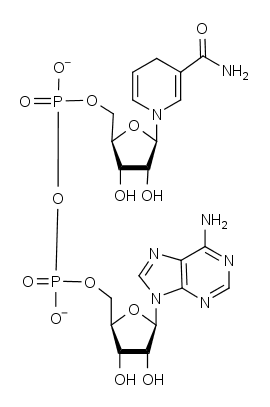
| CAS Number | 443892-10-2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H29N7O14P2 |
| Molecular Weight | 665.4 |
| InChI Key | BOPGDPNILDQYTO-NNYOXOHSSA-N |
| LogP | -5.7 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
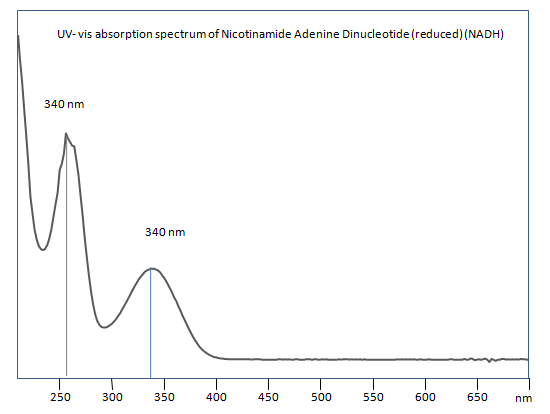
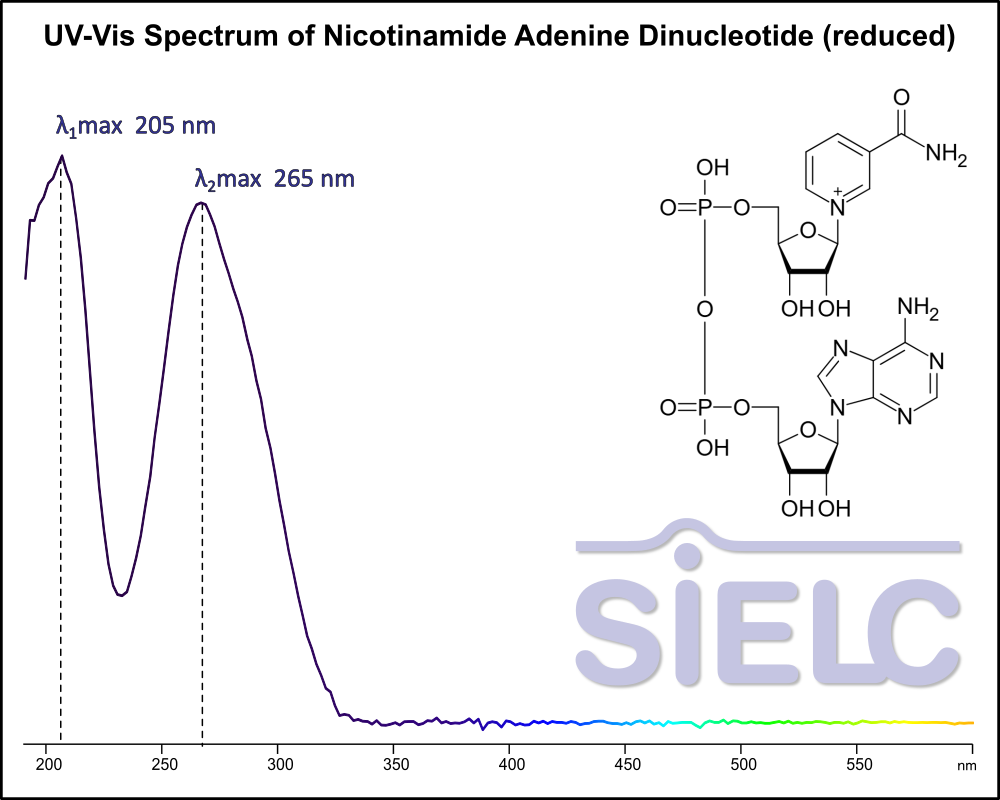
Uv-Vis Spectrum of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (reduced)
January 22, 2026
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (reduced) (NADH) check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

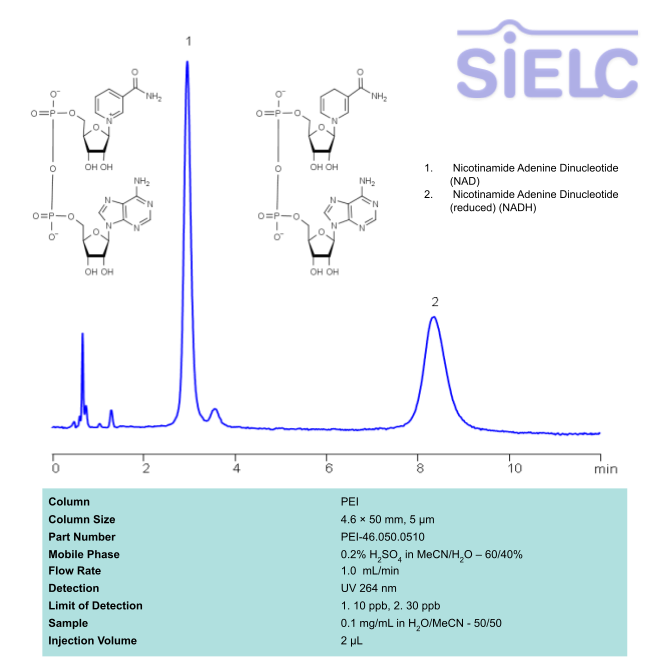
HPLC UV Method for Separation of NAD and NADH on PEI Column
January 20, 2026
HPLC Method for Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD), Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (reduced) (NADH) on PEI by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of SNAD and NADH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD), is a coenzyme found in every single living cell. NAD can exist in two forms: NAD+ and NADH. The conversion of NAD from its oxidized form (NAD+) to its reduced form (NADH), and back, provides the cell with a mechanism for accepting and donating electrons.
NAD and NADH can be retained, separated and UV detected at 264 nm using the PEI column with a simple mobile phase of acetonitrile (ACN) and water with sulfuric acid buffer and detected by UV.
| Column | PEI, 4.6 x 50 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 60/40% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/m |
| Detection | UV 264 nm |
| Class of Compounds | Drug |
| Analyzing Compounds | Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD), Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (reduced) (NADH) |
Application Column
PEI
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 50 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options:
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (reduced) (NADH)

HPLC Separation of NAD and NADH on PEI Column
July 22, 2021
HPLC Method for Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD), Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (reduced) (NADH) on PEI by SIELC Technologies
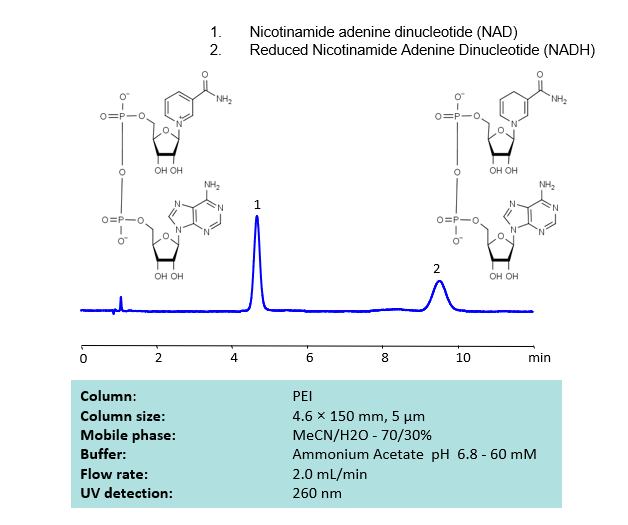
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of SNAD and NADH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD), is a coenzyme found in every single living cell. NAD can exist in two forms: NAD+ and NADH. The conversion of NAD from its oxidized form (NAD+) to its reduced form (NADH), and back, provides the cell with a mechanism for accepting and donating electrons.
NAD and NADH can be retained, separated and UV detected at 260 nm using the PEI column with a simple MS-compatible mobile phase of acetonitrile (ACN) and water with Ammonium Acetate (AmAc) buffer and detected by UV, ELSD, CAD or LC/MS.
| Column | PEI, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | Ammonium Acetate pH 6.8 – 60 mM |
| Flow Rate | 2.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 260 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug |
| Analyzing Compounds | Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD), Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (reduced) (NADH) |
Application Column
PEI
SIELC Technologies offers custom phases for customers who require specific separations not achievable with commercially available HPLC phases. Considering the vast array of compounds and mixtures requiring analysis, tailored LC phases can significantly enhance separation results for unique and challenging applications. To learn more about our special custom LC phases designed for your specific separation needs, please contact SIELC Technologies at research@sielc.com. Our team of experts is ready to guide you through the process and create a custom solution that addresses your particular chromatographic challenges.
Select optionsNicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (reduced) (NADH)