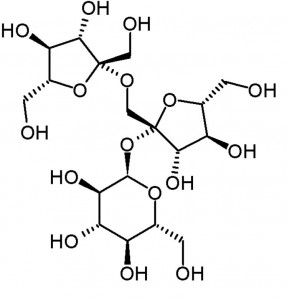
| CAS Number | 562-68-5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H32O16 |
| Molecular Weight | 504.438 |
| InChI Key | ODEHMIGXGLNAKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -5.5 |
| Synonyms |
Applications:
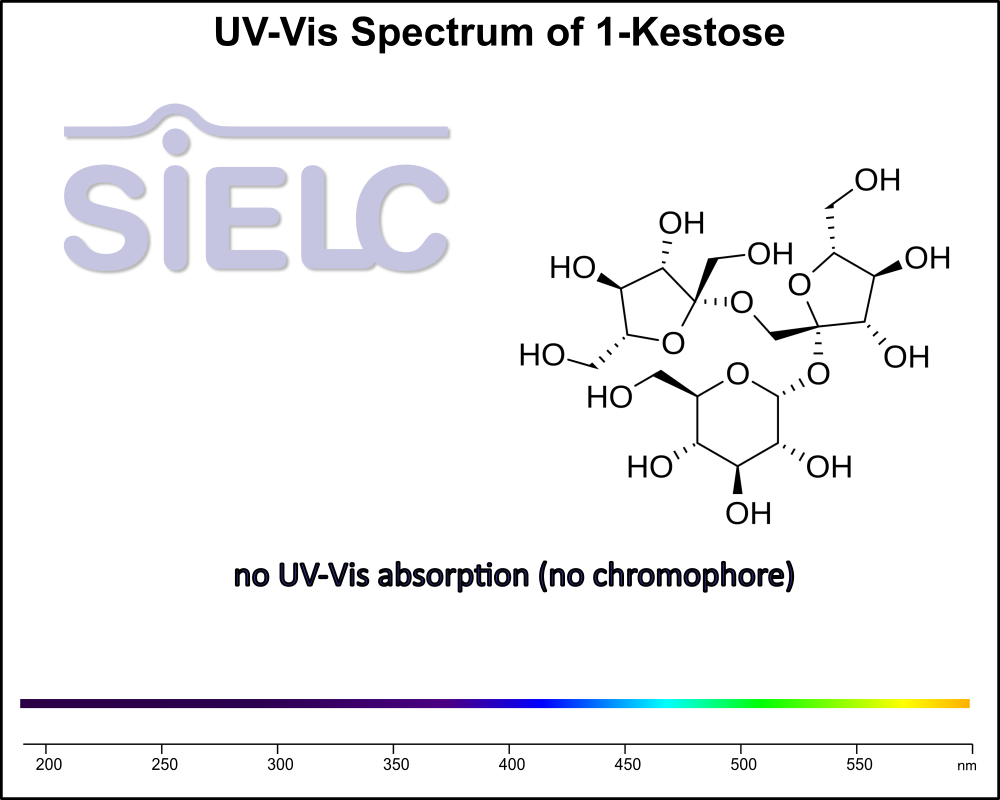
Uv-Vis Spectrum of 1-Kestose
February 12, 2026
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Kestose check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

Separation of Trisaccharides on Obelisc N Column
July 6, 2015
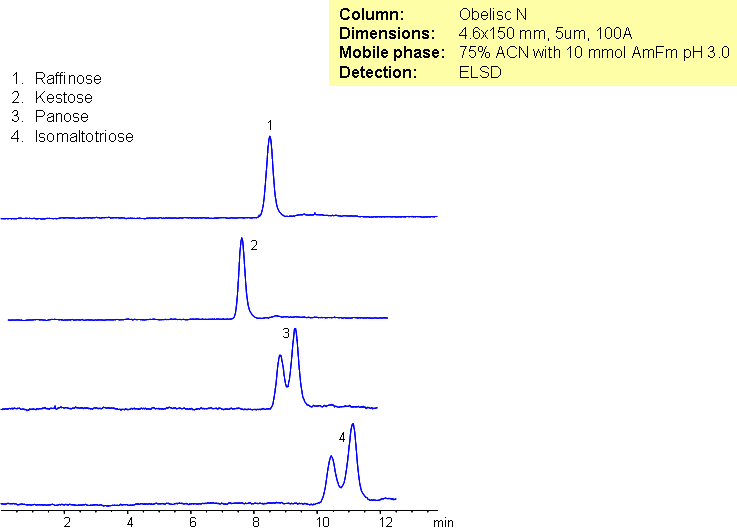
Trisaccharides can be difficult to separate using conventional HPLC columns. The four trisaccharides panose, raffinose, isomaltotriose, and kestose have the same chemical formula, and the all have two glycosidic bonds connecting the three monosaccharides. Obelisc N was used as a stationary phase to separate trisaccharides because it is capable of multiple modes of separation. Obelisc N is a highly polar column that retains polar and charged analytes. Even though the trisaccharides differ only in regio- and stereochemistry they are resolved.
| Column | Obelisc R, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 75% |
| Buffer | AmFm pH 3.0- 10 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Trisaccharides, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Raffinose, Kestose, Panose, Isomaltose |
Application Column
Obelisc N
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Kestose
Panose
Raffinose