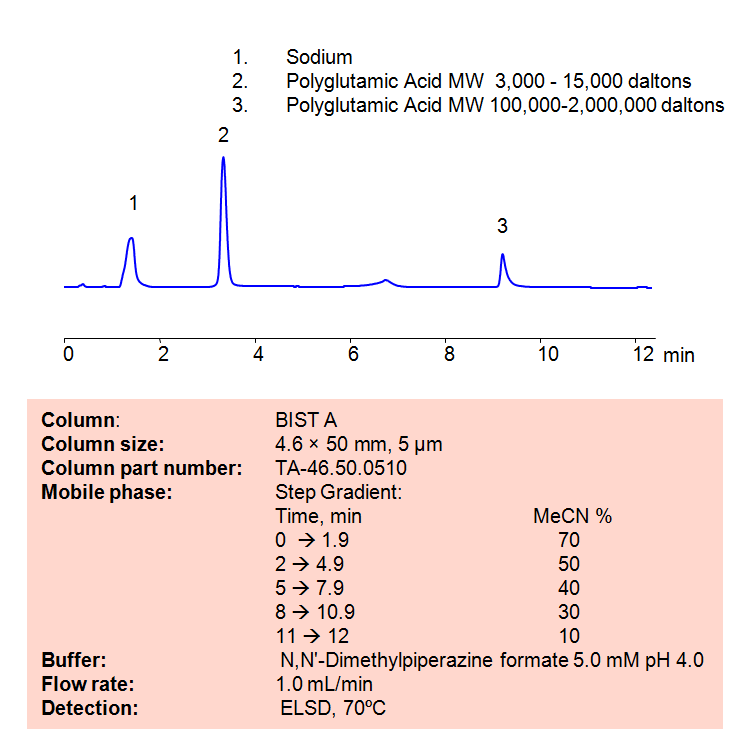
Polyglutamic acid (PGA) is a biopolymer consisting of repeating units of Glutamic acid. PGA can be found and used in a wide variety of industries due to its biodegradable, non-toxic properties, including in the food, medical, and wastewater industries. Using SIELC’s newly introduced BIST™ method, PGA can be retained easily on a negatively-charged, cation-exchange BIST™ A column. There are two keys to this retention method: 1) a multi-charged, positive buffer, such as N,N’-Dimethylpiperazine (DMP), which acts as a bridge, linking the negatively-charged anion analytes to the negatively-charged column surface and 2) a mobile phase consisting mostly of organic solvent (such as MeCN) to minimize the formation of a solvation layer around the charged analytes. Other positively-charged buffers that can generate BIST™ include TMDAP, Calcium acetate, and Magnesium acetate. Using this new and unique analysis method, PGA can be retained with high selectivity and great peak shape. This method can be detected and is compatible with ELSD, CAD, and Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS).
Condition
| Column | BIST™ A, 4.6×50 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN |
| Buffer | N,N’-Dimethylpiperazine formate pH 4.0 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, 70C |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Acid, Polymer, Peptide |
| Analyzing Compounds | Polyglutamic Acid |
Application Column
BIST A
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 50 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

HPLC Method for Analysis of Polyglutamic Acid on BIST A
December 1, 2022
HPLC Method for Polyglutamic Acid on BIST A by SIELC Technologies
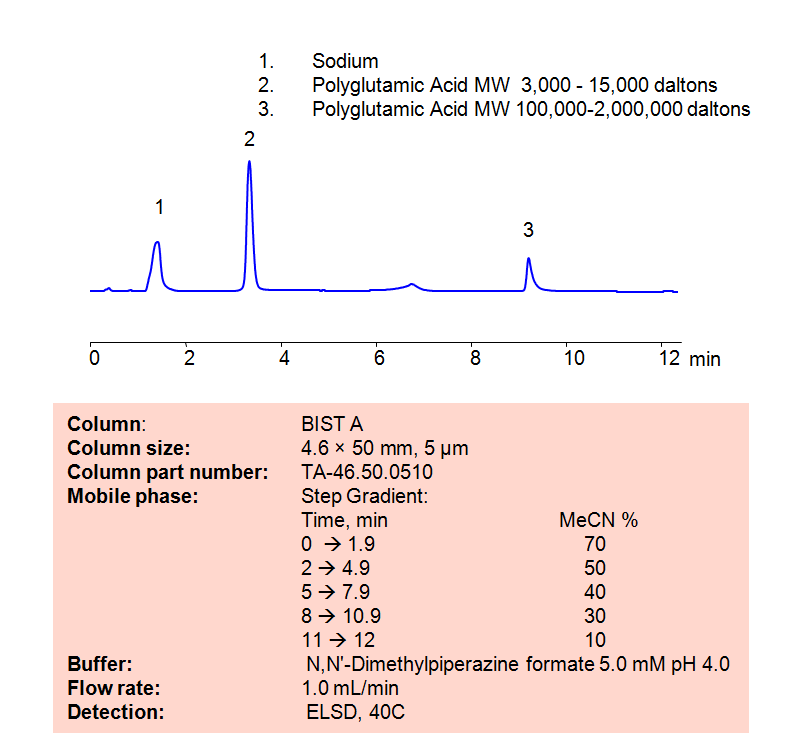
Polyglutamic acid (PGA) is a biopolymer consisting of repeating units of Glutamic acid. PGA can be found and used in a wide variety of industries due to its biodegradable, non-toxic properties, including in the food, medical, and wastewater industries. It has the chemical formula (C5H7NO3)n.
Using SIELC’s newly introduced BIST™ method, Polyglutamic Acid can be retained easily on a negatively-charged, cation-exchange BIST A column. There are two keys to this retention method: 1) a multi-charged, positive buffer, such as N,N’-Dimethylpiperazine (DMP), which acts as a bridge, linking the negatively-charged anion analytes to the negatively-charged column surface and 2) a mobile phase consisting mostly of organic solvent (such as MeCN) to minimize the formation of a solvation layer around the charged analytes. Other positively-charged buffers that can generate BIST™ include TMDAP, Calcium acetate, and Magnesium acetate. Using this new and unique analysis method, PGA can be retained with high selectivity and great peak shape. This method can be detected and is compatible with ELSD, CAD, and Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS).
Condition
| Column | BIST A, 4.6 x 50 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN |
| Buffer | N,N’-Dimethylpiperazine formate pH 4.0 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, 70C |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Acid, Polymer, Peptide |
| Analyzing Compounds | Polyglutamic Acid |
Application Column
BIST A
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 50 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended


