| CAS Number | 525-79-1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H9N5O |
| Molecular Weight | 215.217 |
| InChI Key | QANMHLXAZMSUEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 0.476 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
HPLC MS Method for the Analysis of Cytokinins: A Phytohormone Class and Brassinazole on Primesep 200 Column
September 11, 2024
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) MS Method for Analysis of trans-Zeatin, Kinetin, N6-(Δ2-Isopentenyl)adenine, Thidiazuron, 6-Benzylaminopurine, Brassinazole on Primesep 200 by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode SIELC Technologies
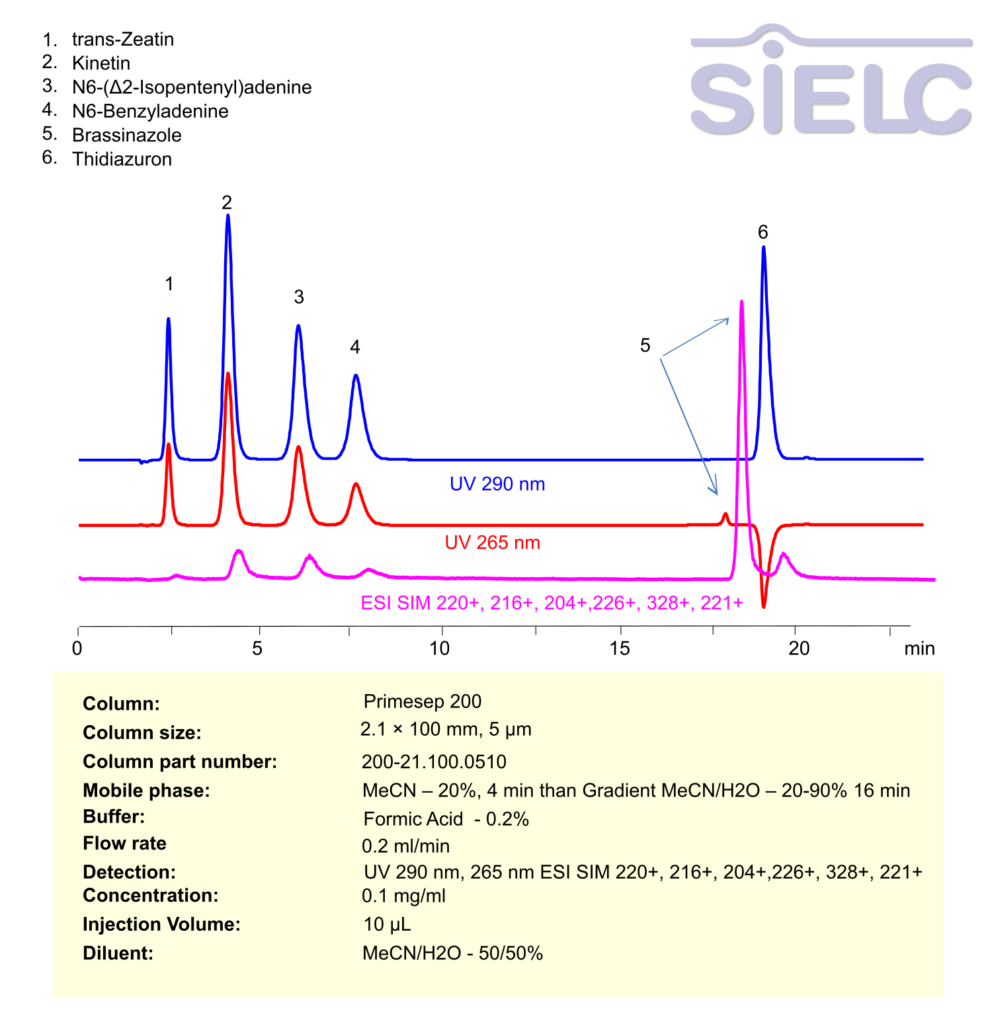
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of trans-Zeatin, Kinetin, N6-(Δ2-Isopentenyl)adenine, Thidiazuron, 6-Benzylaminopurine, Brassinazole
It looks like you’re listing a series of compounds, most of which are cytokinins or related plant hormones. Here’s a brief overview and classification for the compounds you mentioned:
trans-Zeatin:
- A type of cytokinin.
- Naturally occurring in plants and plays a key role in promoting cell division and growth.
Kinetin:
- A synthetic cytokinin.
- Used in plant tissue culture to stimulate cell division.
N6-(Δ2-Isopentenyl)adenine (iP):
- Another cytokinin.
- Found in plants and is involved in regulating growth, development, and differentiation.
N6-Benzyladenine (BA):
- A synthetic cytokinin.
- Commonly used in agricultural practices to enhance plant growth and delay senescence.
Brassinazole:
- Not a cytokinin, but a brassinosteroid biosynthesis inhibitor.
- Used to study the role of brassinosteroids (another class of phytohormones) in plants.
Thidiazuron (TDZ):
- A phenylurea derivative that acts as a cytokinin-like compound.
- Widely used in plant tissue culture to promote shoot regeneration and induce cytokinin-like effects.
trans-Zeatin, Kinetin, N6-(Δ2-Isopentenyl)adenine, Thidiazuron, 6-Benzylaminopurine, Brassinazole can be retained, separated and analyzed using a Primesep 200 mixed-mode stationary phase column. The analysis employs an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase comprising water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and formic acid as a buffer. This method allows for detection using UV 290, 265 nm.
You can find detailed UV spectra of trans-Zeatin, Kinetin, N6-(Δ2-Isopentenyl)adenine, Thidiazuron, 6-Benzylaminopurine, Brassinazole and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
| Column | Primesep 200, 2.1 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 20%, 4 min than Gradient MeCN/H2O – 20-90% 16 min |
| Buffer | Formic Acid -0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 0.2 mg/ml |
| Detection | UV 290 nm, 265 nm ESI SIM 220+, 216+, 204+,226+, 328+, 221+ |
| Class of Compounds | Phytohormone |
| Analyzing Compounds | trans-Zeatin, Kinetin, N6-(Δ2-Isopentenyl)adenine, Thidiazuron, 6-Benzylaminopurine, Brassinazole |
Application Column
Primesep 200
Column Diameter: 2.1 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Brassinazole
Kinetin
N6-(Δ2-Isopentenyl)adenine
Thidiazuron
trans-Zeatin
LC MS Detection

HPLC Method for Analysis of Kinetin Phytohormone on Primesep 100 Column
September 10, 2024
