| CAS Number | 54-31-9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H11ClN2O5S |
| Molecular Weight | 330.740 |
| InChI Key | ZZUFCTLCJUWOSV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 2.03 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
Alltesta HPLC Method for Analysis of Furosemide (Tablet Dosage) on Primesep B
October 7, 2024
Alltesta HPLC Method for Furosemide on Primesep B by SIELC Technologies

High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Furosemide
Furosemide is a loop diuretic commonly used to treat conditions like edema (fluid retention) and hypertension (high blood pressure).
Furosemide can be retained, and analyzed using a Primesep B mixed-mode stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and sulfuric acid as a buffer. Detection is achieved using UV at 275 nm
| Column | Primesep B, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 50/50% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 -0.1% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 275 nm |
| Class of Compounds | Diuretic |
| Analyzing Compounds | Furosemide |
You can view examples of chromatograms obtained using the Allesta instrument and Sielc columns by clicking here.
Application Column
Primesep B
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

HPLC Method for Analysis of Furosemide on Primesep B Column
February 1, 2024
HPLC Method for Analysis of Furosemide on Primesep B by SIELC Technologies
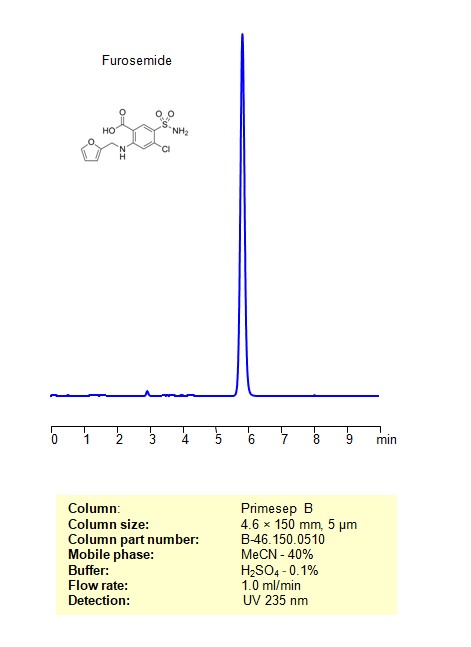
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Furosemide
Furosemide is a medication commonly used to treat conditions such as edema (fluid retention) and hypertension (high blood pressure). It belongs to a class of drugs known as loop diuretics. Furosemide works by increasing the excretion of water and salts (sodium and chloride) from the kidneys.
Mechanism of Action: Furosemide inhibits the reabsorption of sodium and chloride ions in the ascending loop of Henle in the kidneys. This leads to increased urine production and helps reduce fluid retention.
Uses: Furosemide is commonly prescribed for conditions such as edema associated with congestive heart failure, liver cirrhosis, and renal disease. It is also used to treat hypertension.
Furosemide can be retained, and analyzed using a Primesep B mixed-mode stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and sulfuric acid as a buffer. Detection is achieved using UV 235 nm
| Column | Primesep B, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 40% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.1% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 235 nm |
| Class of Compounds | Sulfonamides, sulphonamides, loop diuretics |
| Analyzing Compounds | Furosemide |
Application Column
Primesep B
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

Separation of Furosemide on Newcrom R1 HPLC column
February 16, 2018
Furosemide can be analyzed by this reverse phase (RP) HPLC method with simple conditions. The mobile phase contains an acetonitrile (MeCN), water, and phosphoric acid. For Mass-Spec (MS) compatible applications the phosphoric acid needs to be replaced with formic acid. Smaller 3 µm particles columns available for fast UPLC applications. This liquid chromatography method is scalable and can be used for isolation impurities in preparative separation. It also suitable for pharmacokinetics.
Application Column
Newcrom R1
The Newcrom columns are a family of reverse-phase-based columns. Newcrom A, AH, B, and BH are all mixed-mode columns with either positive or negative ion-pairing groups attached to either short (25 Å) or long (100 Å) ligand chains. Newcrom R1 is a special reverse-phase column with low silanol activity.
Select options



