| CAS Number | 331-39-5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H8O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 180.159 |
| InChI Key | QAIPRVGONGVQAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 1.15 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
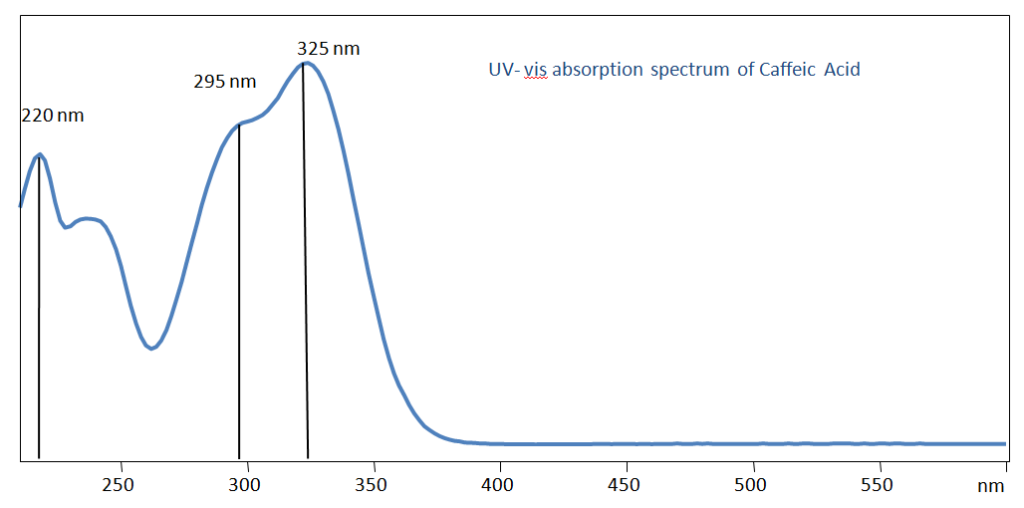
UV-Vis Absorption Spectrum of Caffeic Acid
December 18, 2025
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Caffeic acid check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

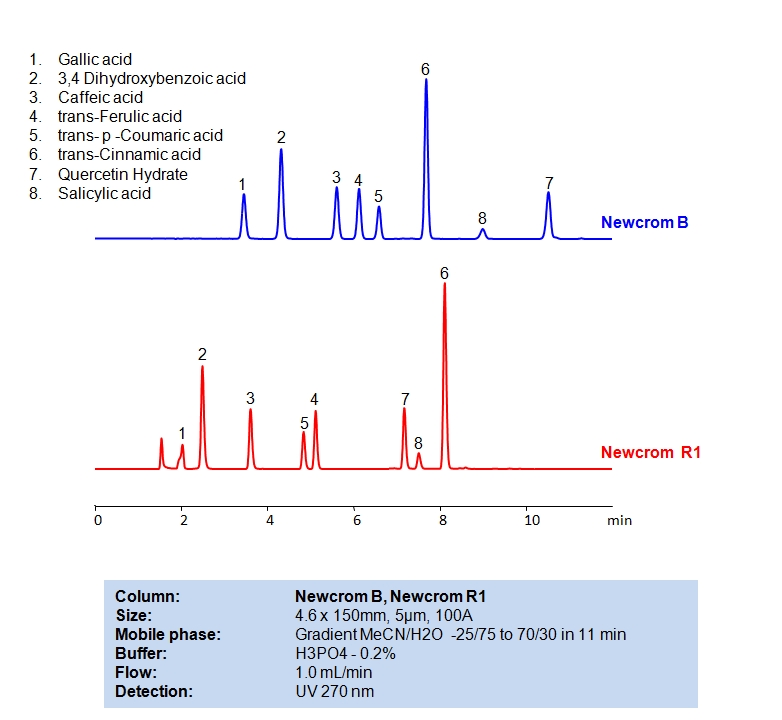
HPLC Separation of Phenolic Acids
March 11, 2021
HPLC Method for Gallic acid, 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, Caffeic acid, Ferulic acid, p-coumaric acid, Cinnamic acid, Salicylic acid, Quercetin on Newcrom B by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Gallic acid, 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, Caffeic acid, Ferulic acid, p-coumaric acid, Cinnamic acid, Salicylic acid, Quercetin.
