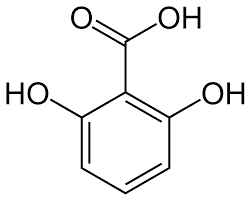
| CAS Number | 303-07-1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C7H6O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 154.12 |
| InChI Key | AKEUNCKRJATALU-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 2.2 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
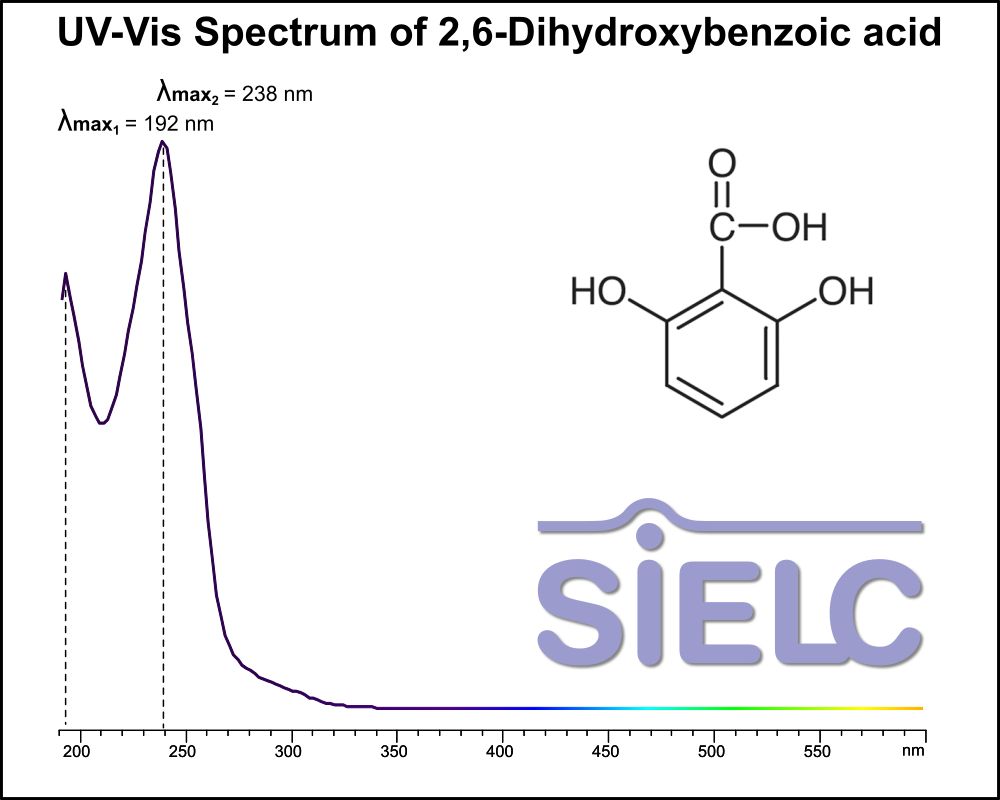
Uv-Vis Spectrum of 2,6-Dihydroxybenzoic
February 13, 2026
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze 2,6-Dihydroxybenzoic acid check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

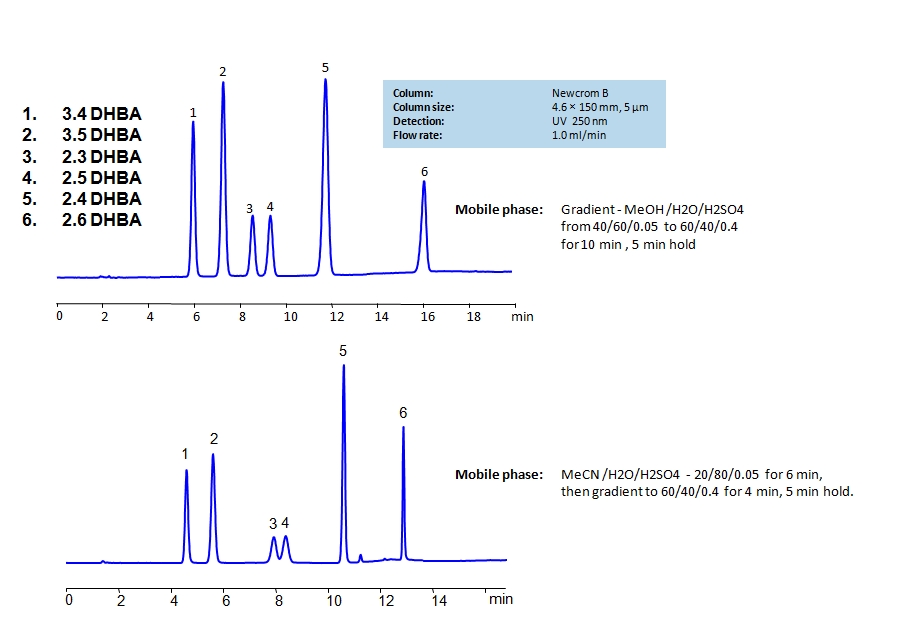
HPLC Separation of Dihydroxybenzoic Acids on Newcrom B Column
April 24, 2020
HPLC Method for 2,3-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, 2,4-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, 2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, 3,5-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, 2,6-Dihydroxybenzoic acid on Newcrom B by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of 2,3-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, 2,4-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, 2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, 3,5-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, 2,6-Dihydroxybenzoic acid.
Dihydroxybenzoic acids are aromatic compounds consisting of a phenolic ring and a carboxylic acid. They all have the same chemical formula C7H6O4.
The six main compounds are structurally similar and are difficult to separate in reverse-phase HPLC. The can be separated by using a mixed-mode Newcrom B column with the mobile phase having either methanol (MeOH) or acetonitrile (ACN) as an organic modifier having different retention characteristics. Using the gradient of organic modifier, water and sulfuric acid (H2SO4) as buffer, dihydroxybenzoic acids can be separated and UV detected at 250nm.
You can find detailed UV spectra of 2,3-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, 2,4-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, 2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, 3,5-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, 2,6-Dihydroxybenzoic acid and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following links for 3.4 DHBA, 3.5 DHBA, 2.4 DHBA, and 2.5 DHBA.
| Column | Newcrom B, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN |
| Buffer | H2SO4 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 250 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | 2,3-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, 2,4-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, 2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, 3,5-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, 2,6-Dihydroxybenzoic acid |
Application Column
Newcrom B
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
2,4-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid
2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid
2,6-Dihydroxybenzoic acid
3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid
3,5-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid