| CAS Number | 586-89-0 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H8O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 164.16 |
| InChI Key | QBHDSQZASIBAAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 1.6 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
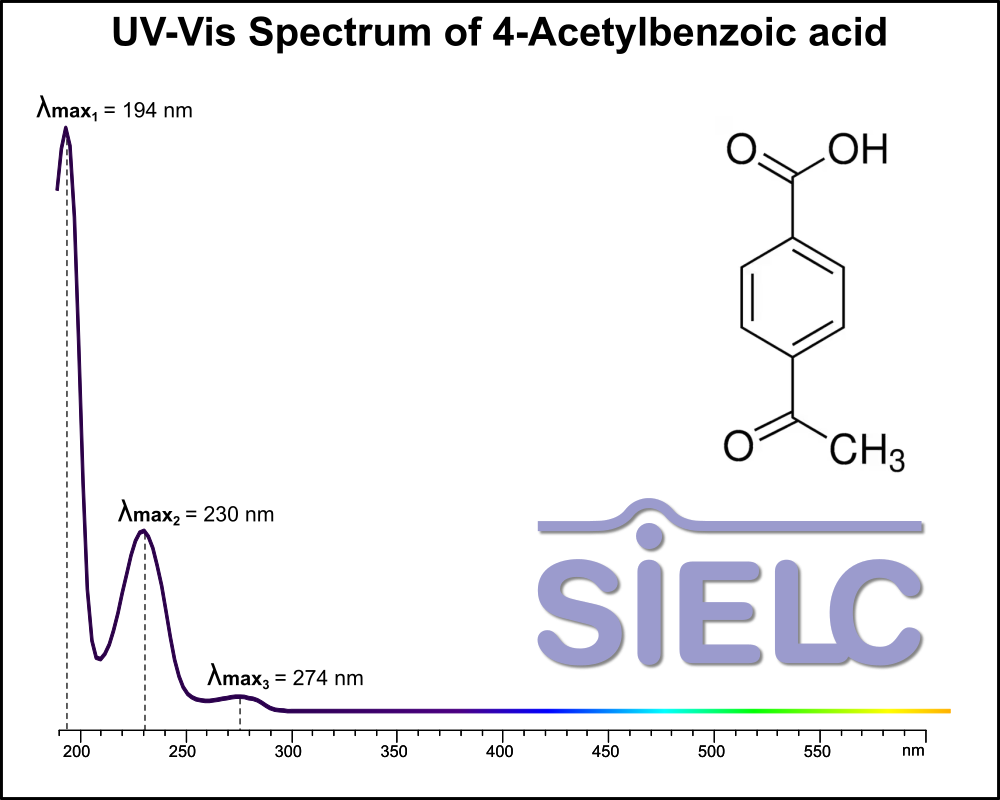
Uv-Vis Spectrum of 4-Acetylbenzoic Acid
February 13, 2026
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze 4-Acetylbenzoic Acid check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

Separation of Benzoic and Acetylbenzoic acid in Hydrogen-Bonding Mode
May 11, 2015
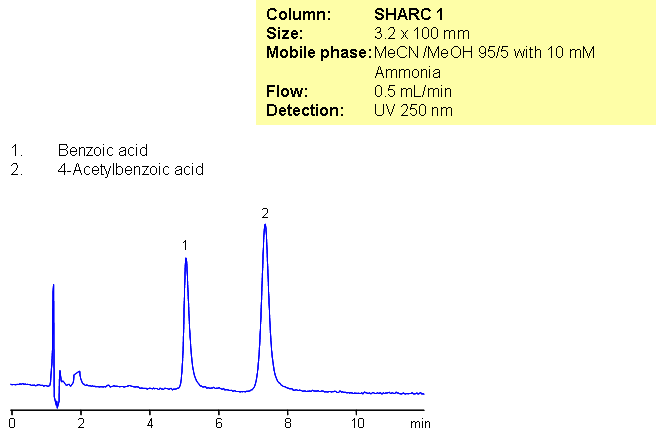
A general approach for analysis of various organic acids with MS detection in negative mode was developed using hydrogen-bonding stationary phase – SHARC 1. A highly sensitive method allows to analyze traces of organic acids in various matrices using ACN/MeOH/ammonia mobile phase. In hydrogen-bonding chromatography acetonitrile is a weaker solvent and alcohol is a stronger solvent. Various gradient and isocratic conditions can be used
| Column | Sharc 1, 3.2×100 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/MeOH – 95/5% |
| Buffer | Ammonia 10mM |
| Flow Rate | 005 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 250 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | Benzoic Acid, Acetylbenzoic acid |
Application Column
SHARC 1
The SHARC™ family of innovative columns represents the first commercially available columns primarily utilizing separation based on hydrogen bonding. SHARC stands for Specific Hydrogen-bond Adsorption Resolution Column. Hydrogen bonding involves an interaction or attraction between a bound hydrogen atom and molecules containing electronegative atoms, such as oxygen, nitrogen, and fluorine.
Select optionsBenzoic Acid
UV Detection