Gallic acid is a naturally-occurring phenolic acid that was a key ingredient in European iron gall ink from its first discovery in the 12th century until the 19th century. In modern times, it’s heavy metal salt, Bismuth subgallate, known by its trade name Devrom, is known for its effects at deodorizing flatulence and stools. It has the chemical formula C7H6O5.
3,4 Dihydroxybenzoic acid, also known as Protocatechuic acid (PCA), is a dihydroxybenzoic acid with the chemical formula C7H6O4. It occurs naturally in stem bark of Boswellia dalzielii, leaves of Diospyros melanoxylon, Açai oil, and roselle. Commercially , it is produced of vanillin. You can find detailed UV spectra of 3,4 Dihydroxybenzoic acid and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
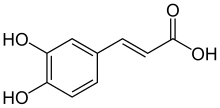
Caffeic acid is an organic compound with the formula (HO)2C6H3CH=CHCO2H. It plays a key role in scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS) that are generated during energy metabolism. Caffeic acid is an active ingredient in caffenol, which is a photographic developer made from instant coffee. Pharmacologically, it is used as an antioxidant in vitro and also in vivo. It also shows immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory activity.
trans-Ferulic acid is a hydroxycinnamic acid derivative with the chemical formula C10H10O4. It is classified as a phenolic phytochemical. Naturally, it can be found in a large number of vegetables, grain, and other plants. It is also released while sweetcorn is being cooked. Salts and esters derived from ferulic acid are called ferulates.
trans-p-Coumaric acid is a major phenolic acid with the chemical formula C9H8O3. It can be found in a wide variety of graminaceous plants. p-Coumaric acid is a natural metabolite contained in many edible plants and its antioxidant activities in reducing oxidative stress and inflammatory reactions have been demonstrated in various experiments.
trans-Cinnamic acid and benzoic acid are two of the major phenolic acids and autotoxins. Cinnamic acid occurs naturally in all green plants, showing significant antimicrobial activity against both bacteria and fungi as well as antioxidant activity. It has the chemical formula C9H8O2.
Quercetin Hydrate is a naturally occurring flavonol, or flavonoid, the yellowish antioxidant pigment found in skins of red grapes, apples, berries, onions, tomatoes, and buckwheat tea. In addition to functioning as a flavonoid, quercetin is also a phytoestrogen. It has the chemical formula C15H10O7.
Salicylic acid (SA) is an o-hydroxybenzoic acid, synthesized by both plants and microorganisms. SA acts as a critical plant hormone regulating various processes, including growth and development, flowering, thermogenesis, ion uptake, stomatal movement, photosynthesis, and plant immunity. SA also has medical applications as a topical treatment for a wide variety of skin conditions, including warts, dandruff, and acne.
Gallic acid, 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, Caffeic acid, Ferulic acid, p-coumaric acid, Cinnamic acid, Salicylic acid, Quercetin can be retained and analyzed using the Newcrom B stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water and acetonitrile (MeCN) with a phosphoric acid buffer. Detection is performed using UV.
| Column | Newcrom B, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN |
| Buffer | H3PO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | 270 nm |
| Column | Newcrom R1, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN |
| Buffer | H3PO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | 270 nm |
| Class of Compounds | Acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Gallic acid, 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, Caffeic acid, Ferulic acid, p-coumaric acid, Cinnamic acid, Salicylic acid, Quercetin |
Application Column
Newcrom B
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Newcrom R1
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Caffeic acid
Cinnamic acid
Ferulic acid
Gallic acid
Quercetin
Salicylic acid
p-coumaric acid

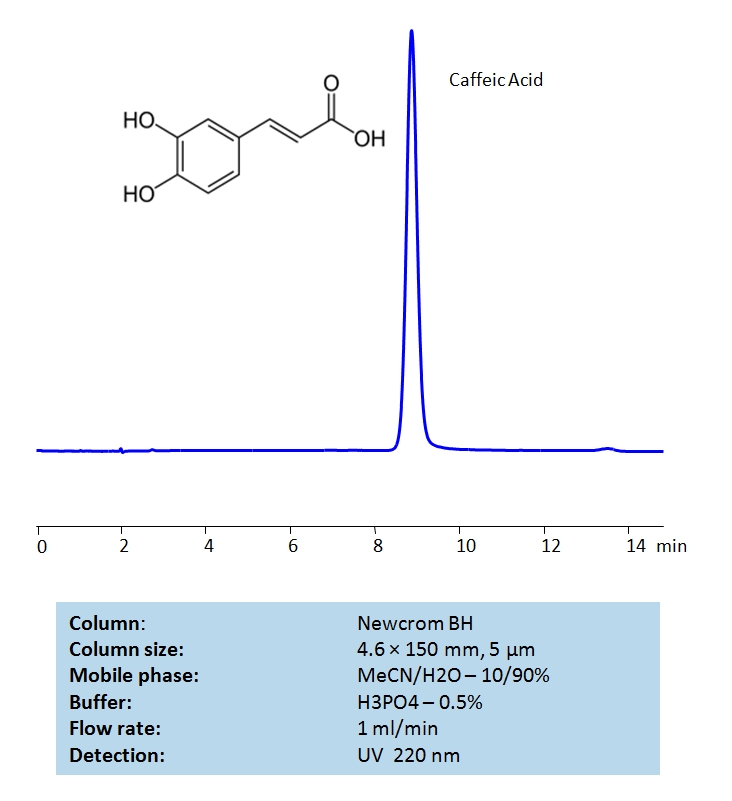
HPLC Method for Determination of Caffeic Acid on Newcrom BH
January 22, 2021
HPLC Method for Caffeic acid on Newcrom BH by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Caffeic acid.
Caffeic acid is a hydroxycinnamic acid, a naturally occurring organic compound. It is a type of phenolic acid found in beverages (such as wine, tea, coffee, and apple juice) and food (such as tomatoes, carrots, strawberries, blueberries, and wheat). It’s found in all plants as it is a key intermediate in the biosynthesis of lignin. Caffeic acid, like other polyphenols, is believed to exhibit many health benefits associated with its antioxidant properties, including the prevention of inflammation, cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and diabetes. Caffeic acid is an organic compound that is significant in the fields of pharmacology and biochemistry.
Caffeic acid is a hydroxycinnamic acid, a type of phenolic acid. Its molecular formula is C9H8O4.
The structure features a catechol group (a benzene ring with two hydroxyl groups) and a propenoic acid moiety.
Caffeic acid has antioxidant properties, helping to protect cells against oxidative stress. It exhibits anti-inflammatory, anticarcinogenic, and antiviral activities. The compound may also have neuroprotective effects and play a role in reducing cardiovascular diseases.
Uses in Research and Industry:
In research, it’s often studied for its potential health benefits.
In industry, it can be used as a precursor for the synthesis of more complex compounds.
Generally, it is considered safe at dietary levels, but like all compounds, it can be toxic at high concentrations.
Caffeic acid can be detected at low UV. Using Newcrom BH mixed-mode column and a mobile phase consisting of acetonitrile (ACN), and water with phosphoric acid (H3PO4) buffer, caffeic acid can be retained and UV detected at 220nm.
| Column | Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 10/90% |
| Buffer | H3PO4 – 0.5% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | 220 nm |
| Class of Compounds | Acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Caffeic acid |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

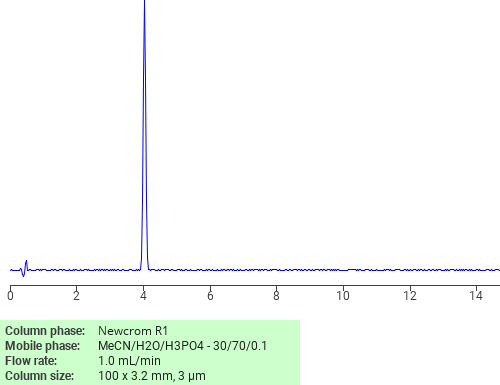
Separation of Caffeic acid on Newcrom R1 HPLC column
February 16, 2018
Caffeic acid can be analyzed by this reverse phase (RP) HPLC method with simple conditions. The mobile phase contains an acetonitrile (MeCN), water, and phosphoric acid. For Mass-Spec (MS) compatible applications the phosphoric acid needs to be replaced with formic acid. Smaller 3 µm particles columns available for fast UPLC applications. This liquid chromatography method is scalable and can be used for isolation impurities in preparative separation. It also suitable for pharmacokinetics.
Application Column
Newcrom R1
The Newcrom columns are a family of reverse-phase-based columns. Newcrom A, AH, B, and BH are all mixed-mode columns with either positive or negative ion-pairing groups attached to either short (25 Å) or long (100 Å) ligand chains. Newcrom R1 is a special reverse-phase column with low silanol activity.
Select options