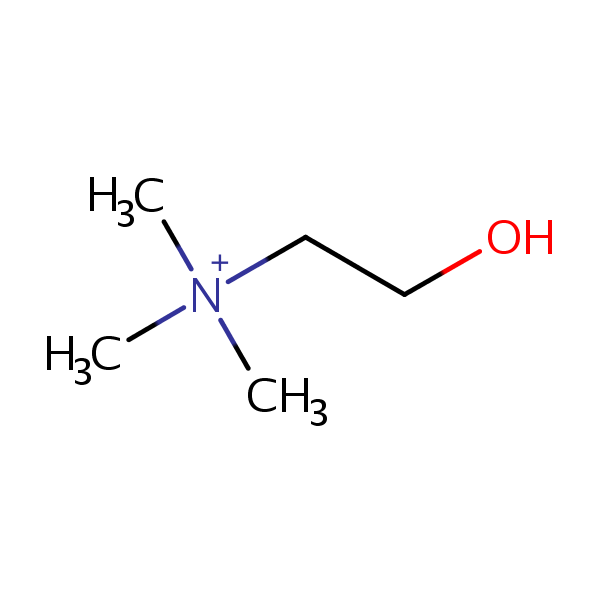
| CAS Number | 62-49-7 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C5H14NO |
| Molecular Weight | 104.172 |
| InChI Key | OEYIOHPDSNJKLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -2.81 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
ELSD HPLC Method for Analysis of Choline on Primesep 100 Column
January 20, 2025
HPLC Method for Choline on Primesep 100 by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Choline
Choline is an essential nutrient that plays a vital role in many physiological processes in the body. While it is not classified as a vitamin or mineral, it is often grouped with the B-complex vitamins due to its similar functions.
Sources of Choline:
Choline can be obtained through diet and is found in a variety of foods:
Rich Sources:
Eggs (especially the yolks)
Liver (beef and chicken)
Fish (salmon and cod)
Soybeans and soy products
Moderate Sources:
Broccoli
Brussels sprouts
Peanuts
Whole grains
Supplements:
Choline supplements, such as choline bitartrate, phosphatidylcholine, or citicoline, are available for those who may have difficulty getting enough through diet alone.
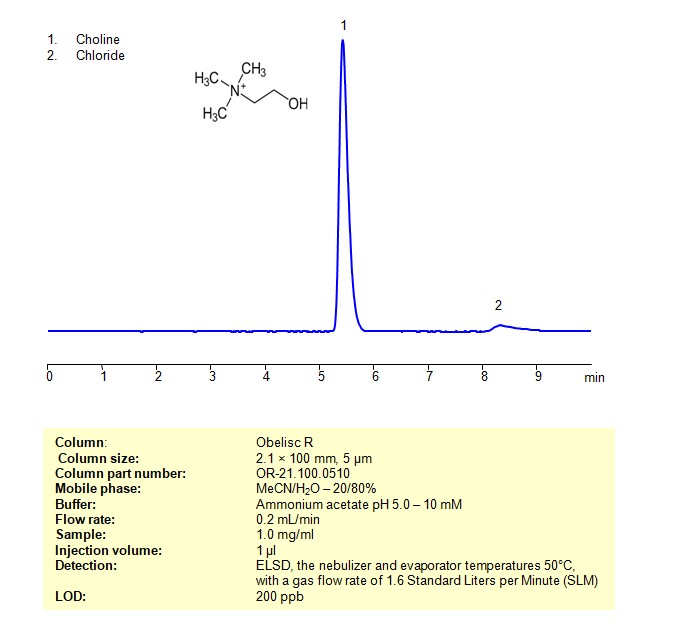
Choline can be retained, and analyzed using a Primesep 100 mixed-mode stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes a gradient method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and TFA as a buffer. Detection is carried out using ELSD
| Column | Primesep 100, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN 40% |
| Buffer | Ammonium Formate pH 3.0 – 40 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, the nebulizer and evaporator temperatures 50°C, with a gas flow rate of 1.6 Standard Liters per Minute (SLM) |
| LOD* | 3 ppm |
*LOD was determined for this combination of instrument, method, and analyte, and it can vary from one laboratory to another even when the same general type of analysis is being performed.
| Class of Compounds | Quaternary ammonium compounds (QACs) |
| Analyzing Compounds | Choline |
Application Column
Primesep 100
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

HPLC ELSD Method for Analysis Acetylcholine and Choline on Obelisc R Column
January 18, 2024
HPLC Method for Analysis of Acetylcholine, Choline on Obelisc R by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Acetylcholine, Choline
Acetylcholine and choline are related compounds that play distinct roles in the body, particularly in the nervous system.
- Choline:
- Definition: Choline is an essential nutrient that belongs to the B-vitamin complex.
- Chemical Structure: Choline is a quaternary ammonium salt containing a positively charged nitrogen atom and is often written as (N(CH_3)_3^+).
- Function: Choline serves as a precursor for the synthesis of various important molecules, including phospholipids (essential components of cell membranes) and the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Choline is crucial for maintaining cell membrane integrity and is involved in liver function.
- Dietary Sources: Choline is found in foods such as eggs, meat, fish, nuts, and certain vegetables. It can also be consumed as a dietary supplement.
- Acetylcholine:
- Definition: Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter, which is a chemical messenger that transmits signals between nerve cells (neurons) or from neurons to muscles.
- Chemical Structure: Acetylcholine is derived from the combination of choline and acetyl coenzyme A. Its chemical formula is (CH_3COOCH_2CH_2N(CH_3)_3^+).
- Function: Acetylcholine plays a crucial role in transmitting signals across synapses, including those between neurons and muscles (neuromuscular junctions). It is involved in muscle contraction, autonomic nervous system functions, and cognitive processes such as memory and learning.
- Synthesis and Release: Acetylcholine is synthesized within nerve cells and released into synapses upon a nerve impulse. Its action is terminated by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, which breaks it down in the synaptic cleft.
In summary, choline is a nutrient that the body uses to synthesize acetylcholine, among other important molecules. Acetylcholine, on the other hand, is a neurotransmitter responsible for transmitting signals in the nervous system. While choline is obtained from the diet or supplements, acetylcholine is a key mediator of nerve and muscle function in the body.
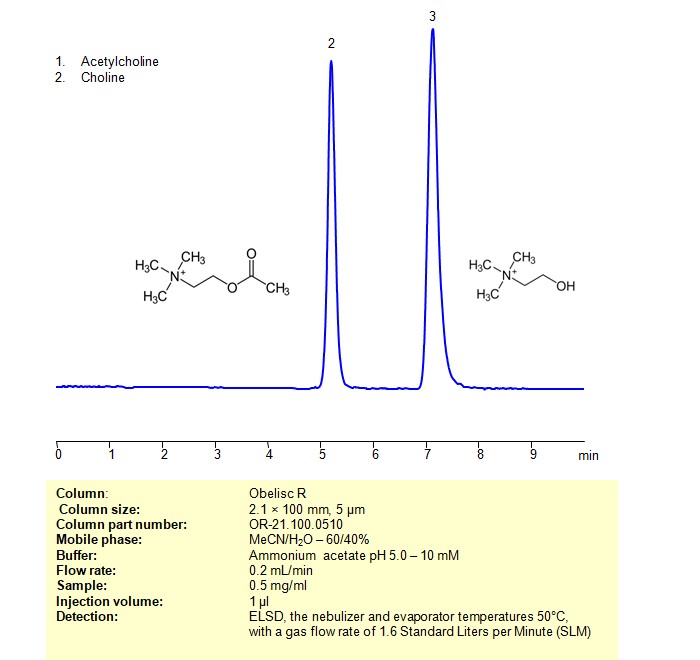
Acetylcholine and Choline can be retained, separated and analyzed using an Obelisc R mixed-mode stationary phase column. The analysis employs an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and ammonium acetate as a buffer. Detection is achieved using ELSD
