| Molecular Formula | C12H16K6O29S6 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 1051.2 |
| InChI Key | VIMPGLZYQCCLIC-NVBZBKOESA-H |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
HPLC Method for Analysis of Sucrose hexasulfate on BIST A+ Column
November 27, 2023
Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
HPLC Method for Analysis of Sucrose octasulfate on BIST A+ Column by SIELC Technologies
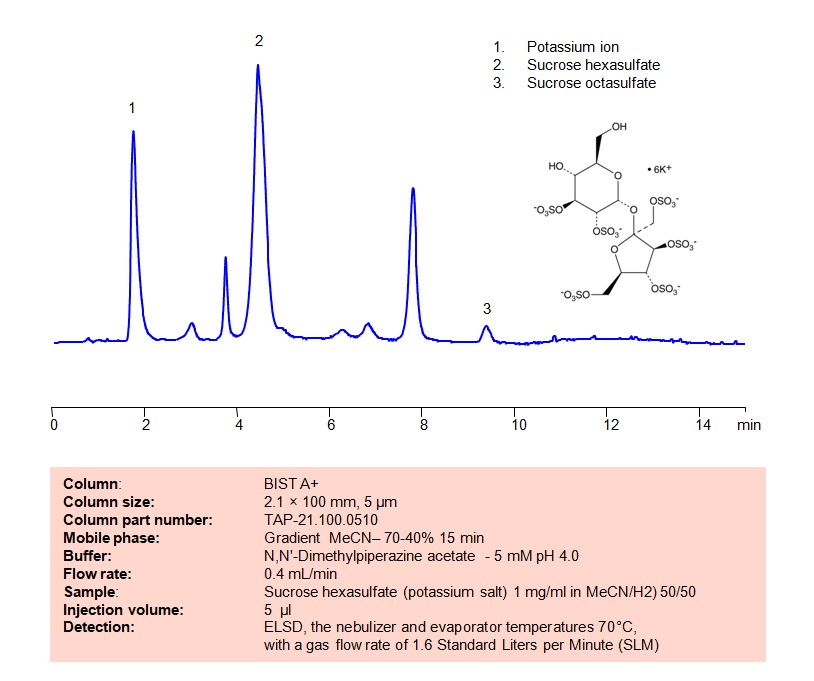
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Sucrose hexasulfate
Sucrose hexasulfate is a chemically modified form of sucrose, where six of the hydroxyl groups in the sucrose molecule are replaced with sulfate groups. This modification significantly alters the properties of the original sugar molecule.
- Structure: Sucrose is a disaccharide made up of glucose and fructose units. In sucrose hexasulfate, six of the hydroxyl (–OH) groups present in these sugar units are substituted with sulfate (–SO4) groups. This sulfation changes the molecule’s chemical behavior.
- Properties: The introduction of sulfate groups makes sucrose hexasulfate more acidic and highly polar compared to regular sucrose. These properties can affect its solubility, reactivity, and interactions with other molecules.
- Uses and Applications: Sucrose hexasulfate, like other sulfated polysaccharides, may have specialized applications in various fields, including biomedical research, pharmaceuticals, and potentially in industrial processes. These applications exploit the unique properties imparted by the sulfate groups.
- Biological and Environmental Impact: Sulfated derivatives of carbohydrates, including sucrose hexasulfate, can have different biological activities compared to their non-sulfated counterparts. They might interact differently with biological systems and could have distinct environmental impacts.
- Synthesis and Availability: The synthesis of sucrose hexasulfate is more complex than that of simple sugars, and it is typically produced for specific research or industrial purposes rather than being widely available as a commodity chemical.
Sucrose hexasulfate is a modified form of sucrose with unique chemical and physical properties due to the presence of sulfate groups, and its applications are more specialized compared to regular sucrose.
Using SIELC’s newly introduced BIST™ method, sucrose hexasulfate can be retained on a negatively-charged, cation-exchange BIST™ A column. There are two keys to this retention method: 1) a multi-charged, positive buffer, such as DMP acetate, which acts as a bridge, linking the negatively charged dye to the negatively-charged column surface and 2) a mobile phase consisting mostly of organic solvent (such as MeCN) to minimize the formation of a solvation layer around the charged analytes. Using this new and unique analysis method, oligonucleotide can be separated, retained, and detected at ELSD
Please read more on oligonucleotides analysis by HPLC in our April’s 2023 newsletter.
Condition
| Column | BIST A+, 2.1 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradienr MeCN – 70-40%, 15 min |
| Buffer | DMP acetate pH 4.0 – 5 mM |
| Flow Rate | 0.4 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, the nebulizer and evaporator temperatures 70°C, with a gas flow rate of 1.6 Standard Liters per Minute (SLM |
| Sample | 1 mg/ml in MeCN/H2O – 50/50% |
| Injection volume | 5 µl |
| LOD* |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Sulfated polysaccharides |
| Analyzing Compounds | Sucrose Hexasulfate |
Application Column
BIST A+
Column Diameter: 2.1 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended


