| CAS Number | 13184-14-0 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H38N6O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 402.5 |
| InChI Key | WBSCNDJQPKSPII-KKUMJFAQSA-N |
| LogP | -5.6 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
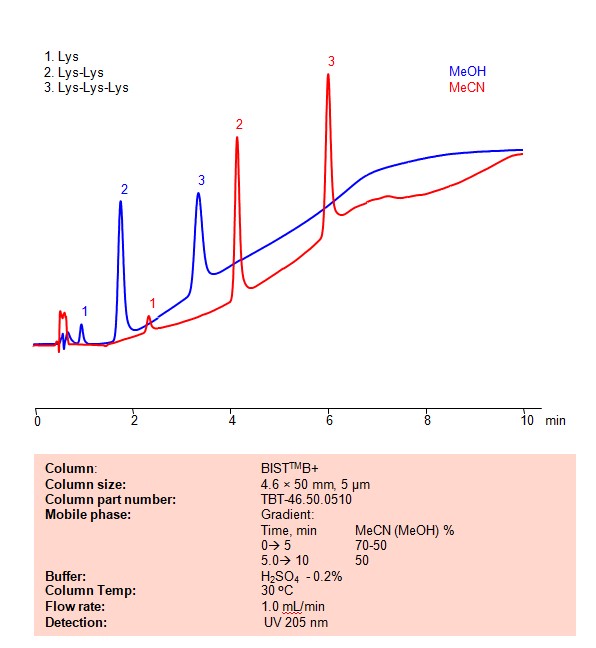
HPLC Method for Separation of Lysine, Dilysine and Trilysine on BIST B+ Column
March 27, 2024
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Lysine, Dilysine, Trilysine on BIST B+ by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
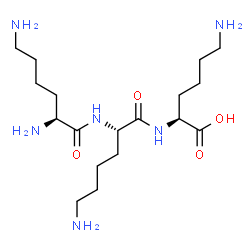
Lysine, dilysine, and trilysine refer to compounds related to the amino acid lysine.
1. Lysine (L-Lysine):
- Type: Lysine is an essential amino acid.
- Structure: It has an α-amino group (which is in the protonated –NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated –COO− form under physiological conditions), and a side chain with a functional group that is a basic, charged (at physiological pH) amino group.
- Role in the Body: As an amino acid, lysine is a building block for proteins. It’s crucial for health, but the body can’t produce it, so it must come from the diet.
- Uses: Lysine has been used in supplements to improve athletic performance, support immune health, and more. It’s also integral in the production of carnitine, a nutrient responsible for converting fatty acids into energy and helping to lower cholesterol.
2. Dilysine:
- Type: This refers to a molecule composed of two lysine units.
- Structure: The two lysine amino acids can be joined via a peptide bond between the carboxyl group of one lysine molecule and the amino group of another, forming a dipeptide. The resulting structure still features the basic side chains of the lysine residues.
- Potential Roles and Uses: While not commonly discussed outside of scientific research, such compounds could play roles in biological signaling or act as building blocks for more complex molecules. They may also be used in certain types of biochemical research or have potential therapeutic properties.
3. Trilysine:
- Type: This compound comprises three lysine molecules.
- Structure: Similar to dilysine, but with three lysine units connected by peptide bonds, resulting in a tripeptide. The basic side chains characteristic of lysine would still be present, and the molecule would carry multiple positive charges under physiological conditions due to these groups.
- Potential Roles and Uses: Trilysine is even less common in general discussion and is primarily a subject of scientific study. It could play a role in biochemical research or be explored for various potential applications, perhaps related to its charge and interaction with other molecules.
For all these compounds, especially dilysine and trilysine, their relevance is often in biochemical research. Scientists may study such peptides to understand cellular mechanisms, explore physiological processes, or develop new materials or medications. The specific properties of these compounds, such as their charge and their ability to participate in various biochemical interactions, can make them valuable for certain applications.
Lysine, dilysine, and trilysine can be retained, separated and analyzed on a BIST B+ mixed-mode stationary phase column using an analytical method with a simple mobile phase of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN) or Methanol (MeOH), and a sulfuric acid as a buffer. This analysis method can be detected using UV at 205 nm.
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analyses of Lysine, Dilysine, Trilysine
Condition
| Column | BIST B+, 4.6 x 50 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN or MeOH |
| Buffer | H2SO4 -0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 205 nm |
Description
Application Column
BIST B+
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 50 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Lysine
Trilysine


