| CAS Number | 9067-32-7 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C28H44N2NaO23+ |
| Molecular Weight | 799.6 |
| InChI Key | YWIVKILSMZOHHF-QJZPQSOGSA-N |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
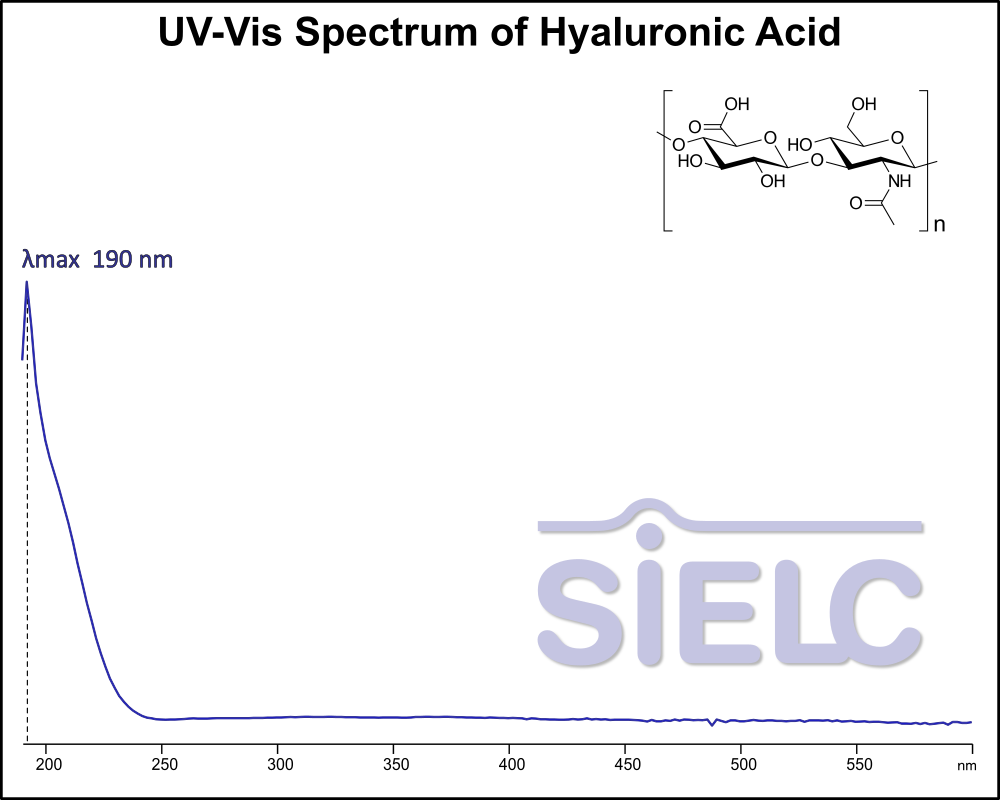
UV-Vis Spectrum of Hyaluronic Acid
December 18, 2025
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Hyaluronic Acid check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

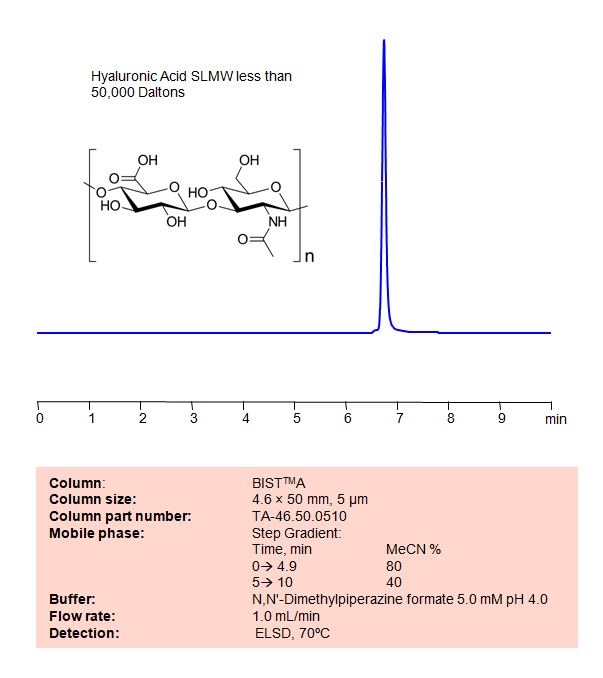
HPLC Method for Analysis of SLMW Hyaluronic Acid on BIST A Column
December 16, 2024
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Hyaluronic Acid on BIST A by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a glycosaminoglycan, a type of molecule made up of long chains of sugar molecules. It’s found naturally in many parts of the body, including the skin, eyes, and joints. Due to its unique properties, hyaluronic acid is used in a variety of medical and cosmetic applications. Here are some key points to know about hyaluronic acid:
- Moisture Retention: One of the most significant properties of HA is its ability to retain water. A single gram of HA can hold up to six liters of water. This makes it a crucial component in skin hydration. When the skin is adequately hydrated, it looks plump, luminous, and youthful.