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) MS Method for Analysis of Kinetin on Primesep 100 by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode SIELC Technologies
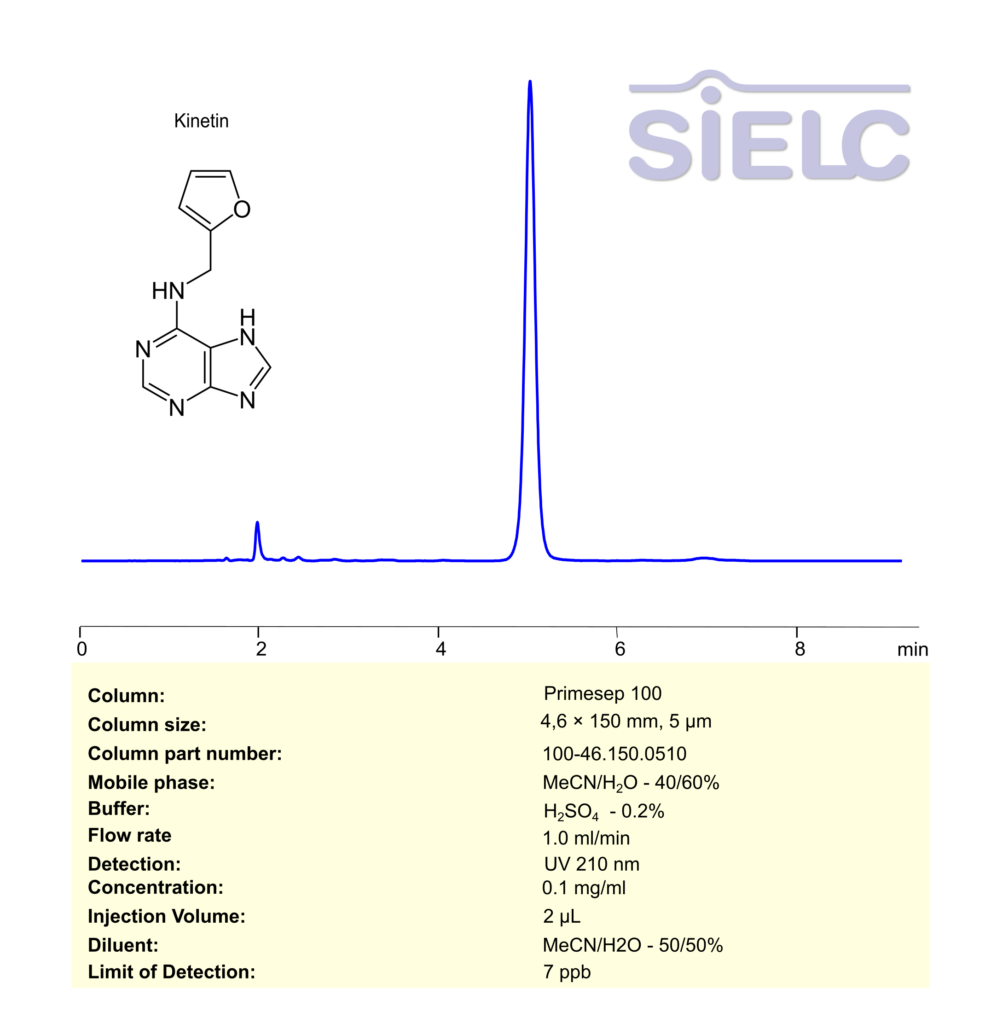
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Kinetin
Kinetin is a type of cytokinin, a class of phytohormones that play a crucial role in promoting cell division, growth, and delaying aging (senescence) in plants. It was one of the first cytokinins discovered and is often used in plant tissue culture and agriculture to enhance plant growth and development. Kinetin is a powerful cytokinin that is critical for cell division, shoot formation, and delaying aging in plants. Its application spans plant tissue culture, agriculture, and even the cosmetic industry.
Key Functions of Kinetin:
- Cell Division: Kinetin promotes cytokinesis (cell division), making it essential for plant tissue growth and regeneration.
- Shoot Formation: It supports the development of shoots and leaves, particularly in tissue culture where it helps balance root-to-shoot growth.
- Delay of Senescence: Kinetin delays the aging process in leaves by maintaining chlorophyll levels and preventing leaf yellowing, effectively slowing down senescence.
- Nutrient Mobilization: It helps in the transport and mobilization of nutrients within the plant, encouraging overall plant vitality and health.
Kinetin was first isolated from degraded DNA in herring sperm in 1955, though it is not commonly found in high concentrations in plants compared to other cytokinins like zeatin. However, kinetin is naturally occurring and has been detected in various plant tissues.
Applications:
- Plant Tissue Culture: Kinetin is frequently used in tissue culture media to promote shoot initiation and growth. It helps in the regeneration of plants from callus and explants.
- Agriculture: Kinetin is used to increase crop yields, improve seedling growth, and extend the shelf life of fruits and vegetables by delaying senescence.
- Cosmetics: Kinetin is also used in anti-aging skin care products due to its ability to delay aging processes in human skin cells, similar to how it affects plant tissues.
