HPLC Method for Analysis of Biopterin, Rhamnopterin, Neopterin, Folic Acid, Aminopterin on Primesep 100 by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
These compounds, including Biopterin, Rhamnopterin, Neopterin, Folic Acid, and Aminopterin, are all related to the chemical structure known as pterin. Pterins are a group of heterocyclic compounds composed of a pteridine ring system, which consists of two fused six-membered rings, a pyrimidine ring and a pyrazine ring. Here’s a brief overview of each:
- Biopterin (or Tetrahydrobiopterin): This is a coenzyme in the synthesis of several neurotransmitters, including dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. It also plays a role in the production of nitric oxide. Deficiencies in the enzyme that recycles tetrahydrobiopterin can lead to phenylketonuria (PKU), a metabolic disorder.
- Rhamnopterin:
- Neopterin: This pteridine derivative is produced by the human immune system upon activation by interferon-gamma and serves as a marker for immune system activation. Elevated levels can be found in various disorders, such as viral infections, autoimmune diseases, or malignancies.
- Folic Acid: Also known as vitamin B9, folic acid is crucial for many functions in the body, including DNA synthesis and repair, cell division, and growth. Folic acid must be obtained through diet or supplementation, as humans cannot synthesize it.
- Aminopterin: An antifolate (folic acid antagonist), aminopterin was one of the first chemotherapy drugs used to treat cancer. It works by inhibiting dihydrofolate reductase, an enzyme that converts folic acid to its active form, thereby interfering with cell growth and division. Aminopterin is highly toxic and has been largely replaced by less toxic and more effective drugs, such as methotrexate.
- It’s important to note that while these compounds all contain a pteridine ring, they have very different biological activities and uses. Always consult with a healthcare provider or relevant professionals for accurate information.
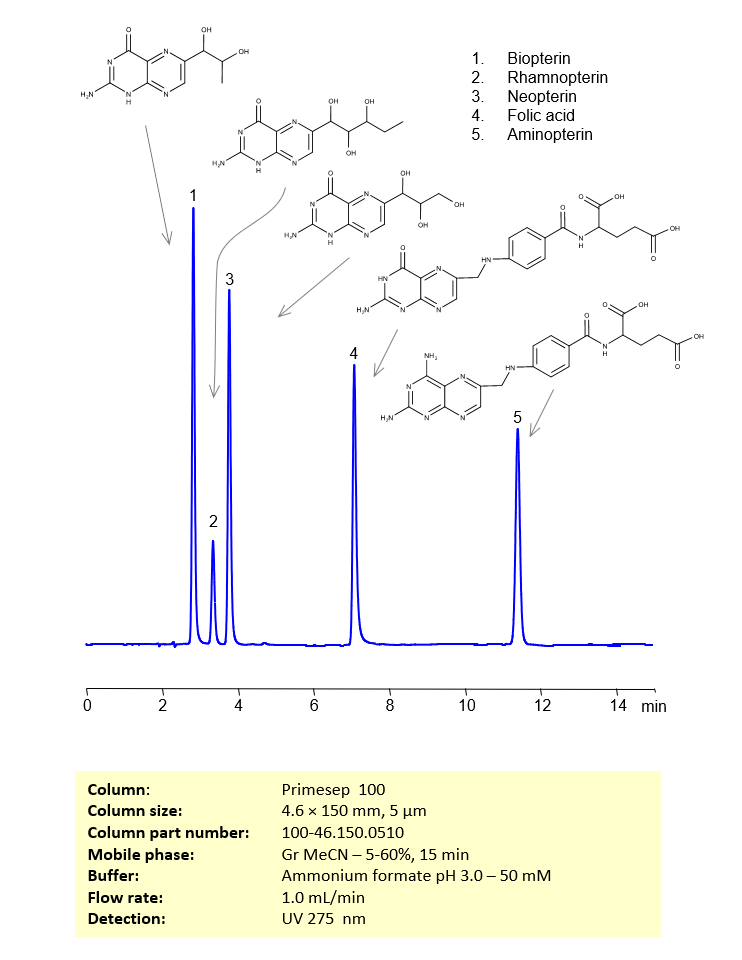
These five pterins can be retained, separated and analyzed using a reverse-phase Primesep 100, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended column. The mobile phase for this method consists of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and ammonium formate, which serves as a buffer. This analytical method can be monitored using UV detection at 275 nm, an Evaporative Light Scattering Detector (ELSD), or any other evaporative detection method such as Charged Aerosol Detection (CAD) or Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry (ESI-MS)
LOD was determined for this combination of instrument, method, and analyte, and it can vary from one laboratory to another even when the same general type of analysis is being performed.
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Biopterin, Rhamnopterin, Neopterin, Folic Acid, Aminopterin
Condition
| Column | Primesep 100, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN -5-60%, 10 min |
| Buffer | Ammonium formate pH 3.0 – 50 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 275 nm |
| Peak Retention Time | 2.21, 3.28, 3.81, 6.85, 11.21 min |
| Sample concentration | 0.02 mg/ml |
| Injection volume | 5 µl |
| Sample diluent | H2O + NaOH |
| LOD | 10 ppb |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Pteridines |
| Analyzing Compounds | Biopterin, Rhamnopterin, Neopterin, Folic Acid, Aminopterin |
Application Column
Primesep 100
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Biopterin
Folic Acid
Neopterin
Rhamnopterin