HPLC Method for Dimethylglycine, Methylglycine (Sarcosine), Trimethylglycine (Betaine), Glycine on Primesep 100 by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Dimethylglycine, Methylglycine (Sarcosine), Trimethylglycine (Betaine), Glycine.
Glycine, also written as Gly or G, is an important amino acid compounds widely used in pharmaceutical, biochemical, and peptide research. It has the chemical formula C₂H₅NO₂. It is water-soluble and plays a critical role in protein synthesis, peptide modification, and metabolic studies. It can be found in meat., eggs. and bones. You can find detailed UV spectra of Glycine and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
Methylglycine, also known as Sarcosine, is an amino acid with the chemical formula C3H7NO2. It is primarily known as a potential disease marker, as it does not typically occur in urine, but it is an intermediate and byproduct of glycine synthesis and degradation. You can find detailed UV spectra of Methylglydine and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
Dimethylglycine is a derivative of glycine with the chemical formula C4H9NO2. While it is found primarily in beans and liver, it is said to have a sweet taste. There has been research done into using Dimethylglycine as treatment for autism, epilepsy, and mitochondrial disease, though no evidence to suggest it’s effectiveness as a treatment was found. You can find detailed UV spectra of Dimethylglycine and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
Trimethylglycine, also known as betaine, is a compound derived from the amino acid glycine with the chemical formula C5H11NO2. It is found in various foods, including beets, spinach, whole grains, and seafood. Trimethylglycine has been studied for its potential health benefits, and it is commonly used as a dietary supplement. It plays a role in a process called methylation, which is important for various biochemical reactions in the body. Some studies suggest that trimethylglycine may have potential benefits for heart health as it is believed to help lower levels of homocysteine, an amino acid linked to an increased risk of heart disease when present in high concentrations. You can find detailed UV spectra of Trimethylglycine and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
Multi-charged molecules, such as oxaloacetate and oxalate, generally have a tendency to exhibit poor peak shape on reverse-phase HPLC columns, where they show significant tailing. Dimethylglycine, Methylglycine (Sarcosine), Trimethylglycine (Betaine), Glycine can be retained with great peak shape on a Newcrom BH mixed-mode column. Oxalic acid can be measured at low UV. Using a Newcrom BH mixed-mode column and a mobile phase consisting of acetonitrile (ACN) and water with sulfuric acid (H2SO4) buffer, oxaloacetic acid and oxalic acid can be retained, separated, and UV detected at 200 nm with precise resolution.
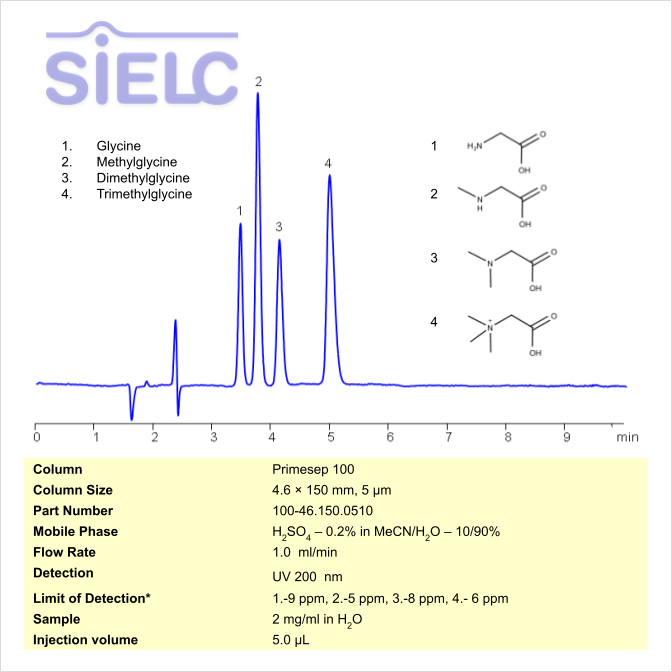
| Column | Primesep 100, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | H2SO4- 2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 200 nm |
| Class of Compounds | Amino Acids |
| Analyzing Compounds | Dimethylglycine, Methylglycine (Sarcosine), Trimethylglycine (Betaine), Glycine |
Application Column
Primesep 100
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Glycine
Methylglycine (Sarcosine)
Trimethylglycine (Betaine)