- Aging and HA: The natural levels of hyaluronic acid in our body decrease as we age. This reduction is one of the factors contributing to the appearance of wrinkles, fine lines, and decreased skin hydration in older individuals.
- Cosmetic Uses: HA is commonly used as a dermal filler in cosmetic procedures. When injected into the skin, it can restore volume, reduce the appearance of wrinkles, and provide a more youthful look. It’s favored by many because of its natural origins and its temporary nature (as opposed to permanent fillers).
- Skincare Products: Due to its hydrating properties, hyaluronic acid is a common ingredient in skincare products like serums, moisturizers, and face masks. It helps draw moisture to the skin, making it look plumper and more hydrated.
- Joint Health: Hyaluronic acid is also found in the synovial fluid of the joints, where it provides lubrication. In some cases, it’s injected directly into the joints as a treatment for osteoarthritis.
- Eye Surgery: In ophthalmology, HA can be used as a viscoelastic agent in procedures like cataract surgery. It helps maintain the shape of the eye during surgery.
- Safety and Side Effects: When used as a dermal filler, there might be side effects like redness, swelling, or bruising at the injection site. These effects are typically temporary. For skincare products, while hyaluronic acid is generally considered safe for most skin types, it’s always a good idea to do a patch test first to ensure there’s no allergic reaction.
- Natural Sources: Hyaluronic acid can be derived from several sources. Some commercial HA is extracted from rooster combs, while others are produced by bacteria in a lab setting. The latter is often preferred in cosmetics due to potential allergens in animal-derived HA.
If you’re considering using products with hyaluronic acid or having procedures that involve HA, it’s essential to consult with a dermatologist or medical professional to ensure it’s the right choice for you.
Using SIELC’s newly introduced BIST™ method, however, hyaluronic acid can be retained, analyzed on a negatively-charged, cation-exchange BIST™ A column. There are two keys to this retention method: 1) a multi-charged, positive buffer, such as N,N’-Dimethylpiperazine (DMP), which acts as a bridge, linking the negatively-charged anion analytes to the negatively-charged column surface and 2) a mobile phase consisting mostly of organic solvent (such as MeCN) to minimize the formation of a solvation layer around the charged analytes. Other positively-charged buffers that can generate BIST™ include TMDAP, Calcium acetate, and Magnesium acetate. Using this new and unique analysis method, hyaluronic acid retained with high selectivity and great peak shape. This method can be detected and is compatible with ELSD, CAD, and Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS).
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analyses of Hyaluronic Acid
Condition
| Column | BIST A, 4.6 x 50 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Step gradient MeCN |
| Buffer | N,N’-Dimethylpiperazine formate 5.0 mM pH 4.0 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, the nebulizer and evaporator temperatures 70 °C, with a gas flow rate of 1.6 Standard Liters per Minute (SLM) (MS- compatible mobile phase) |
| Peak Retention Time | 6.77 min |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Glycosaminoglycan |
| Analyzing Compounds | Hyaluronic Acid |
Application Column
BIST A
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 50 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

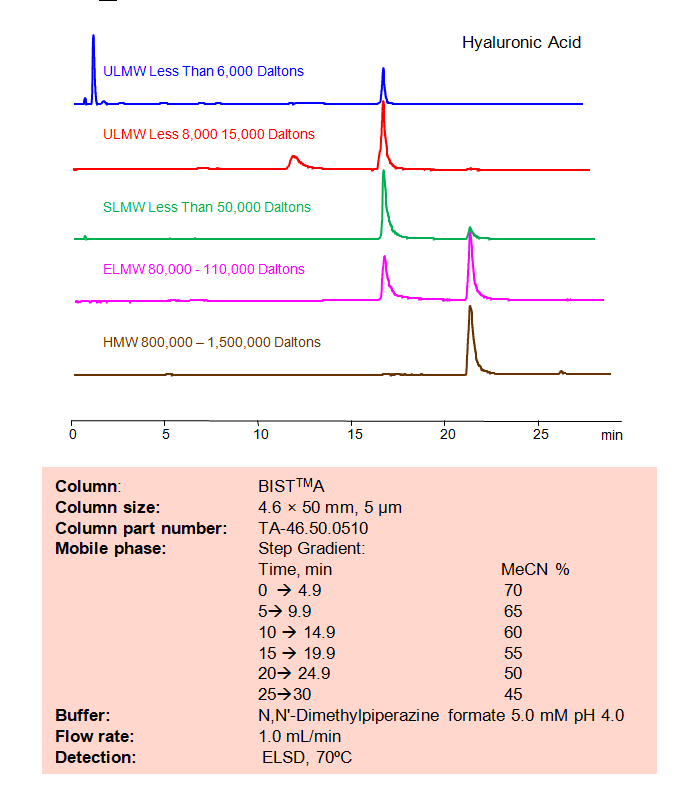
HPLC Method for Analysis of Hyaluronic Acid on BIST A Column
August 25, 2023
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Hyaluronic Acid on BIST A by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a glycosaminoglycan, a type of molecule made up of long chains of sugar molecules. It’s found naturally in many parts of the body, including the skin, eyes, and joints. Due to its unique properties, hyaluronic acid is used in a variety of medical and cosmetic applications. Here are some key points to know about hyaluronic acid:
- Moisture Retention: One of the most significant properties of HA is its ability to retain water. A single gram of HA can hold up to six liters of water. This makes it a crucial component in skin hydration. When the skin is adequately hydrated, it looks plump, luminous, and youthful.
- Aging and HA: The natural levels of hyaluronic acid in our body decrease as we age. This reduction is one of the factors contributing to the appearance of wrinkles, fine lines, and decreased skin hydration in older individuals.
- Cosmetic Uses: HA is commonly used as a dermal filler in cosmetic procedures. When injected into the skin, it can restore volume, reduce the appearance of wrinkles, and provide a more youthful look. It’s favored by many because of its natural origins and its temporary nature (as opposed to permanent fillers).
- Skincare Products: Due to its hydrating properties, hyaluronic acid is a common ingredient in skincare products like serums, moisturizers, and face masks. It helps draw moisture to the skin, making it look plumper and more hydrated.
- Joint Health: Hyaluronic acid is also found in the synovial fluid of the joints, where it provides lubrication. In some cases, it’s injected directly into the joints as a treatment for osteoarthritis.
- Eye Surgery: In ophthalmology, HA can be used as a viscoelastic agent in procedures like cataract surgery. It helps maintain the shape of the eye during surgery.
- Safety and Side Effects: When used as a dermal filler, there might be side effects like redness, swelling, or bruising at the injection site. These effects are typically temporary. For skincare products, while hyaluronic acid is generally considered safe for most skin types, it’s always a good idea to do a patch test first to ensure there’s no allergic reaction.
- Natural Sources: Hyaluronic acid can be derived from several sources. Some commercial HA is extracted from rooster combs, while others are produced by bacteria in a lab setting. The latter is often preferred in cosmetics due to potential allergens in animal-derived HA.
If you’re considering using products with hyaluronic acid or having procedures that involve HA, it’s essential to consult with a dermatologist or medical professional to ensure it’s the right choice for you.
Using SIELC’s newly introduced BIST™ method, however, hyaluronic acid can be retained, analyzed on a negatively-charged, cation-exchange BIST™ A column. There are two keys to this retention method: 1) a multi-charged, positive buffer, such as N,N’-Dimethylpiperazine (DMP), which acts as a bridge, linking the negatively-charged anion analytes to the negatively-charged column surface and 2) a mobile phase consisting mostly of organic solvent (such as MeCN) to minimize the formation of a solvation layer around the charged analytes. Other positively-charged buffers that can generate BIST™ include TMDAP, Calcium acetate, and Magnesium acetate. Using this new and unique analysis method, hyaluronic acid retained with high selectivity and great peak shape. This method can be detected and is compatible with ELSD, CAD, and Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS).
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analyses of Hyaluronic Acid
Condition
| Column | BIST A, 4.6 x 50 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Step gradient MeCN |
| Buffer | N,N’-Dimethylpiperazine formate 5.0 mM pH 4.0 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, the nebulizer and evaporator temperatures 70 °C, with a gas flow rate of 1.6 Standard Liters per Minute (SLM) (MS- compatible mobile phase) |
| Peak Retention Time | 16.74, 22.37 min |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Glycosaminoglycan |
| Analyzing Compounds | Hyaluronic Acid |
Application Column
BIST A
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 50 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended


