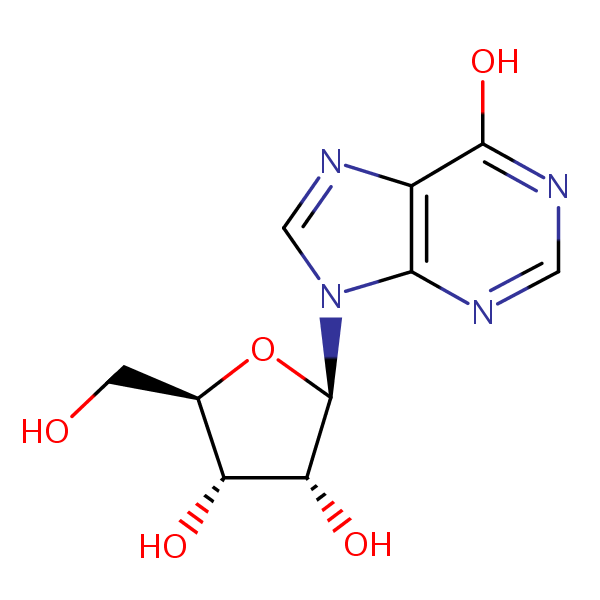
| CAS Number | 58-63-9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H12N4O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 268.230 |
| InChI Key | UGQMRVRMYYASKQ-KQYNXXCUSA-N |
| LogP | -2.10 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
Uv-Vis Spectrum of Inosine
January 14, 2026

If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Inosine check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

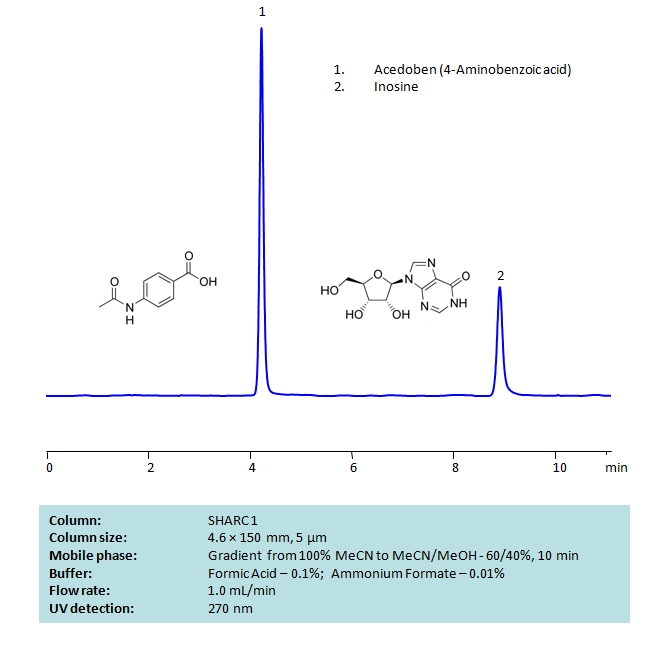
HPLC Separation of Acedoben and Inosine on SHARC 1 Column
December 21, 2020
HPLC Method for 4-Aminobenzoic Acid, Inosine on SHARC 1 by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of 4-Aminobenzoic Acid, Inosine.
Inosine pranobex is an antiviral drug. A combination of inosine and dimepranol acedoben (a salt of acetamidobenzoic acid and dimethylaminoisopropanol) has no effect on viral particles itself. Instead, it acts as an immunostimulant. It is most commonly used to treat the rare measles complication subacute sclerosing panencephalitis in conjunction with intrathecal interferon therapy.
Chromatography of these two compounds can be difficult due to their high polarity. But both compounds can be well retained and separated using anhydrous (water-free) conditions using HPLC on SHARC 1 column, which uses hydrogen-bonding as a separation mechanism. The method uses a gradient of acetonitrile (ACN) and methanol (MeOH) mobile phase with volatile buffer containing Formic Acid 0.1% and AmFm – 0.01%, making the method MS-compatible. Both compounds can also be UV detected at 270 nm.
| Column | SHARC 1, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/MeOH |
| Buffer | Formic Acid 0.1% , AmFm – 0.01% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 270 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Nucleoside monophosphate, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | 4-Aminobenzoic Acid, Inosine |
Application Column
SHARC 1
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Inosine

HPLC Analysis of Inosine on Legacy L1
August 6, 2015
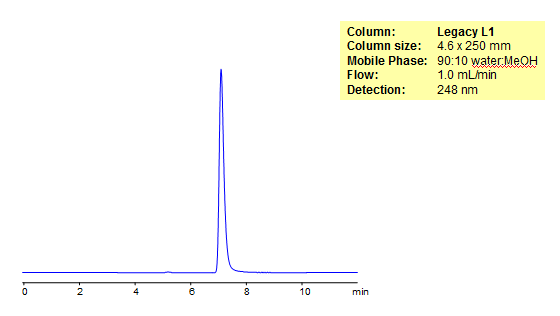
Inosine is a nucleoside made of a hypoxanthine and a ribose ring. As a drug, Inosine is useful for the treatment of various autoimmune diseases. Legacy L1 was used to retain Inosine by reverse phase mechanism. Legacy L1 uses embedded C18 groups on porous silica and is useful for many USP HPLC applications. comparisons to Phenomenex columns are available by request.
| Column | Legacy L1, 4.6×250 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeOH – 10% |
| Buffer | No |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 248 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Nucleoside, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Inosine |
Application Column
Legacy L1
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 250 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

HPLC Separation of Inosine and Deoxyinosine
July 11, 2012
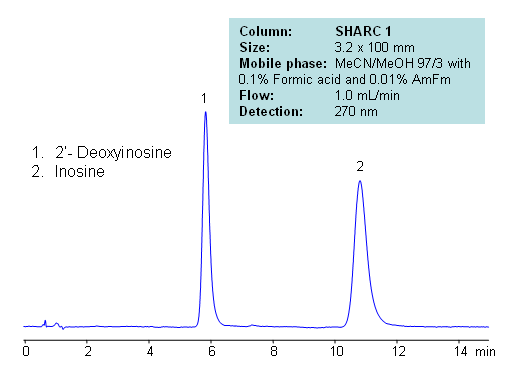
| Column | Sharc 1, 3.2×100 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/MeOH – 97/3% |
| Buffer | Formic Acid 0.1% , AmFm – 0.01% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 270 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Nucleoside monophosphate, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Inosine, Deoxyinosine |
Application Column
SHARC 1
The SHARC™ family of innovative columns represents the first commercially available columns primarily utilizing separation based on hydrogen bonding. SHARC stands for Specific Hydrogen-bond Adsorption Resolution Column. Hydrogen bonding involves an interaction or attraction between a bound hydrogen atom and molecules containing electronegative atoms, such as oxygen, nitrogen, and fluorine.
Select optionsInosine