| Column | Obelisc R, 2.1 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 60/40% |
| Buffer | Ammonium acetate pH 5.0 – 10 mM |
| Flow Rate | 0.2 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, the nebulizer and evaporator temperatures 50°C, with a gas flow rate of 1.6 Standard Liters per Minute (SLM) |
| Samples | 0.5 mg/ml |
| Injection volume | 1 µl |
| LOD* | 200 ppb |
| Class of Compounds | Quaternity amines |
| Analyzing Compounds | Acetylcholine, Choline |
Application Column
Obelisc R
Column Diameter: 2.1 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Choline

HPLC ELSD Method for Analysis of Choline on Obelisc R Column
January 15, 2024
HPLC Method for Analysis of Choline on Obelisc R by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Choline
Choline is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in various physiological processes in the body. It is often grouped with B-vitamins, but it is not officially recognized as a vitamin. Choline serves several important functions, including:
- Cell Membrane Structure: Choline is a component of phospholipids, essential structural components of cell membranes. It helps maintain the structural integrity and fluidity of cell membranes.
- Neurotransmitter Synthesis: Choline is a precursor to acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that is involved in muscle control, memory, and other cognitive functions. Adequate choline levels are important for maintaining proper neurotransmitter balance in the brain.
- Methyl Group Donor: Choline is a source of methyl groups, which are important for various biochemical reactions in the body, including the methylation of DNA, a process that regulates gene expression.
- Brain Development: Choline is particularly important during periods of rapid growth, such as fetal development and early childhood. Adequate choline intake during pregnancy is associated with better cognitive outcomes in children.
- Liver Function: Choline is involved in lipid metabolism and helps prevent the accumulation of fat in the liver. It is essential for the transport and metabolism of fats, and it plays a role in preventing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Muscle Function: Choline is involved in muscle movement and helps regulate the functioning of muscles.
Food Sources:
Choline is found in a variety of foods. Some good dietary sources of choline include:
- Eggs
- Meat, poultry, and fish
- Dairy products
- Nuts and seeds
- Certain vegetables, such as broccoli and Brussels sprouts
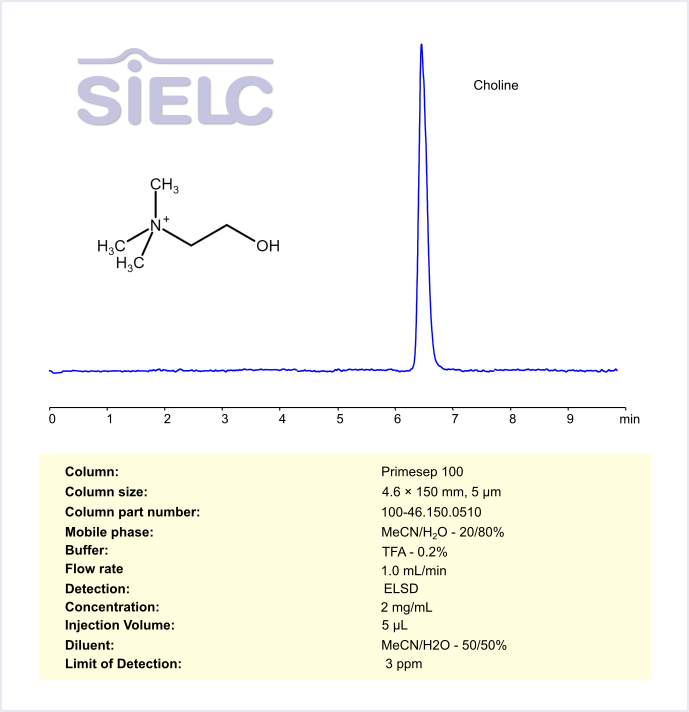