Mechanism of Action:
Kinetin binds to cytokinin receptors in plants, initiating a signaling cascade that leads to gene expression changes, promoting cell division and growth. Its action is often in opposition to auxins, and both hormones work together to balance root and shoot growth.
Kinetin can be retained, separated and analyzed using a Primesep 100 mixed-mode stationary phase column. The analysis employs an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase comprising water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and sulfuric acid as a buffer. This method allows for detection using UV 210 nm.
You can find detailed UV spectra of Kinetin and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
| Column | Primesep 100, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 40% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 -0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 210 nm |
| Sample | 0.1 mg/ml |
| Diluent | MeCN/H2O- 50/50% |
| LOD* | 7 ppb |
| Class of Compounds | Phytohormone |
| Analyzing Compounds | Kinetin |
Application Column
Primesep 100
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

UV-Vis Spectrum of Kinetin
September 9, 2024
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Kinetin check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

HPLC MS Method for Analysis of Kinetin Phytohormone on Primesep 200 Column
September 6, 2024
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) MS Method for Analysis of Kinetin on Primesep 200 by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode SIELC Technologies
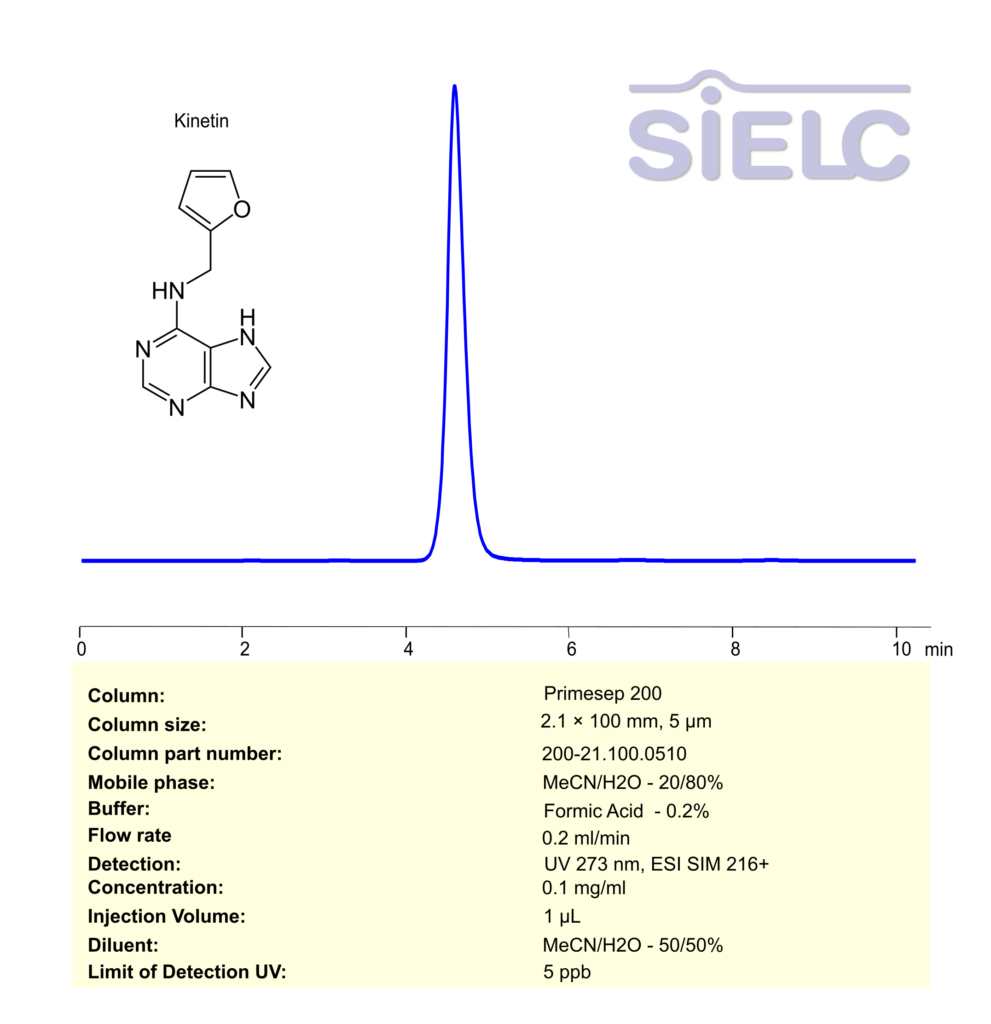
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Kinetin
Kinetin is a type of cytokinin, a class of phytohormones that play a crucial role in promoting cell division, growth, and delaying aging (senescence) in plants. It was one of the first cytokinins discovered and is often used in plant tissue culture and agriculture to enhance plant growth and development. Kinetin is a powerful cytokinin that is critical for cell division, shoot formation, and delaying aging in plants. Its application spans plant tissue culture, agriculture, and even the cosmetic industry.
Key Functions of Kinetin:
- Cell Division: Kinetin promotes cytokinesis (cell division), making it essential for plant tissue growth and regeneration.
- Shoot Formation: It supports the development of shoots and leaves, particularly in tissue culture where it helps balance root-to-shoot growth.
- Delay of Senescence: Kinetin delays the aging process in leaves by maintaining chlorophyll levels and preventing leaf yellowing, effectively slowing down senescence.
- Nutrient Mobilization: It helps in the transport and mobilization of nutrients within the plant, encouraging overall plant vitality and health.
Kinetin was first isolated from degraded DNA in herring sperm in 1955, though it is not commonly found in high concentrations in plants compared to other cytokinins like zeatin. However, kinetin is naturally occurring and has been detected in various plant tissues.
Applications:
- Plant Tissue Culture: Kinetin is frequently used in tissue culture media to promote shoot initiation and growth. It helps in the regeneration of plants from callus and explants.
- Agriculture: Kinetin is used to increase crop yields, improve seedling growth, and extend the shelf life of fruits and vegetables by delaying senescence.
- Cosmetics: Kinetin is also used in anti-aging skin care products due to its ability to delay aging processes in human skin cells, similar to how it affects plant tissues.
Mechanism of Action:
Kinetin binds to cytokinin receptors in plants, initiating a signaling cascade that leads to gene expression changes, promoting cell division and growth. Its action is often in opposition to auxins, and both hormones work together to balance root and shoot growth.
Kinetin can be retained, separated and analyzed using a Primesep 200 mixed-mode stationary phase column. The analysis employs an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase comprising water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and formic acid as a buffer. This method allows for detection using UV 273 nm.
You can find detailed UV spectra of Kinetin and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
| Column | Primesep 200, 2.1 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 20% |
| Buffer | Formic Acid -0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 0.2 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 273 nm, MS ESI SIM 216+ |
| Class of Compounds | Phytohormone |
| Analyzing Compounds | Kinetin |
Application Column
Primesep 200
Column Diameter: 2.1 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
LC MS Detection

Separation of Kinetin on Newcrom R1 HPLC column
May 16, 2018
Kinetin can be analyzed by this reverse phase (RP) HPLC method with simple conditions. The mobile phase contains an acetonitrile (MeCN), water, and phosphoric acid. For Mass-Spec (MS) compatible applications the phosphoric acid needs to be replaced with formic acid. Smaller 3 µm particles columns available for fast UPLC applications. This liquid chromatography method is scalable and can be used for isolation impurities in preparative separation. It also suitable for pharmacokinetics.
Application Column
Newcrom R1
The Newcrom columns are a family of reverse-phase-based columns. Newcrom A, AH, B, and BH are all mixed-mode columns with either positive or negative ion-pairing groups attached to either short (25 Å) or long (100 Å) ligand chains. Newcrom R1 is a special reverse-phase column with low silanol activity.
Select options




