| CAS Number | 100-21-0 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H6O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 166.133 |
| InChI Key | KKEYFWRCBNTPAC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 2.00 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
UV-Vis Spectrum of Terephthalic acid
August 27, 2024
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Terephthalic Acid check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

Separation of Phthalic Acids and Related Impurities
July 2, 2013
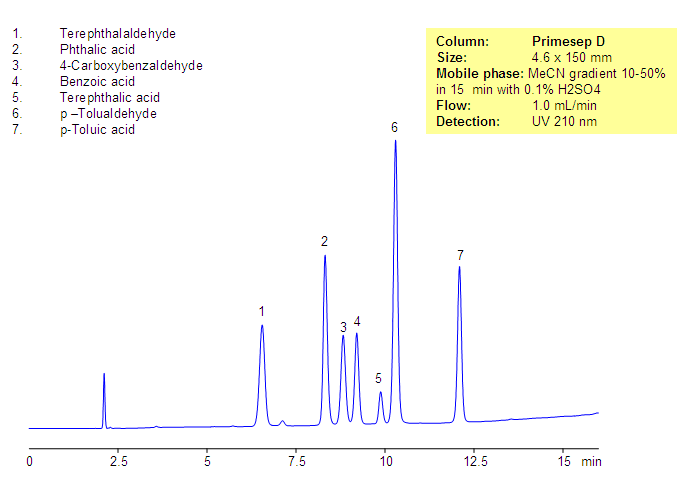
Phthalic acid, phthalic acid isomers, and related products present in the production of phthalic acid were separated on the Primesep D column, based on reversed-phase and in-exchange mechanisms. Neutral, hydrophobic compounds of the phthalic acid production are retained by a reversed-phase mechanism, and phthalic acid and other acidic compounds are retained by a combination of reversed-phase and anion-exchange mechanisms. Resolution and selectivity of this separation can be modified by varying the amount of acetonitrile, buffer concentrations, and buffer pH. This method can be used for monitoring the production cycle of phthalic acid and related impurities.
| Column | Primesep D, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN – 10-50%, 15 min |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.1% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 210 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Terephthalaldehyde, Phthalic acid, 4-Carboxybenzaldehyde, Benzoic acid, Terephthalic acid, p –Tolualdehyde, p-Toluic acid |
Application Column
Primesep D
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsBenzoic Acid
Phthalic Acid
Terephthalaldehyde
Terephthalic Acid
p-Tolualdehyde
p-Toluic Acid

HPLC Separation of Phthalic Acids using Hydrogen Bonding
June 18, 2012
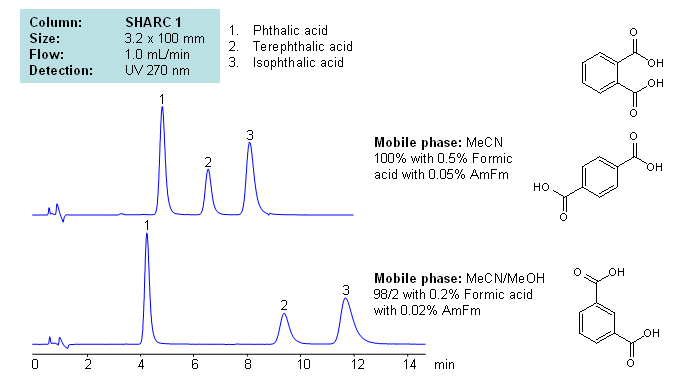
Phthalic acid, isophthalic acid and terephthalic acid are all isomers of each other. Being structurally similar, they can present difficulties to reverse-phase HPLC separation. Methods that require high organic concentrations in the mobile phase can cause dewetting in many reverse-phase columns. SHARC 1 column can be operated in anhydrous conditions and uses hydrogen bonding as the mechanism of separation. Here, phthalic acids were separated in pure acetonitrile (ACN), with the ability to adjust retention times by adding methanol (MeOH) to the mobile phase with formic acid and ammonium formate as buffer, making the method MS-compatible. Can also be UV detected at 270nm.
| Column | Sharc 1, 3.2×100 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/MeOH |
| Buffer | AmFm, Formic acid |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 270 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | Phthalic acid, Terephthalic acid, Isophthalic acid |
Application Column
SHARC 1
The SHARC™ family of innovative columns represents the first commercially available columns primarily utilizing separation based on hydrogen bonding. SHARC stands for Specific Hydrogen-bond Adsorption Resolution Column. Hydrogen bonding involves an interaction or attraction between a bound hydrogen atom and molecules containing electronegative atoms, such as oxygen, nitrogen, and fluorine.
Select optionsPhthalic Acid
Terephthalic Acid