Choline can be retained and analyzed using an Obelisc R mixed-mode stationary phase column. The analysis employs an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and ammonium acetate as a buffer. Detection is achieved using ELSD
| Column | Obelisc R, 2.1 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 20/80% |
| Buffer | Ammonium acetate pH 5.0 – 10 mM |
| Flow Rate | 0.2 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, the nebulizer and evaporator temperatures 70°C, with a gas flow rate of 1.6 Standard Liters per Minute (SLM) |
| Samples | 1 mg/ml |
| Injection volume | 1 µl |
| LOD* | 200 ppb |
| Class of Compounds | Quaternity amines |
| Analyzing Compounds | Choline |
Application Column
Obelisc R
Column Diameter: 2.1 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

HPLC Method for Analysis of Choline on Obelisc R Column
October 10, 2018
HPLC Method for Choline on Obelisc R by SIELC Technologies
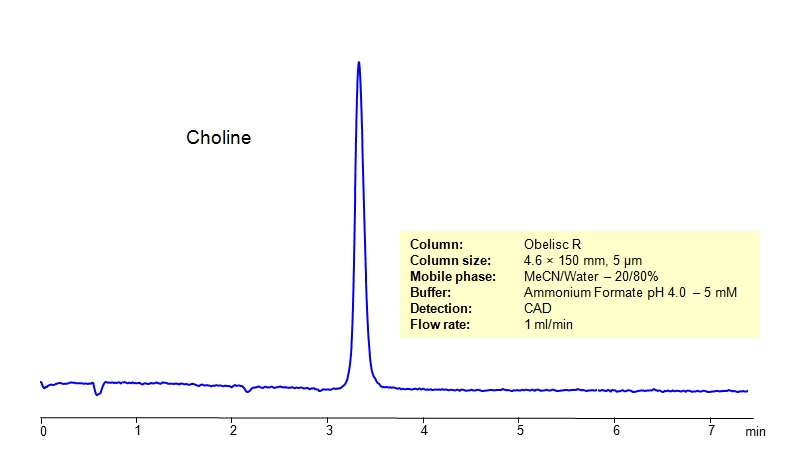
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Ion Exclusion
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method of Choline
Choline is a water-soluble vitamin-like essential nutrient. It is a constituent of lecithin, which is present in many plants and animal organs. Choline is a nutrient related to the B-vitamin family. First discovered in 1862, it wasn’t classified as an essential nutrient until very recently. It can be retained on an Obelisc R column, which has both positive and negative ion-pairs embedded in the stationary phase, allowing for the fine tuning and separation of a wide range of compounds with different ionic properties. Choline can be determined isocratically using a simple MS-compatible mobile phase of acetonitrile (ACN) and water with Ammonium Formate (AmFm) buffer and detected by ELSD, CAD or LC/MS.
| Column | Obelisc R, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 20/80% |
| Buffer | AmFm pH 4.0- 5 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | CAD (Corona) MS- compatible mobile phase |
| Class of Compounds | Drug, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | Choline |
Application Column
Obelisc R
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

HPLC Separation of Succinylcholine and Choline Using a Primesep 200 Column
July 11, 2012
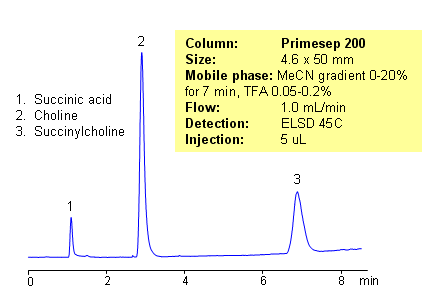
| Column | Primesep 200, 4.6×50 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN 0 – 20 %, 7 min |
| Buffer | TFA – 0.05-0.20% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD 45C |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Paralytic, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Succinic Acid, Succinylcholine, Choline |
Application Column
Primesep 200
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsSuccinic Acid
Succinylcholine