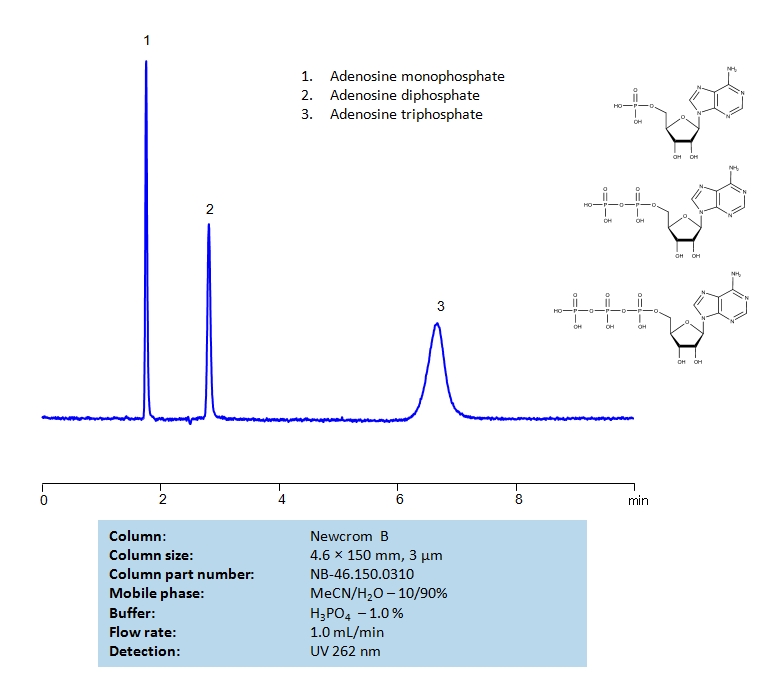
P HPLC Method for Adenosine Diphosphate, Adenosine Monophosphate, Adenosine Triphosphate on Newcrom B by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Adenosine Diphosphate, Adenosine Monophosphate, Adenosine Triphosphate.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleotide with the chemical formula C10H16N5O13P3. It is a primary energy carrier of the cell and is crucial to cellular energy metabolism. ATP is generated in the mitochondria and is used in numerous various cellular processes. It releases energy when a phosphate linkage breaks from it, creating adenosine diphosphate.
Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP), also known as adenosine pyrophosphate, is a compound with the formula C10H15N5O10P2. It is a precursor in the synthesis of DNA and RNA. Medications that block ADP receptors on platelets prevent blood clots in conditions like heart attacks and strokes.
Adenosine Monophosphate (AMP) is a nucleotide with the chemical formula C10H14N5O7P. Due to being a byproduct of ATP and ADP, it can be reused by the body for energy at higher forms. AMP can be converted into cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) to become a second messenger in the body, relaying signals between cells.
Adenosine Diphosphate, Adenosine Monophosphate, Adenosine Triphosphate can be retained and analyzed using the Newcrom B stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water and acetonitrile (MeCN) with a Sulfuric Acid buffer. Detection is performed using UV.
| Column | Newcrom B, 4.6 x 150 mm, 3 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 10/90% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 1.0% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 262nm |
| Class of Compounds | Acid, Hydrophilic |
| Analyzing Compounds | Adenosine Diphosphate, Adenosine Monophosphate, Adenosine Triphosphate |
Application Column
Newcrom B
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 3 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Adenosine Monophosphate
Adenosine Triphosphate