| CAS Number | 1197-18-8 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H15NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 157.213 |
| InChI Key | GYDJEQRTZSCIOI-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -0.894 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
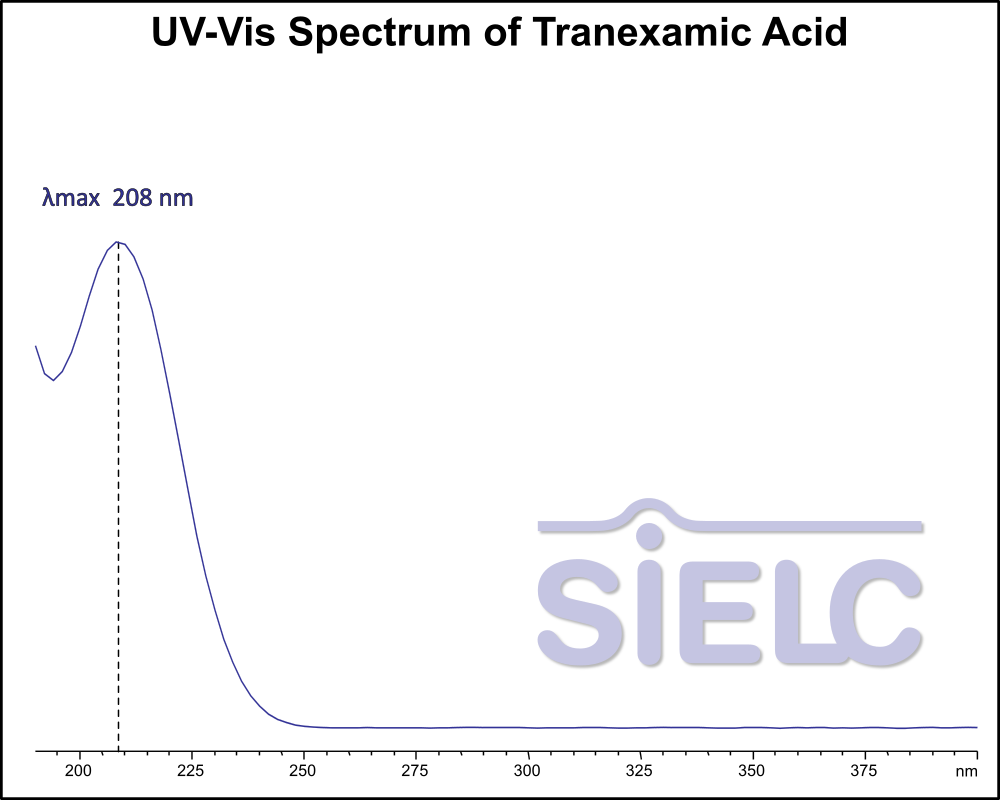
UV-Vis Spectrum of Tranexamic Acid
December 18, 2025
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Tranexamic acid check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

HPLC Method for Separation of Nicotinic Acid, Nicotinamide, Tranexamic Acid on Primesep 100 Column
March 28, 2024
HPLC Method for Separation of Nicotinic Acid, Nicotinamide, Tranexamic Acid on Primesep 100 Column
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode SIELC Technologies
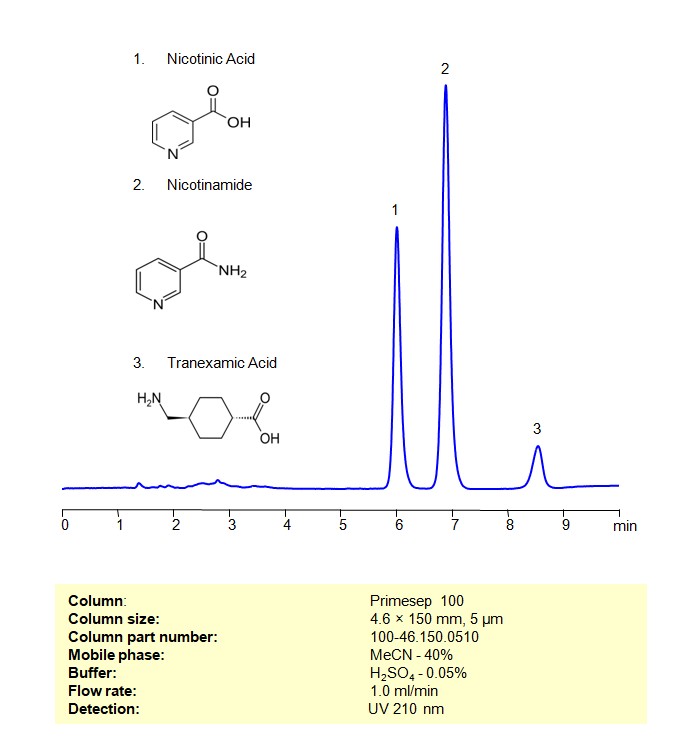
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Nicotinic Acid/Niacin (3-pyridinecarboxylic acid), Nicotinamide, Tranexamic acid
Nicotinic acid and nicotinamide are both forms of vitamin B3, also known as niacin. They play crucial roles in the body’s energy metabolism and are essential for maintaining the health of the skin, nervous system, and digestive system.
- Nicotinic Acid (Niacin): This is one of the two principal forms of vitamin B3. Nicotinic acid is commonly used as a dietary supplement to treat vitamin B3 deficiency, and it’s also prescribed in higher doses to help lower cholesterol levels. It works by dilating blood vessels, which can lead to a flushing sensation, hence it is sometimes referred to as “flushing niacin.”
- Nicotinamide: Also known as niacinamide, this is the other principal form of vitamin B3. Nicotinamide is a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a coenzyme involved in various cellular processes, including energy metabolism. Nicotinamide is often used in skincare products for its anti-inflammatory properties and its ability to improve the appearance of aging skin and reduce hyperpigmentation.
Tranexamic acid, on the other hand, is a synthetic derivative of the amino acid lysine. It is primarily used as an antifibrinolytic agent, meaning it helps to prevent the breakdown of blood clots. Tranexamic acid is commonly used to treat or prevent excessive bleeding, particularly in conditions such as heavy menstrual bleeding, traumatic hemorrhage, and during surgeries where significant blood loss is expected. Additionally, it has been investigated for its potential role in treating melasma, a common skin condition characterized by hyperpigmentation.
Each of these compounds has distinct biochemical properties and medical applications, but they all play important roles in human health and medicine.
Nicotinic Acid, Nicotinamide, Tranexamic Acid can be retained and separated using a Primesep 100 mixed-mode stationary phase column. The analysis employs an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase comprising water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and sulfuric acid as a buffer. This method allows for detection using UV at 210 nm
| Column | Primesep 100, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN 40% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.05% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 210nm |
| Class of Compounds | Acids |
| Analyzing Compounds | Nicotinic Acid/Niacin (3-pyridinecarboxylic acid), Nicotinamide, Tranexamic acid |
Application Column
Primesep 100
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Nicotinic Acid/Niacin (3-pyridinecarboxylic acid)
Tranexamic acid

HPLC – MS Method for Analysis of Tranexamic acid on Primesep 100 Column
December 20, 2023
HPLC Method for Analysis of Tranexamic acid on Primesep 100 by SIELC Technologies
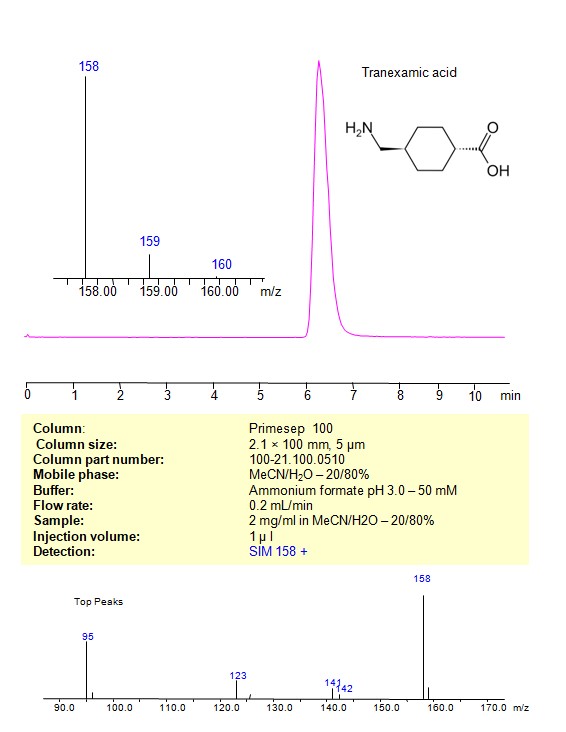
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Tranexamic acid
Tranexamic acid is a medication with significant roles in medicine, primarily used to treat or prevent excessive bleeding.
Chemical Structure: Tranexamic acid (TXA) is a synthetic derivative of the amino acid lysine. Its chemical formula is C8H15NO2. The structure features a lysine molecule with its amino group transformed into an amide.
Mechanism of Action: Tranexamic acid works by inhibiting the activation of plasminogen to plasmin, a molecule responsible for breaking down fibrin clots. By preventing the formation of plasmin, TXA reduces the breakdown of clots, thereby controlling bleeding.
Tranexamic acid is a valuable medication in controlling excessive bleeding in various medical contexts. Its use is supported by substantial research, particularly in emergency and surgical settings, though it must be used with consideration for its potential side effects and contraindications.
Tranexamic acid can be retained and analyzed on a Primesep 100 mixed-mode stationary phase column using an isocratic analytical method with a simple mobile phase of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN), and a ammonium format as a buffer. This analysis method can be detected an Evaporative Light Scattering Detector (ELSD), or any other evaporative detection method (CAD, ESI-MS)
| Column | Primesep 100, 2.1 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 20%, |
| Buffer | Ammonium Formate pH 3.0-50 mM |
| Flow Rate | 0.2 ml/min |
| Detection | SIM 158 + |
| LOD* | 0.2 ppm |
| Spray Voltage: | 1.5 kV |
| Nebulizing gas: | 1.5 L/min |
| Drying gas: | 15 L/min |
| DL temp: | 250 ˚C |
| Heat Block: | 400 ˚C |
| Class of Compounds | Amino acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Tranexamic acid |
Application Column
Primesep 100
Column Diameter: 2.1 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

HPLC Determination of Tranexamic acid (TXA) on Primesep 100 Column
July 2, 2021
HPLC Method for Analysis of Tranexamic acid on Primesep 100 by SIELC Technologies
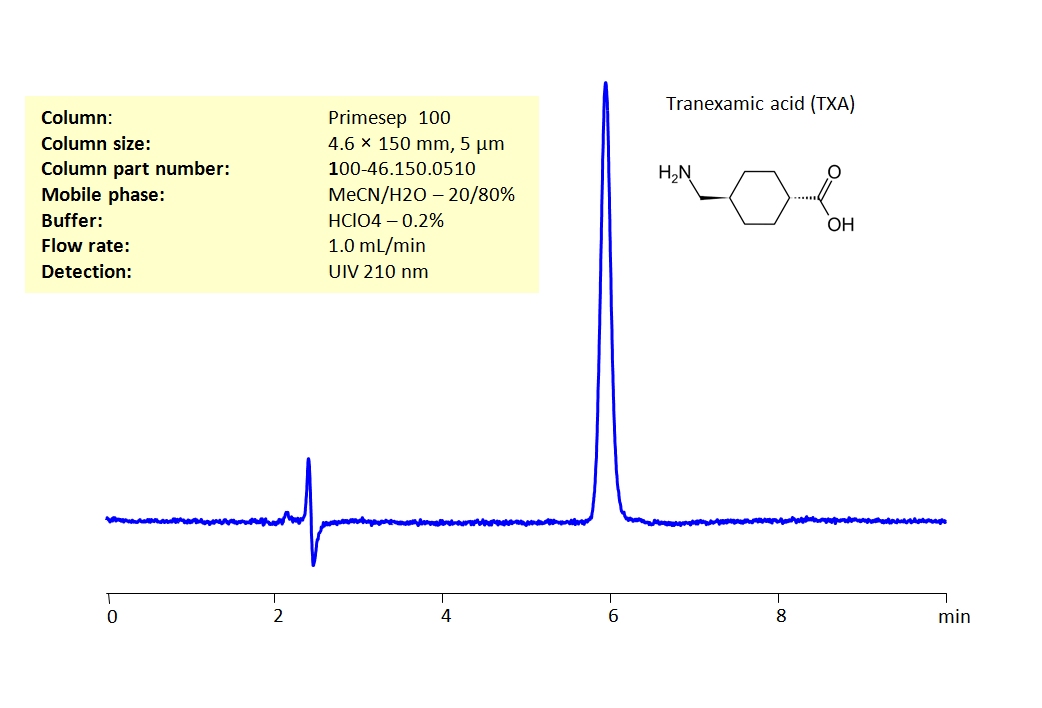
Tranexamic acid (TXA) is a synthetic derivative of the amino acid lysine. It is a medication used to treat or prevent excessive blood loss from major trauma, surgery, tooth removal, nosebleeds, and heavy menstruation. It is also used for hereditary angioedema. It can be taken by mouth, injected into a vein, or applied topically.
Tranexamic acid works by inhibiting the activation of plasminogen to plasmin, an enzyme that degrades fibrin clots, fibrinogen, and other proteins in the extracellular matrix. By inhibiting the activation of plasmin, tranexamic acid stabilizes clots and reduces bleeding.
