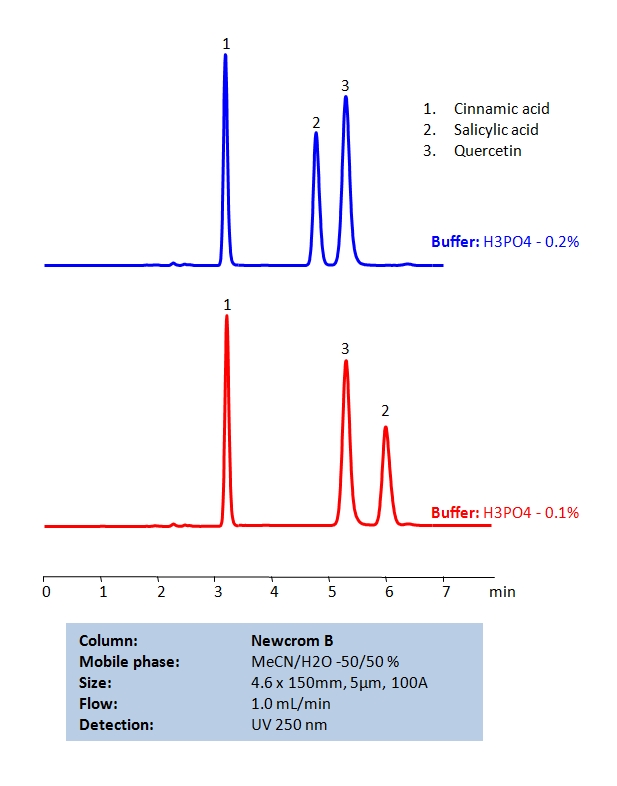
Method for Cinnamic acid, Salicylic acid, Quercetin, on Newcrom B by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method of Cinnamic Acid, Salicylic Acid and Quercetin.
Cinnamic acid and benzoic acid are two of the major phenolic acids and autotoxins. Cinnamic acid occurs naturally in all green plants, showing significant antimicrobial activity against both bacteria and fungi as well as antioxidant activity. It has the chemical formula C9H8O2.
Salicylic acid (SA) is an o-hydroxybenzoic acid, synthesized by both plants and microorganisms. SA acts as a critical plant hormone regulating various processes, including growth and development, flowering, thermogenesis, ion uptake, stomatal movement, photosynthesis, and plant immunity. It has the chemical formula C7H6O3.
Quercetin is a naturally occurring flavonol, or flavonoid, the yellowish antioxidant pigment found in skins of red grapes, berries, apples, onions, tomatoes, and buckwheat tea. In addition to functioning as a flavonoid, quercetin is also a phytoestrogen. It has the chemical formula C15H10O7.
Cinnamic acid, Salicylic acid, Quercetin, can be retained and separated by using a mixed-mode Newcrom B column using an isocratic analytical method with a simple mobile phase of water, acetonitrile (MeCN, ACN), and phosphoric acid (H3PO4) buffer. UV detection at 250 nm.
| Column | Newcrom B, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN -50% |
| Buffer | H3PO4 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | 250 nm |
| Class of Compounds | Acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Cinnamic acid, Salicylic acid, Quercetin, |
Application Column
Newcrom B
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Cinnamic acid
Quercetin
Salicylic acid