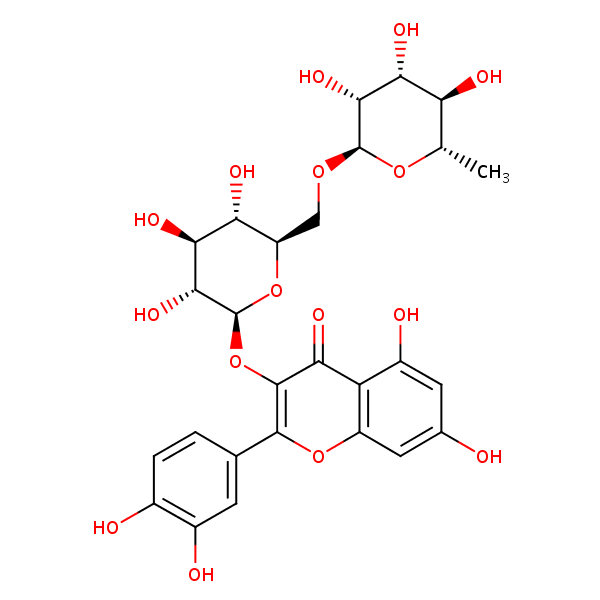
| CAS Number | 153-18-4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C27H30O16 |
| Molecular Weight | 610.521 |
| InChI Key | IKGXIBQEEMLURG-NVPNHPEKSA-N |
| LogP | 0.262 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
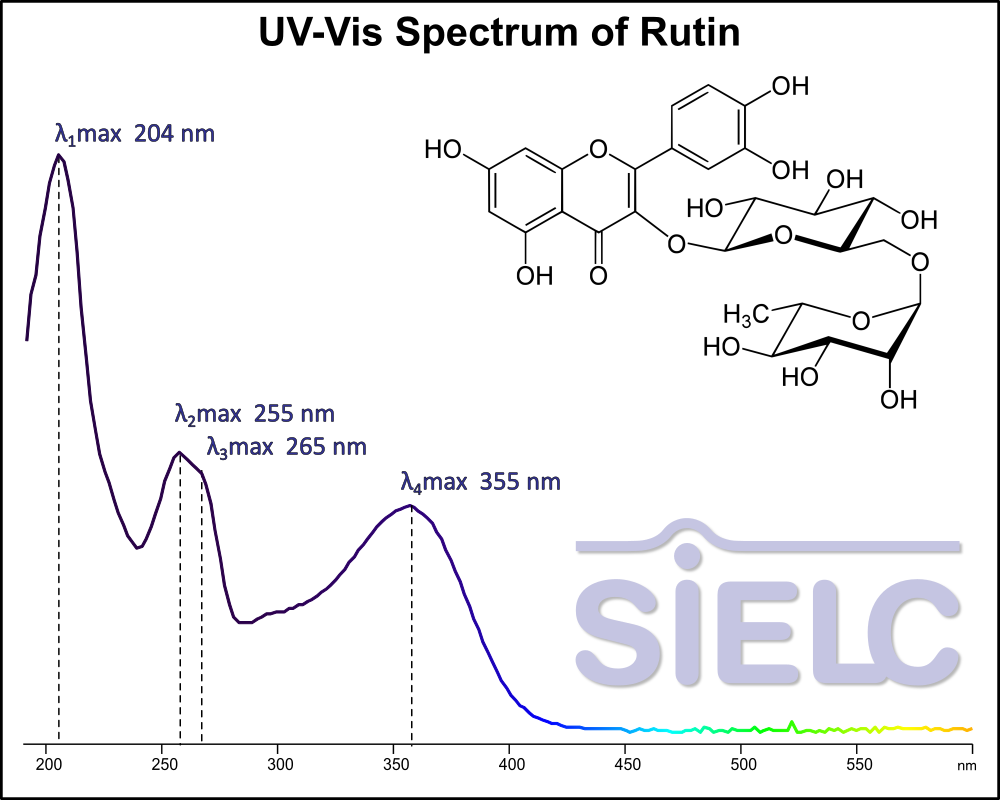
Uv-Vis Spectrum of Rutin
January 28, 2026
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Rutin check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

HPLC Method for Separation of Rutin and Kaempferol on Newcrom R1 Column
February 15, 2024
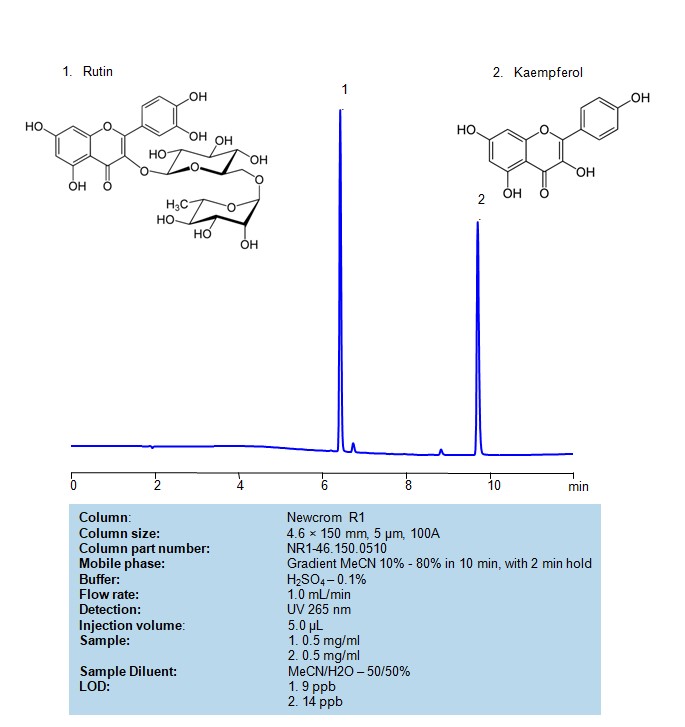
HPLC Method for Analysis of Rutin, Kaempferol on Newcrom R1 Column by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Reversed-phase
Rutin and kaempferol are both natural compounds found in various plants, particularly in fruits and vegetables. They belong to the class of flavonoids, which are a group of polyphenolic compounds known for their antioxidant properties and potential health benefits.
- Rutin:
- Chemical Structure: Rutin, also known as rutoside, quercetin-3-O-rutinoside, or vitamin P, is a glycoside of the flavonoid quercetin. It consists of quercetin bound to the disaccharide rutinose.
- Sources: Rutin is found in various foods, including citrus fruits, apples, berries, buckwheat, and green tea.
- Health Benefits: Rutin is known for its antioxidant properties and has been studied for potential benefits, such as supporting cardiovascular health, reducing inflammation, and promoting blood vessel health.
- Kaempferol:
- Chemical Structure: Kaempferol is a flavonol, a subtype of flavonoids. Its chemical structure includes a flavone backbone with hydroxyl groups.
- Sources: Kaempferol is present in various fruits and vegetables, such as apples, berries, tomatoes, broccoli, tea, and onions.
- Health Benefits: Kaempferol is recognized for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It has been studied for potential effects on reducing the risk of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular diseases and certain types of cancer. Additionally, it may have neuroprotective properties.
Both rutin and kaempferol are considered bioactive compounds, and their presence in a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables is associated with potential health benefits.
Rutin and kaempferolcan be retained, separated and analyzed on a reversed-phase Newcrom R1 column with a mobile phase consisting of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN), and sulfuric acid. This analytical method can be detected with high resolution and peak symmetry at a wavelength of 265 nm using UV detection
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analyses of Rutin, Kaempferol on Newcrom R1 Column by SIELC Technologies
Condition
| Column | Newcrom R1, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN – 10-90%,10 min , 5 min hold |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.1% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 265 nm |
| Injection volume: | 5.0 µL |
| Sample | 1. 0.5 mg/ml 2. 0.5 mg/ml |
| Sample Diluent | MeCN/H2O – 50/50% |
| LOD* | 1. 9 ppb 2. 14 ppb |
Description
| Class of Compounds | flavonoids |
| Analyzing Compounds | Rutin, Kaempferol |
Application Column
Newcrom R1
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Rutin

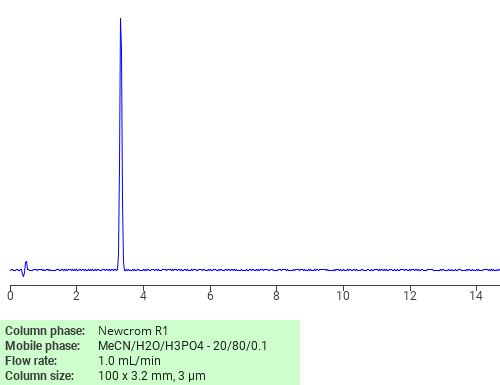
Separation of Rutin trihydrate on Newcrom R1 HPLC column
February 16, 2018
Rutin trihydrate can be analyzed by this reverse phase (RP) HPLC method with simple conditions. The mobile phase contains an acetonitrile (MeCN), water, and phosphoric acid. For Mass-Spec (MS) compatible applications the phosphoric acid needs to be replaced with formic acid. Smaller 3 µm particles columns available for fast UPLC applications. This liquid chromatography method is scalable and can be used for isolation impurities in preparative separation. It also suitable for pharmacokinetics.
Application Column
Newcrom R1
The Newcrom columns are a family of reverse-phase-based columns. Newcrom A, AH, B, and BH are all mixed-mode columns with either positive or negative ion-pairing groups attached to either short (25 Å) or long (100 Å) ligand chains. Newcrom R1 is a special reverse-phase column with low silanol activity.
Select options