Tranexamic acid can be retained on a Primesep 100 mixed-mode column with embedded acidic ion-pairing groups, having great peak shape using an isocratic method of acetonitrile (ACN), water and perchloric acid (HClO4) as a buffer. UV Detection 210nm.
| Column | Primesep 100, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 20/80% |
| Buffer | HClO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 210 nm |
| Class of Compounds | Acid, Drug |
| Analyzing Compounds | Tranexamic acid |
Application Column
Primesep 100
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

HPLC Determination of Tranexamic acid (TXA) on Primesep 200 Column
June 23, 2021
HPLC Method for Analysis of Tranexamic acid on Primesep 200 by SIELC Technologies
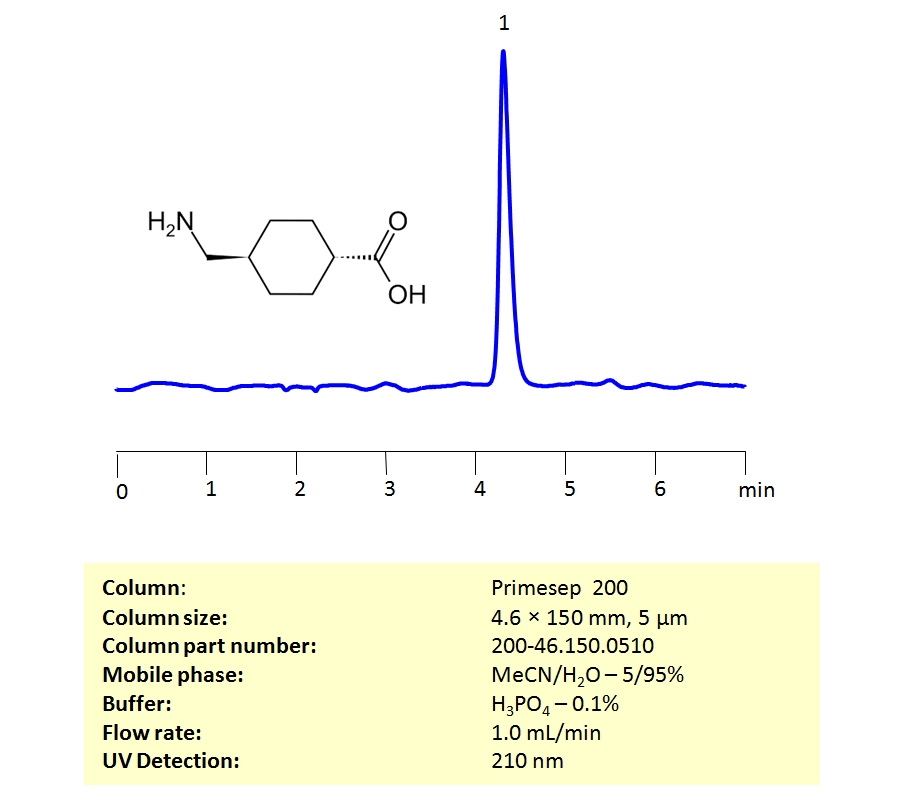
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Tranexamic acid.
Tranexamic acid is a synthetic derivative of the amino acid lysine. Tranexamic acid is an antifibrinolytic agent. It works by blocking the breakdown of blood clots, which prevents bleeding.
Tranexamic acid can be retained on a Primesep 200 mixed-mode column with embedded weak acidic ion-pairing groups, having great peak shape using an isocratic method of acetonitrile (ACN), water and phosphoric acid (H3PO4) as a buffer. UV Detection 210nm.
| Column | Primesep 200, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 5/95% |
| Buffer | H3PO4 – 0.1% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 210 nm |
| Class of Compounds | Acid, Drug |
| Analyzing Compounds | Tranexamic acid |
Application Column
Primesep 200
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

Separation of Tranexamic acid on Newcrom R1 HPLC column
February 16, 2018
Tranexamic acid can be analyzed by this reverse phase (RP) HPLC method with simple conditions. The mobile phase contains an acetonitrile (MeCN), water, and phosphoric acid. For Mass-Spec (MS) compatible applications the phosphoric acid needs to be replaced with formic acid. Smaller 3 µm particles columns available for fast UPLC applications. This liquid chromatography method is scalable and can be used for isolation impurities in preparative separation. It also suitable for pharmacokinetics.
Application Column
Newcrom R1
The Newcrom columns are a family of reverse-phase-based columns. Newcrom A, AH, B, and BH are all mixed-mode columns with either positive or negative ion-pairing groups attached to either short (25 Å) or long (100 Å) ligand chains. Newcrom R1 is a special reverse-phase column with low silanol activity.
Select options